
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Can you help me to solve this problem?
Water is siphoned from the tank shown on the Figure below. Assuming frictionless flow, determine the mass flowrate from the tank in kg/s to 2 decimal places.
Take atmospheric pressure and density of water 105 Pa to be 1000 kg/m3, respectively. Gravitational acceleration is 9.81 m/s2
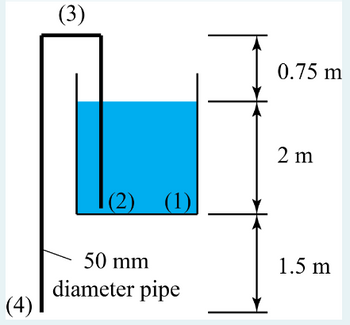
Transcribed Image Text:(3)
(2) (1)
0.75 m
2 m
50 mm
diameter pipe
1.5 m
(4)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please fastarrow_forwardFor a pumper truck pumping water to a fire, the back pressure is the additional pressure on the pump caused by the height of the nozzle. (Another way of thinking of back pressure is as the minimum pressure the pumper must produce in order to make water flow out the end of the nozzle.) Consider a pumper at street level pumping water through a hose to firefighters on the top of the ninth floor of a building. If each floor is 16 feet high, what is the head of water at the mouth of the nozzle?arrow_forwardusing 2 L please solve it in these steps step 1- find velocity of the fluir using bernoullis equation step 2- find the volumetric flow rate step 3- How long it takes to fill the cup using formula Q=V/Tarrow_forward
- A cylindrical tank with a radius of 3ft is filled with water which has a weight density of 62.4 lb/ft^3. The water is to be pumped to a point 2ft above the top of the tank. (a) How much work is performed in pumping all the water from the tank? (B) How much work is performed in pumping 3ft of water from the tank? (C) At what point is 1/2 of the total work done?arrow_forwardPlease solve it quickly I am at the examarrow_forwardComplete Solution please, thanks. 3. A vertical circular stack 30 m high converges uniformly from a diameter of 6 m at the bottom and 4.5 m at the top. Gas with a unit weight of 0.12 N per cubic meter enters the bottom of the tank with a uniform velocity of-assume values with decimals between 3 to 4 m per second- enters the stack. The unit weight increases by 7.5 percent every 2 meters. Find the velocity of flow at every 5 meters along the stack.arrow_forward
- The pressure in a water tower is 20,674 Pascals (N/m2) higher than at an open faucet. The density of water is 1000 Kg/m3. Use Bernoulli’s equation to determine the velocity of outflow from the open faucet. If the height difference between the top water level in the tower and the faucet is 7.2 meters, then the velocity of outflow is ROUND TO 3 DECIMAL PLACESarrow_forwardWater is pumped into a fire hose through a 6 cm diameter pipe with speed 1m/s. The water in the fire hose flows with a pressure of 200000 Pa. At the end of the fire hose is a nozzle (small hole). The pressure decreases to atmospheric pressure (101300 Pa) when the water leaves the nozzle from the hose. There is no change in height moving from the hose to the nozzle. 1. What is the water speed in a 4 cm diameter fire hose? 2. What is the velocity of the water exiting the nozzle (p=1000kg/m³)? 4. What is the diameter of the nozzle? 3. A Fireworker now connects an additional flexible tube to the nozzle (tube and nozzle has same diameter). He lifts the tube to a height of 1 meter above the ground. At what speed does the water come out of the tube? (hint - the pressure at the exit is still atmospheric)arrow_forwardWater flowing in a pipe reaches a point where the cross-sectional area of the pipe is reduced to 1/3 of its previous value. If the speed of the water before the constriction is 1.31 m/s, what is the speed of the water after the constriction?arrow_forward
- AT. 2] a water pump is to be used in a water supply system as shown in the figure. The pressure at point 1 is 70 kPaa and the pressure at point 2 is 101 kPaa. The velocity in the 60-mm pipe is 2 m/s. Find the pump power. Neglect friction, and assume no change of internal energy of the water and no heat transfer between point 1 and 2. Take the density of water at standard condition. 2 m2 10 m Pumparrow_forwardA pump has one inlet and two outlets as shown in the figure all at the same elevation. What pump power is required if the pump is 85% efficient. Neglect pipe lossesarrow_forwardI need help on this questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY