
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781337398909
Author: Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
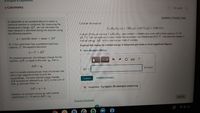
Transcribed Image Text:Chapter 6 Ubjectives
+ Calorimetry
27 of 42
Constants Periodic Table
A calorimeter is an insulated device in which a
chemical reaction is contained. By measuring the
temperature change, AT, we can calculate the
heat released or absorbed during the reaction using
the following equation:
Consider the reaction
C12 H22 O11 (s) + 1202 (g)+12C02 (g) + 11H20(1)
in which 10.0 g of sucrose, C12 H22011, was burned in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 7.50
kJ/ C. The temperature increase inside the calorimeter was found to be 22.0°C. Calculate the change in
internal energy. AE, for this reaction per mole of sucrose.
q= specific heat x mass x AT
Or, if the calorimeter has a predetermined heat
capacity, C, the equation becomes
Express the change in internal energy in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures.
• View Available Hint(s)
q = C x AT
At constant pressure, the enthalpy change for the
reaction, AH is equal to the heat, qpi that is,
AH= qp
kJ/mol
AE =
but it is usually expressed per mole of reactant and
with a sign opposite to that of q for the
surroundings. The total internal energy change,
AE (sometimes referred to as AU), is the sum of
heat, g, and work done, w:
Submit
Previous Answers
* Incorrect; Try Again; 18 attempts remaining
AE = q+ w
However, at constant volume (as with a bomb
calorimeter) w =0 and so AE = qu.
Next>
Provide Feedback
3.28
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The white pigment TiO2 is prepared by the reaction of titanium tetrachioride, TiCl4, with water vapor in the gas phase: TiCl4(g)+2H2O(g)TiO2(s)+4HCl(g). How much heat is evolved in the production of exactly 1 mole of TiO2(s) under standard state conditions?arrow_forwardThe reaction between magnesium metal and water (l) produces solid magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Calculate G for the formation of one mole of Mg(OH)2 at 27C and at 39C.arrow_forwardThe reaction SO3(g)+H2O(l)H2SO4(aq) is the last step in the commercial production of sulfuric acid. The enthalpy change for this reaction is 227 kJ. In designing a sulfuric acid plant, is it necessary to provide for heating or cooling of the reaction mixture? Explain.arrow_forward
- Water gas is produced from the reaction of steam with coal: C(s)+H2O(g)H2(g)+CO(g) Assuming that coal is pure graphite, calculate H for this reaction.arrow_forwardConsider the reaction between methane and oxygen producing carbon dioxide and water. Suppose that the reaction is carried out in a furnace used to heat a house. If q=890kJ and w=+5kJ, what is E? H at 25C?arrow_forwardWhat is the heat gained/released at constant pressure equal1o (qp = ?)? What is the heat gained/released at constant volume equal to (qv = ?)? Explain why H is obtained directly from a coffee-cup calorimeter, whereas E is obtained directly from a bomb calorimeter.arrow_forward
- 9.61 Silane, SiH4, burns according to the reaction, SiH4+2O2SiO2+2H2O , with H=1429 kJ. How much energy is released if 15.7 g of silane is burned?arrow_forward9.47 If 14.8 kJ of heat is given off when 1.6 g of HCl condenses from vapor to liquid, what is Hcond for this substance?arrow_forwardSyngas can be burned directly or converted to methanol. Calculate H for the reaction CO(g)+2H2(g)CH3OH(l)arrow_forward
- 9.63 Reactions of hydrocarhons are often studied in the petroleum industry. One example is 2C3H8(g)C6H6(l)+5H2(g) , with H = 698 kJ. If 35 L of propane at 25C and 0.97 atm is to be reacted, how much heat must he supplied?arrow_forwardWhen a 0.740-g sample of trinitrotoluene (TNT), C7H5N2O6, is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature increases from 23.4 C to 26.9 C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 534 J/C, and it contains 675 mL of water. How much heat was produced by the combustion of the TNT sample?arrow_forwardA gaseous hydrocarbon reacts completely with oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide and water vapour. Given the following data, determine Hf for the hydrocarbon: Hreaction=2044.5KJ/molhydrocarbonHf(CO2)=393.5KJ/molHf(H2O)=242KJ/mol Density of CO2 and H2O product mixture at 1.00 atm, 200.c = 0.751g/L. The density of the hydrocarbon is less than the density of Kr at the same conditions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning