
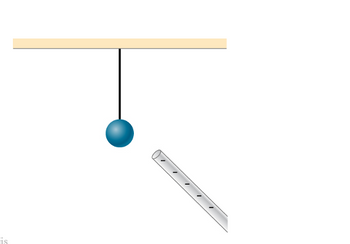
Consider the situation in the figure below; a neutral
A. First, if the rod was not there, what statement best describes the charge distribution of the ball?
1) Since it is a conductor, all the charges are on the outside of the ball.
2) The ball is neutral, so it has no positive or negative charges anywhere.
3) The positive and negative charges are separated from each other, but we don't know what direction the ball is polarized.
4) The positive and negative charges are evenly distributed everywhere in the ball.
B. Now, when the rod is moved close to the ball, what happens to the charges on the ball?
1) There is a separation of charges in the ball; the side closer to the rod becomes positively charged, and the opposite side becomes negatively charged.
2) Negative charge is drawn from the ground (via the string), so the ball acquires a net negative charge.
3) Nothing happens to the charges in the ball.
4) There is a separation of charges in the ball; the side closer to the rod becomes negatively charged, and the opposite side becomes positively charged.
5) Positive charge is drawn from the ground (via the string), so the ball acquires a net positive charge.
C. Which of the following statements is correct about the force being applied to the ball when the rod is nearby?
1) There is no force on the ball from the rod, because the ball is neutral.
2) There is no force on the ball from the rod, because the force of gravity and the string cancel it out.
3) The ball is attracted to the rod.
4) There is no force on the ball from the rod, because they are not touching each other.
5) The ball is repelled by the rod.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

- Two small, identical metal balls with charges 5.0 C and 15.0 C are held in place 1.0 m apart. In an experiment, they are connected for a short time by a conducting wire. a. What will be the charge on each ball after this experiment? b. By what factor will the magnitude of the electrostatic force on either ball change after this experiment is performed?arrow_forwardA sphere has a net charge of 8.05 nC, and a negatively charged rod has a charge of 6.03 nC. The sphere and rod undergo a process such that 5.00 109 electrons are transferred from the rod to the sphere. What are the charges of the sphere and the rod after this process?arrow_forwardThe fundamental charge is e = 1.60 1019 C. Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false. (a) Its possible to transfer electric charge to an object so that its net electric charge is 7.5 times the fundamental electric charge, e. (b) All protons have a charge of +e. (c) Electrons in a conductor have a charge of e while electrons in an insulator have no charge.arrow_forward
- Two small spherical conductors are suspended from light-weight vertical insulating threads. The conductors are brought into contact (Fig. P23.50, left) and released. Afterward, the conductors and threads stand apart as shown at right. a. What can you say about the charge of each sphere? b. Use the data given in Figure P23.50 to find the tension in each thread. c. Find the magnitude of the charge on each sphere. Figure P23.50arrow_forward(a) Two point charges totaling 8.00 C exert a repulsive force of 0.150 N on one another when separated by 0.500 m. What is the charge on each? (b) What is the charge on each if the force is attractive?arrow_forward(a) How strong is the attractive force between a glass rod with a 0.700 C charge and a silk cloth with a 0.600 C charge, which are 12.0 cm apart, using the approximation that they act like point charges? (b) Discuss how the answer to this problem might be affected if the charges are distributed over some area and do not act like point charges.arrow_forward
- A large, metallic, spherical shell has no net charge. It is supported on an insulating stand and has a small hole at the top. A small tack with charge Q is lowered on a silk thread through the hole into the interior of the shell, (i) What is the charge on the inner surface of the shell, (a) Q (b) Q/2 (c) 0 (d) -Q/2 or (e) -Q? Choose your answers to the following questions from the same possibilities, (ii) What is The charge on the outer surface of the shell? (iii) The tack is now allowed to touch the interior surface of the shell. After this contact, what is the charge on the tack? (iv) What is the charge on the inner surface of the shell now? (v) What is the charge on the outer surface of the shell now?arrow_forwardA test charge of +3 C is at a point P where an external electric field is directed to the right and has a magnitude of 4 06 N/C. If the test charge is replaced with another charge of 3 C, what happens to the external electric field at P? (a) It is unaffected. (b) It reverses direction. (c) It changes in a way that cannot be determined.arrow_forwardA Two positively charged spheres with charges 4e and e are separated by a distance L and held motionless. A third charged sphere with charge Q is set between the two spheres and along the line joining them. The third sphere is in static equilibrium. What is the distance between the third charged sphere and the sphere that has charge 4e?arrow_forward
- Assume the charged objects in Figure OQ23.10 are fixed. Notice that there is no sight line from the location of q2 to the location of q1. If you were at q1, you would be unable to see q2 because it is behind q3. How would you calculate the electric force exerted on the object with charge q1? (a) Find only the force exerted by q2 on charge q1. (b) Find only the force exerted by q3 an charge q1. (c) Add the force that q2 would exert by itself on charge q1 to the force that q3 would exert by itself on charge q1. (d) Add the force that q3 would exert by itself to a certain fraction of the force that q2 would exert by itself. (e) There is no definite way to find the force on charge q1.arrow_forward(a) Would life be different if the electron were positively charged and the proton were negatively charged? (b) Does the choice of signs have any bearing on physical and chemical interactions? Explain your answers.arrow_forwardA 2.5-g copper penny is given a charge of 2.0109C . (a) How many excess electrons are on the penny? (b) By what percent do the excess electrons change the mass of the penny?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





