
Concept explainers
A candle (ho = 0.28 m) is placed to the left of a diverging lens (f = -0.061 m). The candle is do = 0.22 m to the left of the lens.
a) Numerically, what is the image distance, di in meters?
b) Is this real or virtual?
c) Numerically, what is the image height, hi?
a)
The image’s distance can be determined by the lens equation as,
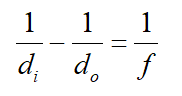
Here, f, di, and do represent the lens’s focal length, the image’s distance, and the object’s distance from the lens, respectively.
Substitute the relevant values.
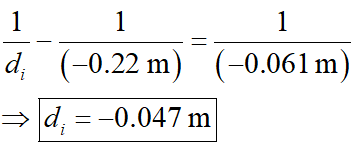
Here, the minus sign is from sign convention, according to which all distances measured in the light’s incident direction is positive and opposite to the light’s incident direction is negative.
The image’s distance is about 0.047 m.
b)
The image is formed on the object’s side, that is, left to the lens. Thus, the object’s image is a virtual image.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 6 images

- please answer vvarrow_forwardA glass sphere (n = 1.50) with a radius of 16.0 cm has a tiny air bubble 4.30 cm above its center. The sphere is viewed looking down along the extended radius containing the bubble. What is the apparent depth of the bubble below the surface of the sphere? 7.936 Apply the equation relating the object distance, image distance, and radius of curvature for a spherical refracting surface. cm Need Help? Read It Master Itarrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forward
- = 1.0). An object (A) is Assume that a thin lens (r, placed in the left side of lens (d = 45mm) and the image of the object is located in the right side of the lens at position (B) (d' = 90mm). 1) Compute the refraction index of the lens (n2); = -r2 = 40mm) is placed in the air (n 2) If placing another negative thin lens (f2 = -180mm) immediately behind the first lens to create a doublet lens in which the spacing between two lenses is zero (as shown in the right figure), what is the focal length of this doublet? 3) Where is the final image position (C) of the object (A) through this new doublet? (Note: Assuming this doublet lens is a combined thin lens too without considering its thickness).arrow_forwardan object of height 5 cm is placed 20 cm in front of a converging lens at focal length 10 cm. Behind the converging lens, and 25cm from it, there is a diverging lens of the focal length of 6 cm. Find the location of the final image, in centimeters, with respect to teh diverging lens. what is the magnification of the final image? what is the height of the final image?arrow_forwardHW Q7arrow_forward
- A) how far from the object should this lens be placed? B) what focal length eyepiece would give an overall magnification of -55? C) what focal length eyepiece would give an overall magnification of -100?arrow_forwardYour friend has glasses. When you look stralght at their eyes when they are wearing glasses, you notice that their eyes appear right-side up and 1.1 times larger in height (and width) compared to when they are not wearing glasses. Assume that their glasses are 2.0 cm away from their eyes. What is the focal length of their glasses? Hint: What Is the object and where is the image?arrow_forwardPlease help me solve the following.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





