
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781133109655
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
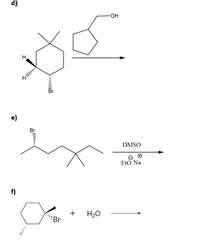
Transcribed Image Text:**Chemical Reactions Illustrations**
### Reaction d)
- **Reactants:**
- A bicyclic compound with a bromine substituent (Br) and two methyl groups on a cyclohexane ring.
- A cyclopentanol, an alcohol derived from cyclopentane.
- **Reaction Conditions:**
- Indicated by an arrow, suggesting a general transformation without specified conditions.
### Reaction e)
- **Reactants:**
- A hydrocarbon chain with a bromine substituent (Br) on one end and multiple alkyl groups.
- The reaction takes place in the presence of DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) and sodium ethoxide (EtO Na).
- **Reaction Conditions:**
- Sodium ethoxide is used as a base with DMSO as the solvent, implying a substitution or elimination reaction.
### Reaction f)
- **Reactants:**
- A cyclohexane molecule with a bromine substituent.
- Water (H₂O).
- **Reaction Conditions:**
- The arrow indicates a transformation, suggesting a potential hydrolysis or substitution reaction.
These diagrams depict organic reactions, showcasing reactants and conditions used to predict the possible transformation products.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ether groups are formed when alcohols are treated with acid. Consider the following question that focuses on acid-catalyzed ether formation using alcohol functional groups. There are 3 unique ether products will be formed when the following reaction is performed. Draw the product of the above reaction that has six carbon atoms and an ether functional group. **Be sure to include all lone pairs of electrons.**arrow_forwardPlease help me check if the information below is correct for both the types of reactions and the special rules or laws to predict predominant products for alcohols. If not please insert the correct information. Please make the information in jot notes. TYPES OF REACTIONS ALCOHOL: Dehydration: This is a reaction where an alcohol loses a water molecule to form an alkene. For example, when ethanol is treated with an acidic catalyst, such as sulfuric acid, it undergoes dehydration to form ethene (CH2=CH2) and water. Oxidation: In this reaction, an alcohol is converted to either a carbonyl compound or a carboxylic acid. For example, primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids, while secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones. Tertiary alcohols are not oxidized under normal conditions. Esterification: This reaction involves the formation of an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst. For example, when ethanol is…arrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] Draw a structural formula for 2,2-dimethyl-1-propanol. • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • Do not include lone pairs in your answer. They will not be considered in the grading. opy aste IFarrow_forward
- 10. Your plane crashes in the Rocky Mountains. Miraculously you survive, and find yourself stranded on a deserted mountain slope. While out gathering berries, you stumble across an abandoned but well-stocked organic laboratory! Mentally thanking your chemistry teacher, you immediately begin making the useful compounds listed below. (Show equations with structures and names and give type of reaction) a) octyl methanoate (a hut deodorizer which smells like oranges) Type of Reaction: Structures and Names:arrow_forwardUnderstanding Organic Chemistry Workbook 3 H,C-CH3 bb H3C-O-C-CH2-C-CH2-CH3 Туре of functional group H,C-CH3 || H3C-0-C-CH2-C-CH2-CH3 IUPAC H2C-CH3 H,C-o-6-CH,-C-CH,-CH, Common Name CH3 9 H3C-CH-C-CI c. Туре of functional group CH3 9 H3C-CH-C-CI IUPAC CH3 O H3C-CH-Ö-CI Common Namearrow_forwardWrite about the history of (Cyclohexene)? with book referencesarrow_forward
- I)sodium ethoxide,ethanol ii) HCl,H2Oarrow_forward10 Chem101 A app.101edu.co Question 4 of 28 Submit What is the IUPAC name for the alkyl halide (haloalkane), C,H,,Br, shown here? A) 1-bromo-2-methylcyclohexane B) 1-bromo-6-methylcyclohexane C) 2-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane D) 6-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane E) 1-bromo-2-methylcycloheptane Brarrow_forwardHow many monochlorination products are possible for the alkane in the picture attached?arrow_forward
- Hydrocarbons like benzene are metabolized in the body to arene oxides, which rearrange to form phenols. This is an example of a general process in the body, in which an unwanted compound (benzene) is converted to a more water-soluble derivative called a metabolite, so that it can be excreted more readily from the body. a.) Classify each of these reactions as oxidation, reduction, or neither.b.) Explain why phenol is more water soluble than benzene. This means that phenol dissolves in urine, which is largely water, to a greater extent than benzenearrow_forwardapp.1 Question 15.a of 16 Ibuprofen is a chiral compound used as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory. Determine the number of chiral centers and the number of possible stereoisomers. How many chiral centers are in this structure? ОН K A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) There are no chiral centers in this molecule.arrow_forwardClick the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. The following reaction has been reported in the chemical literature. Write the structure of the product(s) formed. & H3C CH3 1. Diethyl ether 2. H₂O I I I I draw structure ... Iarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co