
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
![### Physics Problem: Conservation of Energy and Elastic Collision
Starting with an initial speed of 5.00 m/s at a height of 0.357 m, a 2.82-kg ball swings downward and strikes a 4.70-kg ball that is at rest, as shown in the diagram.
#### Diagram Description:
- The diagram shows a 2.82-kg ball on a swing hitting a 4.70-kg stationary ball.
- The swing path is represented as an arc connected to a pivot point above.
#### Questions:
**(a)** Using the principle of conservation of mechanical energy, find the speed of the 2.82-kg ball just before impact.
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(b)** Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 2.82-kg ball just after the collision.
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(c)** Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 4.70-kg ball just after the collision.
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(d)** How high does the 2.82-kg ball swing after the collision, ignoring air resistance?
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(e)** How high does the 4.70-kg ball swing after the collision, ignoring air resistance?
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/d261088c-f753-45e4-ae14-7adbaf3c257c/cc216acb-c4c7-4273-bab7-a0a7ce8ac02b/axbtlwf_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:### Physics Problem: Conservation of Energy and Elastic Collision
Starting with an initial speed of 5.00 m/s at a height of 0.357 m, a 2.82-kg ball swings downward and strikes a 4.70-kg ball that is at rest, as shown in the diagram.
#### Diagram Description:
- The diagram shows a 2.82-kg ball on a swing hitting a 4.70-kg stationary ball.
- The swing path is represented as an arc connected to a pivot point above.
#### Questions:
**(a)** Using the principle of conservation of mechanical energy, find the speed of the 2.82-kg ball just before impact.
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(b)** Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 2.82-kg ball just after the collision.
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(c)** Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 4.70-kg ball just after the collision.
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(d)** How high does the 2.82-kg ball swing after the collision, ignoring air resistance?
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
**(e)** How high does the 4.70-kg ball swing after the collision, ignoring air resistance?
- **Number**: [Input Field] **Units**: [Dropdown for units]
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 12 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
I'm struggling with this practice problem. It's saying b,d,and e are wrong.
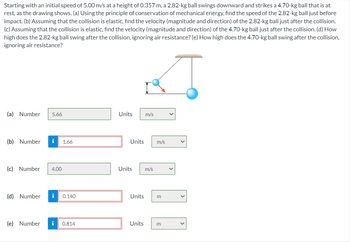
Transcribed Image Text:Starting with an initial speed of 5.00 m/s at a height of 0.357 m, a 2.82-kg ball swings downward and strikes a 4.70-kg ball that is at
rest, as the drawing shows. (a) Using the principle of conservation of mechanical energy, find the speed of the 2.82-kg ball just before
impact. (b) Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 2.82-kg ball just after the collision.
(c) Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 4.70-kg ball just after the collision. (d) How
high does the 2.82-kg ball swing after the collision, ignoring air resistance? (e) How high does the 4.70-kg ball swing after the collision,
ignoring air resistance?
(a) Number 5.66
(b) Number i 1.66
(c) Number 4.00
(d) Number i 0.140
(e) Number i 0.814
Units m/s
Units m/s
Units m/s
Units m
Units m
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
Thank you for your help
Transcribed Image Text:(d) Number
(e) Number
i
IN
i
Units
Units
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
I'm struggling with this practice problem. It's saying b,d,and e are wrong.

Transcribed Image Text:Starting with an initial speed of 5.00 m/s at a height of 0.357 m, a 2.82-kg ball swings downward and strikes a 4.70-kg ball that is at
rest, as the drawing shows. (a) Using the principle of conservation of mechanical energy, find the speed of the 2.82-kg ball just before
impact. (b) Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 2.82-kg ball just after the collision.
(c) Assuming that the collision is elastic, find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the 4.70-kg ball just after the collision. (d) How
high does the 2.82-kg ball swing after the collision, ignoring air resistance? (e) How high does the 4.70-kg ball swing after the collision,
ignoring air resistance?
(a) Number 5.66
(b) Number i 1.66
(c) Number 4.00
(d) Number i 0.140
(e) Number i 0.814
Units m/s
Units m/s
Units m/s
Units m
Units m
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
Thank you for your help

Transcribed Image Text:(d) Number
(e) Number
i
IN
i
Units
Units
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cue ball at rest on a frictionless pool table is hit dead center by a pool stick, giving it an impulse of +1.85 N · s. The ball slides (the combination of hitting the ball dead center and no friction allows this to happen) along the table and makes a head-on elastic collision with another pool ball. If both pool balls have a mass of 0.156 kg, determine the velocity (in m/s) of the second ball the instant after the collision.arrow_forwardA steel ball of mass 0.870 kg is fastened to a cord that is 85.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal, as shown in the figure. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 4.00 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic. Find (a) the speed of the ball and (b) the speed of the block, both just after the collision. (a) Number i Unit (b) Number i Unitarrow_forwardA 1.20-kg ball, moving to the right at a velocity of +2.03 m/s on a frictionless table, collides head-on with a stationary 9.50-kg ball. Find the final velocities of (a) the 1.20-kg ball and of (b) the 9.50-kg ball if the collision is elastic. (c) Find the magnitude and direction of the final velocity of the two balls if the collision is completely inelastic. (a) Number i Units (b) Number Units (c) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- A 1500 kg car traveling eastwards at 25 m / s collides with a 2500 kg load truck going north at a speed of 20 m / s as shown in the figure. Find out the magnitude and direction of the speed of the wreck after the collision, taking into account that the vehicles had a completely inelastic collision.arrow_forwardIn a ballistic pendulum experiment, a small marble is fired into a cup attached to the end of a pendulum. If the mass of the marble is 0.0315 kg and the mass of the pendulum is 0.250 kg, how high ℎ will the pendulum swing if the marble has an initial speed of 5.65 m/s? Assume that the mass of the pendulum is concentrated at its end so that linear momentum is conserved during this collision.arrow_forwardA steel ball of mass 0.600 kg is fastened to a cord that is 80.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 3.00 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic. (a) Find the speed of the ball just after collision. (No Response) m/s (b) Find the speed of the block just after collision. (No Response) m/sarrow_forward
- A steel ball of mass 0.440 kg is fastened to a cord that is 80.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal, as shown in the figure. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 3.10 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic. Find (a) the speed of the ball and (b) the speed of the block, both just after the collision. (a) Number i (b) Number Unit Unitarrow_forwardA bullet of mass m = 8.00 g is fired into a block of mass M = 240 a that is initially at rest at the edge of a table of height h = 1.00 m (see figure below). The bullet remains in the block, and after the impact the block lands d = 1.50 m from the bottom of the table. Determine the initial speed of the bullet. Use the given information to find the velocity of the block after collision with the bullet and then use conservation of momentum to find the initial speed of the bullet. m/s Need Help? Read It Master It Submit Answerarrow_forwardA cue ball traveling at 6.57 m/s makes a glancing, elastic collision with a target ball of equal mass that is initially at rest. The cue ball is deflected so that it makes an angle of 30.0° with its original direction of travel. (a) Find the angle between the velocity vectors of the two balls after the collision. (b) Find the speed of each ball after the collision.arrow_forward
- A cue ball initially moving at 4 m/s strikes a stationary eight ball of the same size and mass. After the collision, the cue ball’s final speed is 1 m/s. Find the cue ball’s angle θ with respect to its original line of motion. This is considered an elastic collision.arrow_forwardA steel ball of mass 0.400 kg is fastened to a cord that is 80.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 2.00 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic. (a) Find the speed of the ball just after collision. m/s (b) Find the speed of the block just after collision. m/sarrow_forwardSituation 7. A ball of mass 0.220 kg that is moving with a speed of collides head-on and elastically with another ball initially at rest. Immediately after the collision, the incoming ball bounces backward with a speed of 3.8m/s. C. Supposed that a ball is dropped from a height of 2.60 m. If the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the ground is 0.60, to what height will it bounce?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON