
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577213
Author: Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Create a conformational analysis using the molecule in the picture. Follow the instruction in the picture when you transform the molecule into its Newman projection. Explain the conformations.
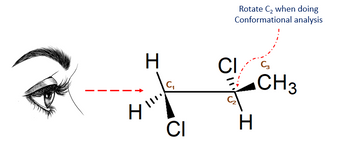
Transcribed Image Text:H
H
CI
Rotate C₂ when doing
Conformational analysis
CI
.I
H
CH3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- /x/Isl.exe/lo_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_dp5pR4ENzvdYC-70kXyMz36BqJhw3sVPj_jpaFLxvGArYxlbmayqa71YYPJBG6RjdYAdGPjGhFLILID-HEX1YcqAB?1oBw7QYjlbavbSPXtx-YCjsh_7mMmrq#item P Course Home Login | Student Veri... Hb Logout MyProgrammingLab Imported From IE O ITEC2110:Summer2... TunesToTube - Upl.. Publix App Web Development.. O KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM Using the Arrhenius equation to calculate k at one temperature fr. Cia 23%#3%# The rate constant of a certain reaction is known to obey the Arrhenius equation, and to have an activation energyE=45.0 kJ/mol. If the rate constant of this -1 -1 reaction is 4.4 x 10 M s at 266.0 °C, what will the rate constant be at 177.0 °C? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. -1 k = \\M -1 x10arrow_forwardof 1) & 2) X 2 ad esc-l 1)LDA, -78% ?arrow_forward-858kcal to mcalarrow_forward
- Hello, could you help me with this one?arrow_forward(asap plzz 10 minarrow_forwardhtProblemID=D143793425&offset%3Dnext CHE154-H Gen Chem I Bronikowski S20 ints Part A a solution that is 0.195 M in HC2 H3O2 and 0.100 M in KC2H3 O2 Express your answer to two decimal places. • View Available Hint(s) AZ¢ pH = %3Darrow_forward
- I need help with the question in the first picture, the second picture is the resources neededarrow_forward15carrow_forward8. Construct a theoretical curve for the titration of HAC by sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The volume of acetic acid: in the beaker is 25 ml and its concentration is 0.02 M. The titrant is NaOH and its concentration is also 0.02 M. Calculate pH versus volume of NaOH, which will be added in increments of 1 mL. Construct this titration curve for 35 mL. Show only the calculations at VNaoH=0, 0 Ve).arrow_forward
- What is the basis for the separation of different compounds by ion ex-change?arrow_forwardQ1) A sada- Lime Sample is 90% NaoH and 10% CaO• If 3gm is dissolved in 250 ml, what is the tutal normadity of the Selution as abase ? How many milliliters of O.57N H2 S@4 would be requiredd to titrate i00 me of the Solution ? Ans.s ( 0.309 N, 60.59 ml) Q12) How much water that required add to 200 ml HNO, ( densly = 1.285 gm/ml) Contains 46 wt% acid to Convert lo wt% acid solution? Ars. : 919.6 mlarrow_forwardHO- 1) DMSO, (COCI)2 2) Et,N :? Editarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning
