
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
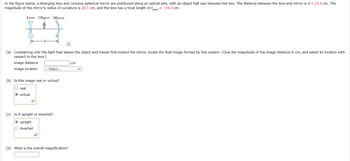
Transcribed Image Text:In the figure below, a diverging lens and concave spherical mirror are positioned along an optical axis, with an object half way between the two. The distance between the lens and mirror is d = 23.6 cm. The
magnitude of the mirror's radius of curvature is 20.1 cm, and the lens has a focal length of flens = -19.0 cm.
Lens Object Mirror
(a) Considering only the light that leaves the object and travels first toward the mirror, locate the final image formed by this system. (Give the magnitude of the image distance in cm, and select its location with
respect to the lens.)
image distance
image location
-Select---
(b) Is this image real or virtual?
O real
O virtual
(c) Is it upright or inverted?
O upright
O inverted
(d) What is the overall magnification?
cm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object is 20 cm to the left of a thin diverging lens having a focal length of-30cm. Where is the image formed? Obtain the image position both by a ray diagram.arrow_forwardAn object is placed a distance do = 19.0 cm in front of a positive (converging) lens of focal length f = 7.0 cm. = Where is the image formed relative to the lens position (positive to the right of the lens)? d₁ = What is the image magnification? m= cm Is the image upright or inverted? no image is formed inverted upright Is the image real or virtual? real O no image is formed virtual W doarrow_forwardAn object is 11 cm in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of -7 cm Determine the location of the image.arrow_forward
- The mirror equation relates the object distance, d0, the image distance, di, and the focal length, f, of a mirror as1 / d0 + 1 / di = 1 / fWhile in other topics, distance and length are strictly non-negative, in optics we introduce the following sign conventions: Object distance is positive for a real object and negative for a virtual object. Image distance is positive for a real image and negative for a virtual image. Focal length is positive for a converging mirror and negative for a diverging mirror (a) Select the best choice to complete this statement. A real object placed in front of a converging mirror creates a real image under all circumstances. under no circumstances. when the object is between the focal point and the mirror. when the object is farther than the focal length from the mirror. (b) Select the best choice to complete this statement. A real object placed in front of a diverging mirror creates a virtual image under all circumstances. under no circumstances.…arrow_forwardThe lens and mirror shown in the figure below are separated by d-100 m and have focal lengths of +750 cm and -50 0 cm, respectively An object is placed at p-100 m to the left of the lens Object Lens IHI -1.00 m- Mirror What is the position of the final image formed by light that has gone through the lens twice? Choose What is the overall magnification of the image? Is the image upright or inverted? Choose Choose...arrow_forwardUsing a thin bi-convex lens (f = 10 cm) an image is generated that is twice as large as the small object. a) Calculate the object distance as well as the image distance if the image is upright. b) Sketch the optical path of the system indicating the central ray, the parallel ray as well as the focal ray.arrow_forward
- Determine the image distance and size for a 10.00-cm tall object placed a) 60.0 cmb) 10 cm from a concave mirror having a focal length of 30.0 cm. Draw light ray diagrams for each case.arrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forwardA lens forms an inverted, double-sized image of an object placed 9 cm away. Calculate the focal length of the lens.(Give your answer in centimeters)arrow_forward
- a) You are holding a convex lens at arm's length and looking at a distant street-light. You observe the up-side down image of the street light to be on your side of the lens and 60.0 mm from the lens. You then train the lens on your study lamp. If your study lamp is 100.0 mm from the lens, how far will the image of the lamp be from the lens (in mm)? b)If your study lamp bulb is spherical of diameter 27.0 mm, what will be the diameter of its image (in mm)?arrow_forwardAn image is located 346 mm behind a 204 mm focal length lens. A) Find the object distance. B) Find the magnification of the image. C) Is the image upright or inverted? factor of 4 or when you place it 8.0 cm behind a lens thearrow_forwardUsing Ray Tracing Method and Mathematical Method, locate the image of a 2-cm object if placed on the following distances from a diverging lens with 3-cm focal length: 3 cm from the optical centermake a graph and mathematical methoduse ophysics for the graph (concave conves lenses)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON