
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The diagram at the right represents the interference pattern created by two water waves. The waves were created by two objects bobbing up and down in phase at the same frequency. Point P on the pattern is a distance of 36.9 cm from S1 and 61.5 cm from S2. Determine the wavelength (in cm) of the water waves.
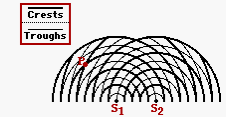
Transcribed Image Text:Crests
Troughs
S2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please solvearrow_forwardWhat is the equation that describes this relationship in the graph? What are the units of the slope, and what is the meaning of the slope? Explain!arrow_forwardTwo sources of electromagnetic waves (light waves) are emitting coherent waves at a frequency of 717 THz. These two sources are located a distance d apart and aimed at point A, as shown below. If the top source is located a distance 3.0 meters away from point A, find the minimum, nonzero, distance d that will give constructive interreference. Enter your answer in millimeters. 4₁ Laser Laser d Aarrow_forward
- Public television station KQED in San Francisco broadcasts a sinusoidal radio signal at a power of 316 kW. Assume that the wave spreads out uniformly into a hemisphere above the ground. At a home 4.00 km away from the antenna, what average pressure does this wave exert on a totally reflecting surface? Pau 2.10x10-11 Pa Submit Previous Answers Part B Correct At a home 4.00 km away from the antenna, what are the amplitudes of the electric and magnetic fields of the wave? Emaz. Bmaz 1.54,5.13×10-9 N/C,T Submit Previous Answers Part C Correct At a home 4.00 km away from the antenna, what is the average density of the energy this wave carries? Ο ΑΣΦ ? that = 3.77.109 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer * Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Part D J/m³ For the energy density in part (c), what percentage is due to the electric field? 50.0 % Submit Previous Answers Part E Correct For the energy density in part (c), what percentage is due to the magnetic field? 50.0 % Submit Previous…arrow_forwardplease help with #8arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows the wave crests for two sources that are totally in phase. For each of the labeled points, determine whether the light intensity (not the wave amplitude) is a minimum or a maximum. B S, Maximum Minimum Neither Submit Answer Tries 0/100arrow_forward
- Draw a figure to show the resultant wave produced when two coherent waves (with equal amplitudes x) interact in phase. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave? If the phase difference between the coherent waves is changed to 60º, what will be new amplitude?arrow_forwardPlease download the following worksheets, which show 4 separate grids. Each grid has two different waves (e.g., Wave and Wave B). Your goal is to draw the resulting wave (i.e., Wave C) if the two waves would have been superposed on top of each other. To do this, you'll need to add the two amplitudes (height of the Wave A and Wave B on the y-axis) at a given point on the x-axis to get the resulting one. For example, using number 3 as an example: a. At point 0 on the x axis, Wave A has an amplitude of 0, and Wave B has an amplitude of 0, so Wave C at point 0 would be 0. b. At point 4 on the x axis, Wave A has an amplitude of 6, and Wave B has an amplitude of 4, so Wave C at point 3 would have an amplitude of 10. c. At point 8 on the x axis. Wave A has an amplitdue of 0, and Wave B has an amplitude of -4, so Wave C at point 8 would be -4. You do not have to find the points for every single point along the x-axis, but just enough to get the general shape of the resulting wave. Once you…arrow_forwardThere are 4 waves of wavelengths: λ1 = 10m, λ2 = = 620 × 10⁹m, 12 = 450 × 10¯⁹m, λ4 = 30 x 10-10m. The subscripts in the answer part follow the same rule as it was given for the wavelengths: 1 refers to the 1st wave, 2nd refers to the 2nd waves, 3rd refers to the 3rd wave, 4 refers to the 4th wave. Select all that apply: the 4th wave is an UV radiation. The 2nd frequency corresponds to the radio wave range. All the wavelengths correspond to the electromagnetic spectrum only one wavelength is part of the visible spectrum The radiation with the highest energy is the 1st wave. The radiation with the highest energy is the 4th wave. The relation between their frequencies is f₁ f2 > f3 < f4 The speeds of the waved depends on their wavelength. The 1st frequency corresponds to the radio wave range.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON