
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A horizontal pipe has an abrupt expansion from D1 = 5 cm to D2 = 10 cm. The water velocity in the smaller section is 8 m/s and the flow is turbulent. The pressure in the smaller section is P1 = 410 kPa. Taking the kinetic energy correction factor to be 1.06 at both the inlet and the outlet, determine the downstream pressure P2, and estimate the error that would have occurred if Bernoulli’s equation had been used.
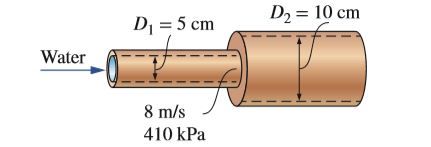
Transcribed Image Text:D2 = 10 cm
DI = 5 cm
Water
8 m/s
410 kPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Lane has two pipes connected to each other that transport water because he is very thirsty. The given density of water is ρ = 997 kg/?3. The flow rate of water through the pipes is R = .009463522m^3/s, but they have different diameters. The first pipe has a measured pressure P1 =12.927 MPa and a velocity of v = 28.894 m/s. The second pipe has a measured velocity of v = 63.525 m/s.A) What is the pressure in the second pipe?B) What is the diameter of the second pipe?arrow_forwardDrinking water from a large bottle placed on high ground references Inside the Damacana with an on / off valve at the end a plastic hose is immersed. On/off valve of hose with diameter 3 mm the found tip is 80 cm below the ground. Water in Damascus (P = 1000 kg/m3) fill a cup with a volume of 0.2 L for the state that the level is 60 cm calculate the time required. Casualties are negligible. 60 CT 80 m Please choose one:arrow_forwardA horizontal pipe of diameter 550 mm is suddenly contracted to a diameter of 300 mm. The pressure intensity in large pipe is given as 14 N/cm2 and the flow velocity in the larger pipe is 2 m/s. Find:- (a) The rate of flow of water through a horizontal pipe. (b) Loss of head due to sudden contraction. (c) Pressure intensity in smaller pipe.arrow_forward
- Show Complete Solutionarrow_forwardcould you please help me calculate theheigth in metres of the fluid at time t= 100sarrow_forwardPetrol (ρ=750 kg/m3) flows through a pipeline with inlet diameter 8 cm and outlet diameter 4 cm. The inlet and outlet gauge pressures measured to be 400 kPa and 130 kPa respectively. Assuming the pipeline to be horizontal and neglecting friction, calculate the outlet velocity (V2) of water by using continuity and Bernoulli’s equation.arrow_forward
- A cylindrical container with a massless and frictionless piston is filled with water up to a height h, as shown in the schematic. What mass m should be placed on the piston so that the water flow rate through the opened valve doubles? Consider that piston area A₁ = 0.05 m², valve area A₂ = A1/8, h = 0.9 m, Pwater = 1000 kg/m³, and g = 9.80 m/s². piston area: A₁ m = ? Т h/5 valve area: A₂arrow_forwardSolve it fast.arrow_forwardA two storey building has two faucets, one in the basement and one in the firstfloor. The maximum water (ρ = 1000 kg/m3) velocity at the basement faucet, when the first floor faucet is closed, is 13 m/s. The faucet diameter is 1.5 cm.Neglect all losses. What would be a maximum height (from the basement floor) for a faucet,to still get a maximum exit velocity of 6 m/s?arrow_forward
- Can you help me to solve this problem? Water is siphoned from the tank shown on the Figure below. Assuming frictionless flow, determine the mass flowrate from the tank in kg/s to 2 decimal places. Take atmospheric pressure and density of water 105 Pa to be 1000 kg/m3, respectively. Gravitational acceleration is 9.81 m/s2arrow_forwardThere is a storage tank with a height of 5 m. Initially the tank is empty. The cross- sectional area of the tank is 1m?. There is a hole in the storage tank at a level of 2m from the bottom of the tank. The relationship between the volumetric flowrate through the hole and the level of the tank is q=vh. In addition there are two valves at the top and bottom of the tank for inlet and outlet streams. Suddenly, the two valves at the top and bottom of the tank are opened where inlet and outlet stream volumetric flowrates became 1m/s and 0.2m2/s. a)Determine the time for the liquid level to reach 2marrow_forwardWater flows through a corner valve at a flow rate of Q=0.75 m³/s . The pressure just upstream of the valve is P₁ = 500 kPa and the pressure just downstream is P₂ = 300 kPa. The inside pipe diameters of the valve inlet and exit are respectively, D₁ = 5 cm and D₂ = 12 cm. If the flow through the valve occurs in a horizontal plane, determine the head loss, h₂ (in meters) and the rate of loss of available energy (in W) across the valve. D2 Diarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY