
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please correct my understanding of this question.
-In the equation of the moment at point A, there is a value, 36(11.5). I assume that is a force from the distributed load.
-If you are finding the moment at point A, wouldn't you only need one value from the distributed load which is 27(10)?
So my question is how do you get the value of 36 and 11.5, separately. And what is it for?
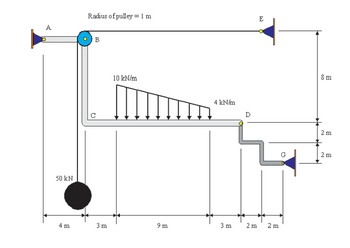
Transcribed Image Text:50 kN
4 m
Radius of pulley = 1m
B
3 m
10 kN/m
9 m
4 kN/m
3 m
D
2 m
E
2 m
8 m
2m
2 m
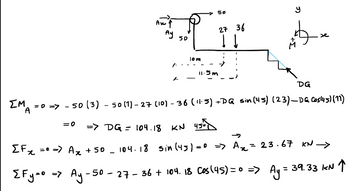
Transcribed Image Text:ΣΜ
Az F
Ау
:0
1-
50
lom
-
50
11.5m
DG
= 0 => 50 (3) - 50 (1)-27 (10) - 36 (11.5) +DQ sin (45) (23)_ DG Cos145) (11)
A
=> DG = 104.18 KN 45°1
27 36
↓↓
内
[Fx = 0 => Ax + 50_104.18 sin (45) = 0 => A₂ = 23.67 KN →
ΣFy=0 => Ay -50 - 27 - 36 + 104. 18 Cos (45) = 0 => Ay = 39.33 KN ↑
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- T·r T (from torsion) = Tr4 J ="- (Solid rod) F Onormal = A o (from bending) M•y - (Solid rod) The solid rod shown in the figure below has diameter of 1.25 in. If it is subjected to the force of 60 lb, determine the state of stress at point A using the principle of superposition. Neglect the weight of the rod, and the stress due to the I %3D I 4 transverse shear force. 60 lb k-10 in.- 15 in. Front View -20 in. Вarrow_forwardProblem 8.61 Part A The two blocks used in a measuring device have negligible weight. The spring is compressed 4 in. when in the position shown. The end of the screw is smooth and the coefficient of static friction at all other points of contact is μ= 0.29. (Figure 1) Determine the smallest axial force P which the adjustment screw must exert on B in order to start the movement of B downward. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure k = 20 lb/in. A 60° 45° B 1 of 1 P= Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Unitsarrow_forwardQuestion 5 T/2 В 1200 Nm A homogeneous steel shaft (G=83GPA) is loaded as shown in the above Figure. Assuming T = 300 N-m, determine the torsional force in N-m in Member BC. Note: Include sign (+/-), assuming the direction of Torsion (T) at D is positive Given: AB: Length = 1.75m, Diameter = 75mm BC: Length = 1.50m, Diameter = 60mm AB: Length = 1.00m, Diameter = 40mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning