
Concept explainers
The Cost of Capital: Cost of New Common Stock
If a firm plans to issue new stock, flotation costs (investment bankers' fees) should not be ignored. There are two approaches to use to account for flotation costs. The first approach is to add the sum of flotation costs for the debt, preferred, and common stock and add them to the initial investment cost. Because the investment cost is increased, the project's expected return is reduced so it may not meet the firm's hurdle rate for acceptance of the project. The second approach involves adjusting the cost of common equity as follows:
The difference between the flotation-adjusted
Quantitative Problem: Barton Industries expects next year's annual dividend, D1, to be $1.80 and it expects dividends to grow at a constant rate g = 4.2%. The firm's current common stock price, P0, is $20.60. If it needs to issue new common stock, the firm will encounter a 5.2% flotation cost, F. Assume that the cost of equity calculated without the flotation adjustment is 12% and the cost of old common equity is 11.5%. What is the flotation cost adjustment that must be added to its cost of
%
What is the cost of new common equity considering the estimate made from the three estimation methodologies? Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Do not round intermediate calculations.
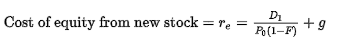
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

- What effect would a decreased cost of capital have on a firm's future investments?arrow_forwardThe optimal capital structure for firms in stable industries can reasonably contain ________________ than firms in volatile industries. Select one: A. more debt B. less debt C. an equal amount of debt D. There is no relationship between the cyclical nature of an industry and optimal capital structurearrow_forwardHow does a cost-efficient capital market help reduce the prices of goods and services? Describe the different ways in which capital can be transferred from suppliers of capital to those who are demanding capital. Is an initial public offering an example of a primary or a secondary market transaction? Indicate whether the following instruments are examples of money market or capital market securities. a. US Treasury bills b. Long-term corporate bonds c. Common stocks d. Preferred stocks e. Dealer commercial paper Briefly explain what is meant by the term efficiency continuum.arrow_forward
- If a firm plans to issue new stock, flotation costs (investment bankers' fees) should not be ignored. There are two approaches to use to account for flotation costs. The first approach is to add the sum of flotation costs for the debt, preferred, and common stock and add them to the initial investment cost. Because the investment cost is increased, the project's expected rate of return is reduced so it may not meet the firm's hurdle rate for acceptance of the project. The second approach involves adjusting the cost of common equity as follows: Cost of equity from new stock = r, D1 +8 Po(1-F) The difference between the flotation-adjusted cost of equity and the cost of equity calculated without the flotation adjustment represents the flotation cost adjustment. Quantitative Problem: Barton Industries expects next year's annual dividend, D1, to be $1.90 and it expects dividends to grow at a constant rate g = 4.3%. The firm's current common stock price, Po, is $25.00. If it needs to issue…arrow_forwardWhat is the connection between capital budgeting decisions and the enterprise’s cost of capital? Would an enterprise ever decide to embark on a project whose rate of return would be less than its cost of capital? Why or why not?arrow_forwardSeveral factors affect a firm’s need for external funds. Evaluate the effect of each following factor and place a check next to each factor that is likely to increase a firm’s need for external capital—that is, its AFN (additional funds needed). Check all that apply. The firm increases its dividend payout ratio. The firm switches its supplier for the majority of its raw materials. The new supplier offers less favorable credit terms and thus reduces the trade credit available to the firm, resulting in a reduction in accounts payable. The firm improves its production system and increases its profit margin. Accounts payable and accrued liabilities represent obligations that the firm must pay off. Assuming everything else holds constant, if they increase, the firm’s AFN will_________ .arrow_forward
- BIE The Cost of Capital: Weighted Averige cost of capital The firm's target capital structure is the mix of debt, presured stack, and common equity the firm plans to mise funds for future projects. The target proportions of debt, preferred stock, and common equity, along with the cost of these I components, are used to calculate the firm's weighted average cost of capital (WACC). If the firm will not have to issue new common study then the cost of retained earnings is used in the firm's WACC calculation. However, if the firm will I have to issue new common stock, the cost of new common stock should be used in the firm's WALC calculation. Barton Industines expects that its target capital Structure for finds in the future for its raising capital budget will consist of 40% debt, 5% prefence stock, and 55% common equity. Note that the firm's marginal tax rate is 25%. Assume that the firm's cost of debt, rd is 10.0%, the firm's cost of preferred stock, rp is 9.2.%. and the firm's cost of…arrow_forward1.1. 1.7. Which item should be included on cash flow estimation in capital budgeting analysis? a. interest b. sunk cost d. cannibalization c. depreciation Other things held constant, which of the following event is most likely to increase WACC? a. increase tax rate b. increase stock price c. increase in the use of debt d. increase in dividend payout ratio Which of the following is not a means by which ownership implies corporate control? a. appointing a CEO b. proxy fight c. preemptive right d. classified stock 1.3. DAarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





