
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337406659
Author: WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
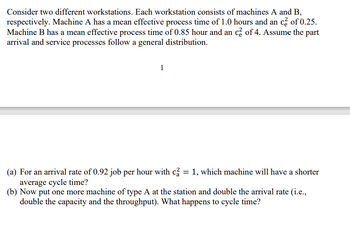
Transcribed Image Text:Consider two different workstations. Each workstation consists of machines A and B,
respectively. Machine A has a mean effective process time of 1.0 hours and an c² of 0.25.
Machine B has a mean effective process time of 0.85 hour and an c² of 4. Assume the part
arrival and service processes follow a general distribution.
1
(a) For an arrival rate of 0.92 job per hour with c2 = 1, which machine will have a shorter
average cycle time?
(b) Now put one more machine of type A at the station and double the arrival rate (i.e.,
double the capacity and the throughput). What happens to cycle time?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the answer in this number 2?arrow_forward5. The DMV Licensing office has a single line for customers waiting for the next available clerk. There are two clerks who work at the same rate. On average customers arrive every 8 minutes and the average service rate is 5 per hour for each of the two clerks. The arrival rate of customers follows a Poisson distribution, while the service time follows an exponential distribution. d.) Because the state has received less than expected tax receipts, the DMV is thinking of cutting one position. Is this a good idea? Why?arrow_forward. At a car washing service facility customers arrive at the rate of 8 cars per hour. The service can manage an average of 12 cars per hour. The arrivals follow a Poisson distribution and the service follows a Exponential distribution. Calculate a) Utilization of the system b) Average number of customers in the system c) Average time customers spend in the systemarrow_forward
- Kolkmeyer Manufacturing Company is considering adding two machines to its manufacturing operation. This addition will bring the number of machines to nine. The president of Kolkmeyer asked for a study of the need to add a second employee to the repair operation. The arrival rate is 0.06 machines per hour for each machine, and the service rate for each individual assigned to the repair operation is 0.5 machines per hour. Compute the operating characteristics if the company retains the single-employee repair operation. If required, round your answers to four decimal places. P0 = fill in the blank 1 Lq = fill in the blank 2 L = fill in the blank 3 Wq = fill in the blank 4 hours W = fill in the blank 5 hours Compute the operating characteristics if a second employee is added to the machine repair operation. If required, round your answers to four decimal places. P0 = fill in the blank 6 Lq = fill in the blank 7 L = fill in the blank 8 Wq = fill…arrow_forwardCustomers arrive at a one window drive according to a poison distribution with mean of 10 minutes and service time per customer is exponential with mean of 6 minutes. The space in front of the window can accommodate only three vehicles including the serviced ones. Other vehicles are have to wait outside this space. Calculate:a. A. probability that an arriving customer can drive directly to the space in front of the windowb. Probability that an arriving customer will have to wait outside the directed space c. How long an arriving customer is expected to wait before getting the service?arrow_forwardConsider a bank branch that has three distinct customer arrival patterns throughout the day, as measured by average arrival rates (below). Morning (8:30 - 11:30): arrival 1 = 47 per hour. %3D Lunch (11:30 - 1:30): arrival 2 = 70 per hour. Afternoon (1:30 - 4:00): arrival 3 = 30 per hour. Regardless of the time of day, the average time it takes for a teller to serve customers is 3.17 minutes. Because of competition with other banks in the area, management has developed an internal goal to keep the average customer wait before service to be less than 4 minutes. With that in mind, answer the following: a. During the morning period, what is the minimum number of tellers that the bank needs to hire to achieve the 4-minute service goal mentioned above? [ Select] b. During lunch, what is the minimum number of tellers that the bank needs to hire to achieve the 4 minute service goal mentioned above? [ Select ] c. In the afternoon, what is the minimum number of tellers that the bankarrow_forward
- The time from when a patient is discharged from North Shore Hospital to the time the discharged patient’s bed is ready to be assigned to a new patient is referred to as the bed assignment turnaround time. If the bed turnaround time is excessive, it can cause problems with patient flow and delay medical procedures throughout the hospital. This can cause long waiting times for physicians and patients thus creating customer dissatisfaction. The admissions RN has assigned a patient care associate to measure the bed turnaround time for a randomly selected bed each morning., afternoon, and evening for 30 days. Following are the bed turnaround time sample observations: Day Day Bed Turnaround Times (min) 1 1 127 135 167 144 151 2 2 140 155 122 135 119 3 3 112 128 97 118 131 4 4 223 135 154 187 150 5 5 181 155 160 172 166 6 6 103 158 145 124 149 7 7 146 135 167 150 178 8 8 104 122 115 137 129 9 9 136 158 137 148 156 10 10 145 163 106 139 170 11 11 84 146 125 98…arrow_forwardTown Taxi uses three dispatchers to handle requests for service and to dispatch the cabs. The telephone calls that are made to Town Taxi use a common number. When all dispatchers are busy, the caller hears a waiting song until the first dispatchers becomes available. The telephone system will assign available dispatcher to the waiting callers according to FCFS. Assume that the arrival of calls follows a Poisson distribution, with an average of 35 calls per hour. Also assume that the time that each dispatcher spends with a customer follows Exponential distribution and each dispatcher takes an average of 3 minutes with each caller. 15.What is the average time in minutes that a customer spends in the system? 3.8 mins 7 mins 4.8 mins 8.9 minsarrow_forwardKolkmeyer Manufacturing Company is considering adding two machines to its manufacturing operation. This addition will bring the number of machines to nine. The president of Kolkmeyer asked for a study of the need to add a second employee to the repair operation. The arrival rate is 0.06 machines per hour for each machine, and the service rate for each individual assigned to the repair operation is 0.5 machines per hour. Compute the operating characteristics if the company retains the single-employee repair operation. If required, round your answers to four decimal places. P0 = fill in the blank 1 Lq = fill in the blank 2 L = fill in the blank 3 Wq = fill in the blank 4 hours W = fill in the blank 5 hours Compute the operating characteristics if a second employee is added to the machine repair operation. If required, round your answers to four decimal places. P0 = fill in the blank 6 Lq = fill in the blank 7 L = fill in the blank 8 Wq = fill…arrow_forward
- A university is considering setting up an information desk manned by one employee. Based on information obtained from similar information desks, it is believed that people will arrive at the desk at the rate of 18 per hour. It takes an average of 2 minutes to answer a question. It is assumed that arrivals are Poisson and answer times are exponentially distributed. 3. Find the proportion of the time that the employee is busy. 4. Find the average number of people receiving and waiting to receive information. 5. Find the average number of people waiting in line to get information.arrow_forwardCustomers arrive at a video rental desk at the rate of 14 per minute(Poisson).Each server can handle 4.668 customers per minute(Poisson). If there are 6 servers, determine the probability of 5 or fewer customers in the system. a. 0.03 b. 0.025 c. 0.049 d. 0.901arrow_forward3 The M/M/1 Queue During peak time, customers arrive at a bank teller window (with a single teller) at a rate of 23 per hour, where the teller can serve 25 per hour. This problem will allow you to investigate (via a simple extension of the mean queue size formula) the effect of highly-variable service times on our familiar queuing metrics. The diagram below stylizes the queuing system: Waiting Service Calculate the marginal probability P (T > oT). a. O b. 0.25 O c. 0.63 O d. 0.75 Calculate the mean time a customer spends at the bank (waiting time plus service time) in minutes. O a. 30 minutes O b. 27.6 minutes O c. 2.4 minutes O d. 7 minutesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259667473
Author:William J Stevenson
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259666100
Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781285869681
Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781478623069
Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:Waveland Press, Inc.