
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
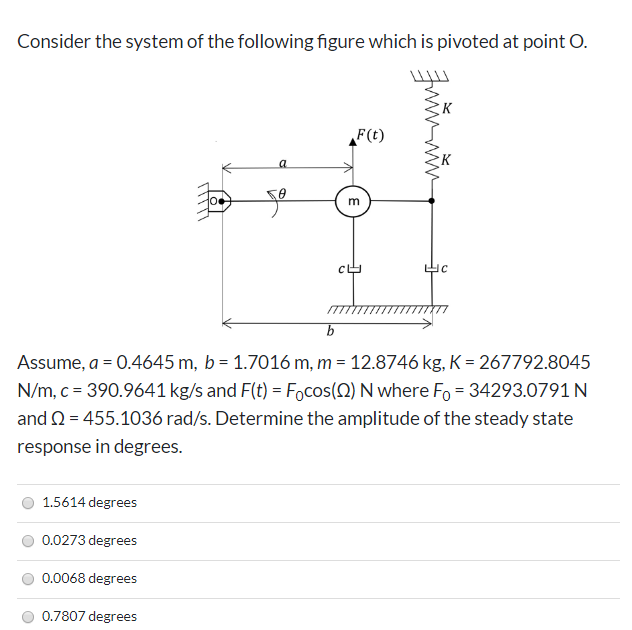
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the system of the following figure which is pivoted at point O.
F(t)
m
Assume, a = 0.4645 m, b = 1.7016 m, m = 12.8746 kg, K = 267792.8045
N/m, c = 390.9641 kg/s and F(t) = Focos(N) N where Fo = 34293.0791 N
and Q = 455.1036 rad/s. Determine the amplitude of the steady state
response in degrees.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use Triple Integral to solve the problem.arrow_forwardThe ideal gas law, discovered experimentally, is an equation of state that relates the observable state variables of the gas--pressure, temperature, and density (or quantity per volume): PV = NkBT (or pV = nRT), Figure L₂ Lx 1 of 1 Part A Find the magnitude of the average force (F) in the x direction that the particle exerts on the right-hand wall of the container as it bounces back and forth. Assume that collisions between the wall and particle are elastic and that the position of the container is fixed. Be careful of the sign of your answer. Express the magnitude of the average force in terms of m, vr, and L₂. ► View Available Hint(s) Submit Part B IVE ΑΣΦ ? Imagine that the container from the problem introduction is now filled with N identical gas particles of mass m. The particles each have different x velocities. but their average x velocity squared. denotedarrow_forwardIn the figure, link 2 rotates with constant angular velocity 02. A slider link 3 moves outwards with a constant relative velocity Vop, where Q is a point on slider 3 and P is a point on link 2. The magnitude and direction of Coriolis component of acceleration is given by Qon 3 V ОР P on 2 (A) 2002 Vop; direction of Vop rotated by 90° in the direction 002 (B) ₂ Vop; direction of Vop rotated by 90° in the direction 00₂ (C) 2002 Vo/p; direction of Vop rotated by 90° opposite to the direction of 2 (D) ₂ Vqp; direction of Vop rotated by 90° opposite to the direction 002arrow_forward
- Fundamental.7 deals with the equation of motion. The use of the equation of motion to solve this problem is mandatory. Solution using other approaches (conservation of energy...) will be automatically considered false. For the problem related to Fundamental.7 sketches of the system showing: • the respective velocity and acceleration and the frame of reference considered • the forces acting on the system of considered, in other words, a free body diagram (FBD) are mandatory. Their absences will automatically make the problem false. Z Lft 0 The 6-lb man lies against the cushion for which the coefficient of static friction is 0.7. The angle the cushion has is 56° Determine the smallest angular velocity he rotates about the z-axis, at L=9-ft from G, to ensure the man will not slip.arrow_forward2) A single degree of freedom mechanical system is provided in the figure, with coordinate markings. Note that all the cables are inflexible, and I, stands for the total inertia of the concentric pulleys. y m 2m mo 3r 2k k momo ||| equivalent system: keq meq Ceq x b) Express the coordinates y and 0 as a function of the generalized coordinate, x. d) Following an energy equivalence approach, and using the coordinate transformations obtained in part (a), determine the equivalent mass, the equivalent spring stiffness, and the equivalent damping coefficient. e) Express the equation of motion of the system, using x, the downward displacement of the block (2m) from the system's equilibrium position as the generalized coordinate. (Use symbolic expressions and show your work, do NOT generate the response).arrow_forwardA 50.0N weight uniform 4 metre long beam is hanging from a cord held out at a 30° angle as shown. And unknown weight not shown in the diagram is also hanging 1 m from the X on the diagram. A) The tension in the cord is measured with a spring balance and found to be 130 N. find the counter clockwise torque from the cord about the X shown in the diagram. B) balance torques to find the torque from the unknown weight that is not shown in the diagram Hint: add the unknown weight to the diagram and do not forget to include the weight of the beam in your calculationarrow_forward
- L W (1) (25pts) Find the description of the linear acceleration vector of the mass center of the segment (B) as functions of the distance (r), angular displacement (0), angular velocity (0), and angular acceleration (a). (2) (bonus: 5pts) Find the mass moment of inertia of the lower leg about the knee joint. Assume that the lower leg can be modeled as a cylinder. The length of the lower leg L is 30cm, and the diameter D is 4cm. The mass of the lower leg segment is 2kg. * This is a bonus problem - you learned how to calculate the mass moment of inertia in physics.arrow_forwardFluid Mechanicsarrow_forwardplease solve showing all stepsarrow_forward
- Q2: You ride your bike along a straight line from your house to a store (1000 m) away. On your way back, you stop at a friend's house which is halfway between your house and the store. Find: a. What is your displacement? b. What is the distance you have traveled?arrow_forward2 PARTs (A &B)- SOLVE CAREFULLY!! Please Write Clearly and Box the final Answer(s) ( Use images Below - Pay attention to numbers given)arrow_forwardDont use Ai. Physicsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY