
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
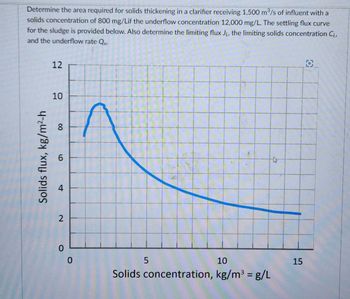
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the area required for solids thickening in a clarifier receiving 1,500 m³/s of influent with a
solids concentration of 800 mg/Lif the underflow concentration 12,000 mg/L. The settling flux curve
for the sludge is provided below. Also determine the limiting flux JL, the limiting solids concentration CL,
and the underflow rate Qu.
Solids flux, kg/m²-h
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0
5
BAT
10
Solids concentration, kg/m³ = g/L
15
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A complete mixed activated sludge process (CMAS) is to be designed to treat 5MGD of primary effluent having a BOD5 of 180 mg/L. The NPDES permit requires that the effluent BOD5 and TSS concentration be 20 mg/L or less on an annual average basis. The following biokinetic coefficient obtained at 15C: Y = 0.6 mg VSS/mg BOD5, k = 2.85d-1, Ks = 70 mg/L BOD5, and kd = 0.041 d-1. Assume that the MLVSS concentration in the aeration basisn is maintained at 2500 mg/L. Determine: a. The minimum MCRT (d) b. The MCRT necessary to meet the NPDES permit requirement (d) c. The volume of the aeration basin (ft3)arrow_forwardA complete-mixed activated sludge process is to be designed to treat 5.0 MGD of primary effluent having a BOD5 of 180 mg/L. The requirement is that the effluent BOD5 and TSS concentration be 20 mg/L or less on an annual average basis. The following biokinetic coefficient obtained at 15°C: Y = 0.6 mg VSS/mg BOD5, k=2.85d-¹, Ks = 70 mg/L BOD5, and kå = 0.041 d¹¹. Assume that the MLVSS concentration in the aeration basin is maintained at 2,500 mg/L. Determine: a. The minimum MCRT (d) b. The MCRT necessary to meet the requirement (d) C. The volume of the aeration basin (ft³)arrow_forwardAfter initial mixing of a wastewater discharge in a 5-m-deep river, the DO concentration in the river is 7 mg/L and the temperature is 22°C. The average flow velocity in the river is 6 cm/s.(a) If the ultimate BOD of the mixed river water is 15 mg/L, the rate constant for BOD at 20°C is 0.5 d−1, there is negligible removal of BOD by sedimentation, and the reaeration rate constant at 20°C is 0.7 d−1, estimate the minimum DO concentration in the river.(b) How far downstream of the outfall location will the minimum DO concentration occur?arrow_forward
- The minimum temperature of the water is 5 °C, the free chlorine residual in the effluent from the basin is to be 2 mg/L, the first-order decay coefficient for chlorine is assumed to be 0.2 h-¹, and the flow rate is 1.5 x 104 m³/d. The pH of the water varies between 7.2 and 8.0. Make the calculations for a plug-flow basin. Cta values for achieving 99.9% reduction of Giardia lamblia Temperature (°C) Disinfectant pH ≤1 5 10 15 20 25 Free chlorineb 6 165 116 87 58 44 29 (2 mg/L) 7 236 165 124 83 62 41 8 346 243 182 122 91 61 9 500 353 265 177 132 88 Ozone 6-9 2.9 1.9 1.4 0.95 0.72 0.48 Chlorine 6-9 63 26 23 19 15 11 dioxide Chloramine 6-9 3800 2200 1850 1500 1100 750 (preformed) aC is in mg/L and t is in minutes Ct values depend on the concentration of free chlorine Calculate the dosage of chlorine kg/day) and the detention time minutes) required for 99.9% reduction of G. lamblia. 121.5 486 118 91 40 45 151.5arrow_forward12.50 Determine the activated-sludge aeration volume required to treat 2.64 mgd with a BOD of 120 mg/l based on the criteria of a maximum BOD loading of 40 lb/1000 ft³/day and a minimum aeration period of 5.0 hr. Assuming an operating F/M of 0.20 lb BOD/day per lb of MLSS, calculate the MLSS to be maintained in the aeration tank. Estimate the operat- ing sludge age (mean cell residence time), assuming an effluent suspended solids of 30 mg/l and the daily amount of waste-sludge solids from Figure 13.1. Determine the diame- ter and side-water depth of two identical final clarifiers of the type shown in Figure 10.12 for this activated-sludge system.arrow_forward2. The average wastewater flow from a community of 20,000 is 125 gpcd. The 5 day, 20 deg C BOD is 250 mg/L. The suspended solids content is 300 mg/L. A final plant effluent of 50 mg/L of BOD is to be achieved through the use of two sets of identical settling tanks and trickling filters operating in parallel. The settling tanks are to be designed to a standard of 1000 gpd/^2. The trickling filters are to be 6^ deep and operated at an organic loading of 55 lbm/1000^3 d. There is no recirculalon. (1) What settling tank surface area is required? In ft^2 (2) What settling tank diameter is required? In ft (3) Estimate the BOD removal in the settling tanks? In percent % (4) What is the trickling filter diameter? In ft File Explorer O Expert Q&A | Cheq... (66) Thesearrow_forward
- 8 Determine the solid loading rate on a secondary circular clarifier (diameter = 20 m) if the plant influent load is 2 ML/d. The recycle flow from secondary clarifier to the activated sludge system (aeration basin) is set to 10% of the influent load. It is also known that the aeration basin produces an MLSS (mixed liquor suspended solids) concentration of 3000 mg/L.arrow_forward2. The average wastewater flow from a community of 20,000 is 125 gpcd. The 5 day, 20 deg C BOD is 250 mg/L. The suspended solids content is 300 mg/L. A final plant effluent of 50 mg/L of BOD is to be achieved through the use of two sets of identical settling tanks and trickling filters operating in parallel. The settling tanks are to be designed to a standard of 1000 gpd/^2. The trickling filters are to be 6^ deep and operated at an organic loading of 55 lbm/1000^3 d. There is no recirculalon. (1) What settling tank surface area is required? In ft^2 (2) What settling tank diameter is required? In ft (3) Estimate the BOD removal in the settling tanks? In percent % (4) What is the trickling filter diameter? In ft domeved Wardarrow_forwardThe 750-bed Associated Center of Medical Excellence (ACME) Hospital has a small activated sludge plant to treat its wastewater. The average daily Medical Center discharge is 1,250 L per day per bed, and the average soluble BOD5 after primary settling is 450 mg/L. The aeration tank has effective liquid dimensions of 10.0 m wide by 25.0 m long by 3.5 m deep. The plant operating parameters are as follows: MLVSS = 2,750 mg/L MLSS = 1.25 (MLVSS) Settled sludge volume after 30 min = 250 mL/LDetermine the following: aeration period, F/M ratio, SVI, solids concentration in return sludge.arrow_forward
- A complete-mixed activated sludge process (CMAS) is to be designed to treat 6.0 MGD of primary effluent having a BOD5 of 190 mg/L. The requirement is that the effluent BOD5 and TSS concentrations be 20 mg/L or less on an annual average basis. The following biokinetic coefficient obtained at 15°C: Y = 0.6 mg VSS/mg BOD5, k = 2.85 d-1, Ks = 70 mg/L BOD5, and kd = 0.041 d-1. Assume that the MLVSS concentration in the aeration basin is maintained at 2,500 mg/L. Determine: a. The minimum MCRT (d) b. The MCRT necessary to meet the requirement (d) c. The volume of the aeration basin (ft3)arrow_forward9-2. A flow of 20,000 maay which contains 100 mg/L of suspended solids is coagulated with 50 mg/L of alum. If 90 percent of the solids and chemical precipitates is removed in sedimentation estimate: (a) Total dry mass of sludge produced per day. (b) Total wet mass produced per day, assuming the sludge is 5 percent solids by weight. (c) Total volume produced per day, assuming the specific gravity of the wet sludge is 1.05.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning