
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Experiments to study vision often need to track the movements of a subject’s eye. One way of doing so is to have the subject sit in a magnetic field while wearing special contact lenses that have a coil of very fine wire circling the edge. A current is induced in the coil each time the subject rotates his eye. Consider an experiment in which a 20-turn, 6.0-mm-diameter coil of wire circles the subject’s cornea while a 1.0 T magnetic field is directed as shown. The subject begins by looking straight ahead. What emf is induced in the coil if the subject shifts his gaze by 5.0° in 0.20 s?
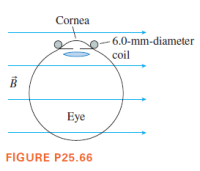
Transcribed Image Text:Cornea
- 6.0-mm-diameter
coil
Eye
FIGURE P25.66
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A velocity selector in a mass spectrometer uses a 0.110 T magnetic field. What electric field strength (in volts per meter) is needed to select a speed of 4.50 ✕ 106 m/s?arrow_forwardA scalloped hammerhead shark swims at a steady speed of 1.0 m/s with its 83-cm-wide head perpendicular to the earth's 52 μT magnetic field. Answer in mV please.arrow_forwardThe figure represents an electromagnetic brake that uses eddy currents. An electromagnet hangs from a railroad car near one rail. To stop the car, a large current is sent through the coils of the electromagnet. The moving electromagnet induces eddy currents in the rails, whose fields oppose the change in the field of the electromagnet. The magnetic fields of the eddy currents exert force on the current in the electromagnet, thereby slowing the car. The direction of the car's motion and the direction of the current in the electromagnet are shown correctly in the picture. Determine which of the eddy currents shown on the rails is correct. Explain your answer. This answer has not been graded yet. Narrow_forward
- A loop of wire with radius r= 0.081 m is in a magnetic field with magnitude B as shown in the graph. B changes from B1 = 0.34 T to B2= 6.5 T in At = 7.5 s at a constant rate. Express the magnetic flux going through a loop of radius r assuming a constant magnetic field B. Express the change in the magnetic flux going through this loop, AP, in terms of B , B2 and r. Calculate the numerical value of 4P in T m². Express the magnitude of the average induced electric field, E, induced in the loop in terms of 4P, r and At. E = Calculate the numerical value of E in N/C. E =arrow_forwardWe drop a magnet with mass 2 kg through a conducting loop starting from height 2.35 meters above the ground. The resistance of the loop plus the induced current dissipates some of the energy as heat. We observe the mass landing with a speed of 0.6 meters/second. How much energy was lost to heat? You may take g to be 9.8 m/s^2 and ignore all other forces than gravity and electricity + magnetism. Joulesarrow_forwardConsider the mass spectrometer shown schematically in the figure below. The magnitude of the electric field between the plates of the velocity selector is 3.00 x 103 v/m, and the magnetic field in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber has a magnitude of 0.0300 T. Calculate the radius of the path for a singly charged ion having a mass m = 2.48 x 10 26 kg. Bo in Detector array Bin x Velocity selectorarrow_forward
- Consider the mass spectrometer shown schematically in the figure below. The magnitude of the electric field between the plates of the velocity selector is 2.20 x 10³ V/m, and the magnetic field in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber has a magnitude of 0.0300 T. Calculate the radius of the path for a singly charged ion having a mass m = 1.86 x 10-26 kg. x Need Help? X X P X m x x * % X x Detector array Velocity selector Bo, in X Read It X x X X É x x X X 100 V **** +9 Watch It X * x x * * * X x x Xarrow_forwardA square loop of conductive wire Is laid flat against this computer screen. Each side of the square is 3.0m long. A 5.0T magnetic field passes through the loop, oriented so that it points directly out of your screen. If the magnetic field drops to only 2.0T over the course of 1.5 seconds, what emf will be produced in the square loop?arrow_forwardA patient with a pacemaker is mistakenly being scanned for an MRI image. A 10.0 cm long section of pacemaker wire moves at a speed of 11.1 cm/s perpendicular to the MRI unit's magnetic field and a 22.0 mV Hall voltage is induced. What is the magnetic field strength?arrow_forward
- A magnetic field has a magnitude of 0.00090 T, and an electric field has a magnitude of 4.1 × 103 N/C. Both fields point in the same direction. A positive 1.7-μC charge moves at a speed of 4.4 × 106 m/s in a direction that is perpendicular to both fields. Determine the magnitude of the net force that acts on the charge.arrow_forwardA magnetron in a microwave oven emits electromagnetic waves with frequency f = 3500 MHz. What would be the value of the magnetic field strength required for a single electron to move in circular paths with this frequency? O 0.205 T 0.305 T 0.135 T 0.125 Tarrow_forwardThe strengths of the fields in the velocity selector of a Bainbridge mass spectrometer are B = 0.55 T and E = 1 x 105 V/m, and the strength of the magnetic field that separates the ions is Bo=0.75 T. A stream of singly charged Li ions is found to bend in a circular arc of radius 2.32 cm. What is the mass of the Li ions? m x10 -26 kgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON