
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
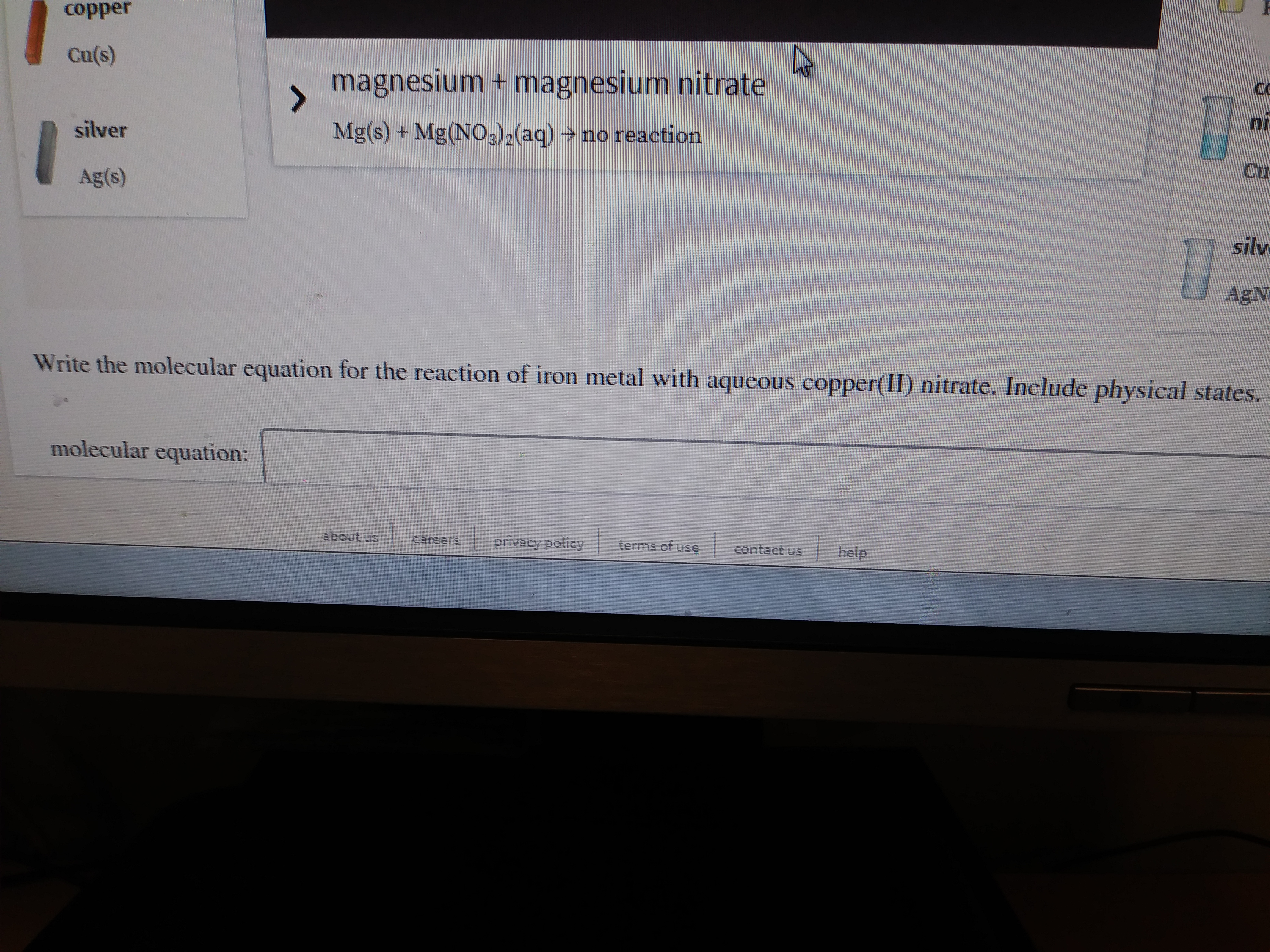
Transcribed Image Text:copper
Cu(s)
magnesium + magnesium nitrate
silver
Mg(s) + Mg(NO3)2(aq) → no reaction
Cu
Ag(s)
silv
AgN
Write the molecular equation for the reaction of iron metal with aqueous copper(II) nitrate. Include physical states.
molecular equation:
about us
Careers
privacy policy
terms of use
help
contact us
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Predict the reactants of this chemical reaction. That is, fill in the left side of the chemical equation. Be sure the equation you submit is balanced. (You can edit both sides of the equation to balance it, if you need to.) Note: you are writing the molecular, and not the net ionic equation. →> KCIO O̟(aq) + H¸ 2 H₂O (1) ローロarrow_forwardBlast furnaces extract pure iron from the iron(III) oxide in iron ore in a two step sequence. In the first step, carbon and oxygen react to form carbon monoxide: 2 C(s)+O,(9)→2CO(g) In the second step, iron(III) oxide and carbon monoxide react to form iron and carbon dioxide: Fe,0,(s)+3 CO(g)→2 Fe(s)+3 CO,(9) Write the net chemical equation for the production of iron from carbon, oxygen and iron(III) oxide. Be sure your equation is balanced.arrow_forwardCopper (II) chloride, CuCl2(aq) solution is reacted with aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3(aq) solution. Write a BALANCED EQUATION for this reaction.arrow_forward
- What is the correct chemical equation for the double replacement reaction of iron (III) chloride with calcium hydroxide? FeCl2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + Fe(OH)2 Fe3Cl + CaOH → CaCl + Fe3OH 2 FeCl3 + 3 Ca(OH)2 → 3 CaCl2 + 2 Fe(OH)3 2 FeCl3 + 3 Ca(OH)2 → Fe2Ca3 + 2 Cl3(OH)3 2 FeCl3 + 3 Ca(OH)2 → Fe2Ca3 + 6 ClOHarrow_forwardIdentify each of the following types of reactions S8 (s) + 6 O2 (g) –4 S203 (g) Reaction type: [ Select ] 3 Sr(OH)2 (aq) + 2 AuCl3 (aq) 3 SrCl2 (aq) + 2 Au(OH)3 (s) Reaction type: [Select ] 2 MgO (s) 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) Reaction type: [ Select ] 2 C2H6 (g) + 7 O2 (g) 4 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) Reaction type: [Select] CaCl2 (aq) + 2 Ag 2 AgCI (aq) + Ca (s) Reaction type: [ Select ]arrow_forwardThe US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) places limits on the quantities of toxic substances that may be discharged into the sewer system. Limits have been established for a variety of substances, including cadmium, which is limited to 5.0 µg/L. If an industry is discharging cadmium as cadmium(II) phosphate (Cd3(PO4)2), what is the maximum permissible molarity of that substance?arrow_forward
- When a solution of ammonium chloride is added to a solution of lead(II) nitrate, Pb(NO3)2, a white precipitate, lead(II) chloride, forms. Write a balanced net ionic equation for this reaction. Both ammonium chloride and lead(II) nitrate exist as dissociated ions in an aqueous solution.arrow_forwardAspirin, C6H4(OCOCH3)CO,H, is produced by the reaction of salicylic acid, Cg H4(OH)CO,H, and acetic anhydride, (CH, CO)20. [References] C6H4 (OH)CO,H(s) + (CH3 CO)2O(4) 4 CH4 (OCOCH3)CO,H(s) +CH,CO, H(e) If you mix 160. g of each of the reactants, what is the maximum mass of aspirin that can be obtained? Mass 3D Submit Answer Try Another Version 10 item attempts remaining pt -pt I pt I pt 1 pt I pt US 2 DELLarrow_forwardBalance the chemical equation below using the smallest possible whole number stoichiometric coefficients. Fe(s) + O₂(g) + H₂O(1) → Fe(OH)₂ (aq) ロ→ロ X 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY