
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Constants I Peric
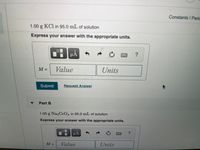
1.00 g KCl in 95.0 mL of solution
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
µA
M =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
1.00 g Na2CrO4 in 95.0 mL of solution
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
HẢ
M =
Value
Units
C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help me answer questions 1 and 2. (Questions attached below) 1. When you arrive at the lab, 2.0 M H2SO4(aq) and 2.0 M HC2H3O2(aq) will be present. Youwill need to dilute these solutions using beakers and graduated cylinders from your drawerand DI water.i. Calculate the volume of the 2.0 M HC2H3O2(aq) and DI water needed to create 50.0 mLof 1.05 M HC2H3O2(aq).ii. Calculate the volume of the 2.0 M H2SO4(aq) and DI water needed to create 50.0 mL of0.75 M H2SO4(aq). 2. A 48.33-mL sample of 0.150 M NaBr is titrated into 50.00 mL of 0.145 M AgNO3. Bothsolutions had the same initial and final temperatures. The reaction occurred in a calorimeterwith a known heat capacity and produced 1546.03 J of heat.i. Write a balanced equation that is occurring.ii. Determine the theoretical yield of the solid.iii. Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction (kJ/mole of precipitate).arrow_forward72.1 g C2 H6O in 2.18 L of solution Express your answer using three significant figures. ? M molarity = Submit Request Answer Part C 12.59 mg KI in 110.4 mL of solution Express your answer using four significant figures. |V ΑΣφ molarity = Submit Request Answer Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardCalculate the mass of potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) molar mass=204.22 P) (₁ your answer has the correct number of significant digits. g KHP 0 x10 X g mol required to neutralize 20.00 mL of a 0.250 M NaOH solution. Be surearrow_forward
- My teacher says the answer is 0.84 M, but how?arrow_forwardA solution is 2.25% by mass of KBr . How many grams of KBr are in 250.0 g of solution? Group of answer choices 0.900 g 225 g 117 g 5.62 garrow_forward5.00 mL of stock solution is diluted to 25.00 mL, producing solution ALPHA. 10.00 mL of solution ALPHA is diluted to 25.00 mL, resulting in solution BETA. 10.00 mL of solution BETA is then diluted to 25.00 mL, producing solution GAMMA. dilution factor for ALPHA from stock solution = 0.167 dilution factor for BETA from ALPHA solution = 0.0476 part c and d?arrow_forward
- What volume must 100.0 mL of 0.500 M sulfuric acid solution be diluted to prepare 0.200 M sulfuric acid solution? Group of answer choices 140. mL 150. mL 250. mL 350. mL 40.0 mLarrow_forwardMake sure answer has correct significant digitsarrow_forwardHow many moles of solute are present in the following solutions? 480 mLmL of 1.6 MM HNO3HNO3 Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forward
- Determine the mass of NaCI needed to make the following solution: 4.7% NaCI in a total volume of 95 mL Give your answer in units of grams, rounded to two places after the decimal place.arrow_forwardHi! Could you please help me into putting the formula into the format as above? Thank you!arrow_forwardAn analytical standard solution was prepared by diluting 200 mL of a stock solution to 400 mL. If 20 mL of the resulting solution was further diluted to 120 mL, what is the final solution concentration given that the original stock solution had a concentration of 0.4 M.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY