
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Solve for all forces
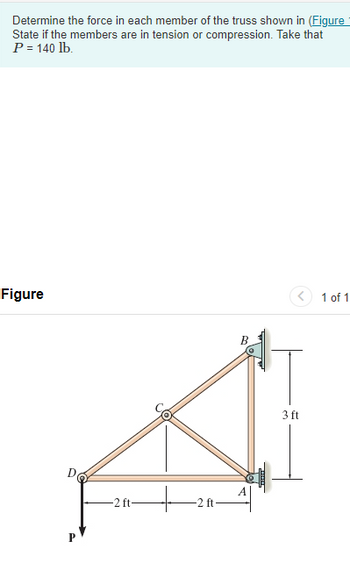
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the force in each member of the truss shown in (Figure
State if the members are in tension or compression. Take that
P = 140 lb.
Figure
-2 ft-
-2 ft
B
3 ft
1 of 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve NA and NB, I got NB correct and NA wrong. Please show all work.arrow_forwarduse the FORCE METHOD please!arrow_forwardLearning Goal: To be able to solve three-dimensional equilibrium problems using the equations of equilibrium. Part A As with two-dimensional problems, a free-body diagram is the first step in solving three-dimensional equilibrium problems. For the free-body diagram, it is important to identify the appropriate reaction forces and couple moments that act in three dimensions. At a support, a force arises when translation of the attached member is restricted and a couple moment arises when rotation is prevented.For a rigid body to be in equilibrium when subjected to a force system, both the resultant force and the resultant couple moment acting on the body must be zero. These two conditions are expressed as The J-shaped member shown in the figure(Figure 1) is supported by a cable DE and a single journal bearing with a square shaft at A. Determine the reaction forces Ay and Az at support A required to keep the system in equilibrium. The cylinder has a weight WB = 5.60 lb , and F = 1.50 Ib…arrow_forward
- The beam is made from a soft linear elastic material having a constant EI. If it is originally a distance from the surface of its end support, determine the length a that rests on this support when it is subjected to the uniform load w0, which is great enough to cause this to happen.arrow_forwardDetermine the resultant of forces A and B. The value of A is 87 N and the value of B is 90 N.arrow_forwardGiven: The beam below is welded to the wall at the left end. The beam is of length L. There is a distributed load across the length of the beam. Wo Find a. Identify the boundary conditions you would use to solve for the deflection curve y(x). Note: you do not need to solve for y(x). b. Sketch the deflection you expect the beam to exhibit under this load.arrow_forward
- A structure consists of two thin rectangular plates having the same dimensions (shown in figure) and same mass, m = 8 kg esch. The two plates are welded together to form a rigid body that may rotate in the plane. Determine, for this rigid body, the moment of inertia ly about the fixed point P. P is frisedarrow_forwardEngineering Mechanics Topic: FORCES IN SPACE Hi! Please help me with this problem. I would really appreciate it you solving it in a step by step process including its detailed free body diagram. Thank you so much!arrow_forwardKnowing that the resultant of the couple and the two forces shown is a force R acting through point O, determine P and R.arrow_forward
- Shown below are 4 different rigid bodies, supported in different ways. For each of the rigid bodies, with proper free body diagrams, please determine all the support reactions. Value of the applied forces is F = 100 N, P = 200 N and L = 3 m. a. In figure a, support is a pin at A and a roller at D. Pin at A resists translation in the horizontal and vertical direction, and roller at D only resists translation in the vertical direction. b. In figure b, support at A is a pin it similar to part a of the problem), and support at D is a roller on an incline: note that here, the roller support reaction will be normal to the incline. c. In figure c, support at A is a roller, and support at D prevents translation in the horizontal direction, and also prevents rotation. So, there will be two support reactions at D. Think of what they may be? d. In figure d, support at A is a cantilevered end. B 30° (a) (b) |F | F |P (c) (d) /3arrow_forward50 kN A 200 mm B 350 mm a a 60 mm 200 mm - change the length of segment BC from 350 mm to 312 mm 50 mm 20 mm 20 mm D 20 mm 50 kN Provide the internal normal force diagram for the figure above with the following modifications:arrow_forwardPlease correct my understanding of this question. -In the equation of the moment at point A, there is a value, 36(11.5). I assume that is a force from the distributed load. -If you are finding the moment at point A, wouldn't you only need one value from the distributed load which is 27(10)? So my question is how do you get the value of 36 and 11.5, separately. And what is it for?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning