
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
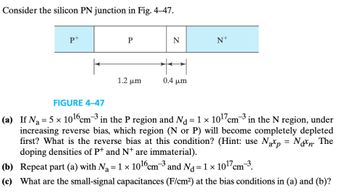
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the silicon PN junction in Fig. 4-47.
P+
Р
N
N+
0.4 μm
1.2 μη
FIGURE 4-47
(a) If N₁ = 5 × 10¹6 cm³ in the P region and N₁ = 1 × 10¹7 cm³ in the N region, under
increasing reverse bias, which region (N or P) will become completely depleted
first? What is the reverse bias at this condition? (Hint: use Nap = Non. The
doping densities of P+ and N+ are immaterial).
(b) Repeat part (a) with N₁ = 1 × 1016 cm³ and Nd = 1 × 10¹7 cm³.
(c) What are the small-signal capacitances (F/cm²) at the bias conditions in (a) and (b)?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- quick solution pleasearrow_forwardHow do you identify the anode of an unmarked diode? When the forward current of a diode increases, its forward resistance The current flowing in a reverse-biased diode circuit is extremely while the resistance of the diode is extremely The Vz of a zener diode will fairly constant even if the power supply voltage The series resistor Rs is used with the zener diode to the zener current Iz to a level.arrow_forwardA silicon diode with a forward resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with a 500Ω resistor. If an A.Cvoltage of 20V peak is connected across the series combination of the diode and the resistor what willbe the peak value of the current through the diode and the peak output voltage? What will be the peakvalue of the current through the diode and the peak output voltage if the diode were ideal?arrow_forward
- Consider a step pn junction made of silicon. The p- and n-sides are doped such that Ec – EF = 0.21 eV on the n-side and EF – Ey = 0.18 eV on the p-side. The pn junction is under zero bias and kept at T = 300 K. Find the doping density in the n-side in unit of cm-3. Answers within 5% error will be considered correct. Enter answer herearrow_forwardAfter solving a circuit with ideal diodes (Vf=0), what check is necessary for diodes initially assumed to be on? Off? We must check to see that reverse voltage appears across all diodes assumed to be on, and we must check to see that forward current flows in diodes assumed to be off We must check to see that forward current flows in diodes assumed to be on, and we must check to see that reverse voltage appears across all diodes assumed to be offarrow_forwardWhat is the zero-bias junction capacitance/cm2 for a diode with NA = 1018/cm3 on the p-type side and ND = 1020/cm3 on the n-type side? What is the diode capacitance with a 3-V reverse bias if the diode area is 0.05 cm2?arrow_forward
- just got rejected, this is the whole questionarrow_forwardWhat is the zero-bias junction capacitance per cm2 for a diode with NA =1018/cm3 on the p-type side and ND = 1015/cm3 on the n-type side. What is the diode capacitance with a 9 V reverse bias if the diode area is 0.02 cm2?arrow_forward10+ D NAME: The diodes in the circuit below have a saturation current Is = 10-¹4A. The NMOSFET has a threshold voltage of +1V and a K parameter of 10mA/V². > ID = Is (evo/VT - 1) a) Use the exponential diode model b) Oops. Someone built the circuit below, and apparently made a mistake selecting the components. They measure the voltage VA and it is equal to 1.9V. Based on VA = 1.9V, determine the expected value of V₂. +1 -3 V AVD -0.4 3-V 3-2V0 I VA=1.9V 041 VA to calculate VA. 2.2 ΚΩ +10V T 100 Ω NMOSFET VB Ins=4.05marrow_forward
- Help please not sure about answerarrow_forwardPlease solve the problemarrow_forwardActivity 1: The following circuit uses two diodes D1, and D2 with threshold voltage of 0.7 V for each and one Zener diode D3 with same threshold voltage and reverse breakdown voltage of 5.1 V. 10Vp 500Hz R1 1kQ D1 V2 -2V D2 D3 RL 3kQ Vo (1-A) Explain the operation of the Zener diode in forward and in reverse bias. (1-B) Analyze the circuit thoroughly assuming many source values that lead to all possible cases of diodes states. For each case (Hint: 4 cases), re-plot the circuit and develop the relation between the output voltage and the source voltage. (1-C) Draw input and output waveforms accurately over 4-ms period. Identify the diodes states on the graph based on the categorization of cases from part (1-B).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,