
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

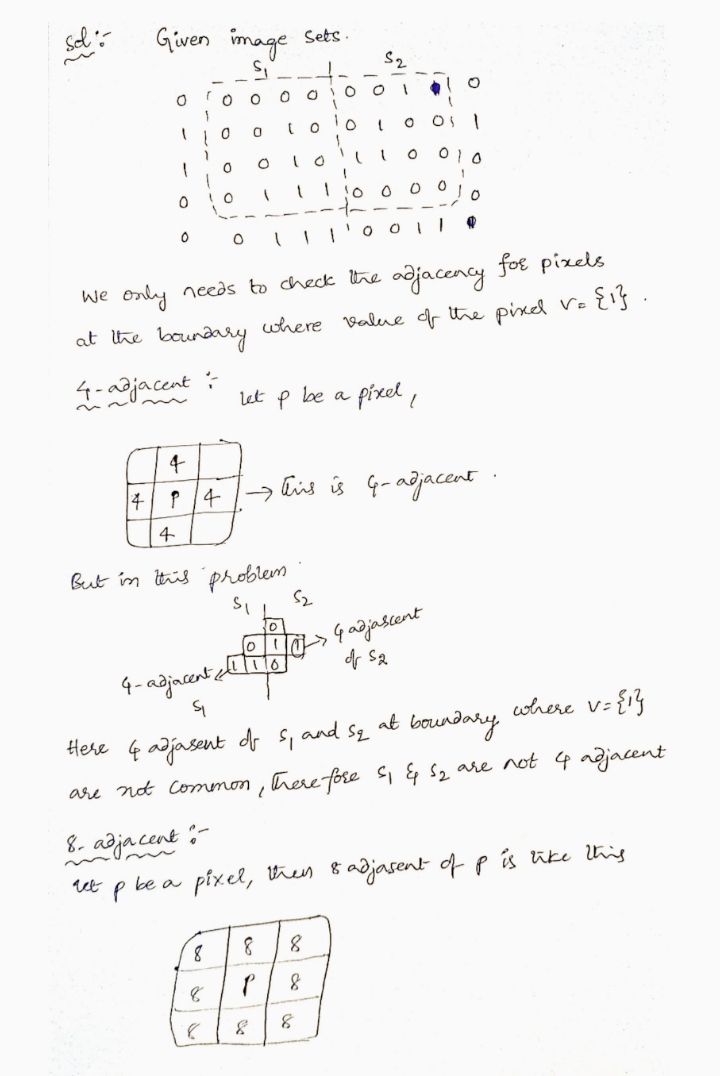
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the two image subsets, S, and S, in the
following figure. With reference to Seetion 2.5,
and assuming that V = {1}, determine whether
these two subsets are:
(a)* 4-adjacent.
(b) 8-adjacent.
(c) m-adjacent.
S,
0.
0i0
手
Seotion 25 unr
ha "Divat Rolotionchinu lootuao
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- i) State the image formation model.c ii) Consider the image shown in the following figure. For V= {1}, determine whether these two subsets are (a) 4-adjacent, (b) 8- adjacent, or (c) m-adjacent. 1 (Q) 2 1 1 1 3 3 1 2 2 (P) 1 2. 2) 1, 1.arrow_forwardIn computer graphics, interpolation is a standard technique.Pick one that doesn't make use of interpolation if you can avoid it.Change the orientation of the B picture by 90 degrees Bezier curve (c) Reducing the distance between (d) Ray-tracingDefend the use and need of interpolation.arrow_forwardPlease solve it , theoretical part of digital image processing course ; - If you have the following image, apply region growing from the shaded seed point using 8-connectivity and a predicate of “the absolute difference is less than or equal 25”.arrow_forward
- By using Karnaugh map, minimize each boolean functions (SOP form) -> If you're uploading pic or image as the answer, please upload it correctly as I was unable to see the answer for this question after it was answered. So I had to post a new question.Thank youarrow_forwardThe pixels in a 3 x 3 image sub-block are as follows: 3 4 2 9 ? 1 3 7 3 (a) Estimate the unknown pixel in the center using both a mean and a median estimator. (b) Repeat if the pixel of value 1 is changed to 25. Are both the mean and median affected? Why or why not?arrow_forwardConsider two images. One should be relatively large, like 512 x 512 pixels that contains several sparsely populated points with magnitude 255, and the other is small such as 15 x 15 that contains a non-symmetric object like, with the object white and the background black for both images. Perform both the correlation, and convolution of the two images separately and correctly label each result. Make the resulting image the same size as the larger input image.arrow_forward
- Explain the concept of duality in projective geometry and its applications in computer graphics, such as the duality of points and lines in 2D transformations.arrow_forwardThis is energyBalance.m in the first image in the second image are the questions according from image 1arrow_forwardConsider the following edge-weighted digraph with 8 vertices and 13 edges. V->W weight A->E 1 A->B B->C C->F 4 C->D D->G F->E 39 23 F->B 26 F->A 16 G->F G->C 40 34 H->D 95 H->G 17 Here is a graphical representation of the same edge-weighted digraph: (A) -3---->(B) -39-->(D) 16 95 (E)- -23- (F). 40 (G) (H) Suppose that you run the Bellman-Ford algorithm to compute the shortest paths from H to every other vertex. What is the distTo[] array immediately after the end of three passes of the algorithm (pass 1, 2, and 3)? Each pass consists of relaxing the 13 edges in the order given above. Here is the distTo[] array before the beginning of pass 1: v A B CDE F H. distTo(v] Answer Your answer should be a sequence of 8 integers, separated by whitespace,arrow_forward
- The figure shown above is a binary images I in which white piİxels have values of one and black pixels have values of zero. First compute derivatives of the image intensities in the x and y directions following the numerical way to obtain Ix and Iy : Ix(i,j)= (I(i+1,j)-I(i-1,j))/2 and Iy(i,j) = (I(i,j+1)-I(i,j-1))/2. For the computation of Ix(i,j) on pixels in the first column Ix(i, j) = I(i+1,j) - I(i,j) or of Iy(i,j) on pixels in the first row Iy(i,j) = I(i,j+1) - I(i,j). For the computation of Ix(i,j) on pixels in the last column Ix(i,j) = I(i,j) - I(i-1,j) or of Iy(i,j) on pixels in the last row Iy(i,j) = I(i,j) - I(i,j-1). Calculate the response R of the Harris corner detector at each pixel based on Ix and ly, assuming (i) a value of k=0.05 in the calculation, (ii) that products of derivatives are summed over an equally weighted 3 by 3 pixel window around each pixel, (iii) that the image is padded with zeros when computing at pixels on the edge. ANSWER: R= (to 2 decimal places)arrow_forwardExplain,....arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY