
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Consider the reaction
2SO2(g) + O2(g)→2SO3(g)
Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AGxn for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 18.91 mm Hg.
ANSWER:
kJ/mol
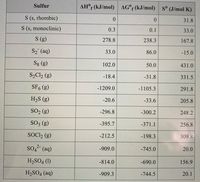
Transcribed Image Text:Sulfur
AH° (kJ/mol) AG°f (kJ/mol) s° (J/mol K)
S (s, rhombic)
31.8
S (s, monoclinic)
0.3
0.1
33.0
S (g)
278.8
238.3
167.8
S2 (aq)
33.0
86.0
-15.0
Sg (g)
102.0
50.0
431.0
S2C12 (g)
-18.4
-31.8
331.5
SF. (g)
-1209.0
-1105.3
291.8
H2S (g)
-20.6
-33.6
205.8
SO2 (g)
-296.8
-300.2
248.2
SO3 (g)
-395.7
-371.1
256.8
SOC, (g)
-212.5
-198.3
309.8
so, (aq)
2-
-909.0
-745.0
20.0
H2SO4 (1)
-814.0
-690.0
156.9
H2SO4 (aq)
-909.3
-744.5
20.1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the Gibbs free energy change (∆GRXN) in kJ that occurs when one mole of solid iron (III) oxide is produced from solid iron and water. (One decimal place) The unbalanced chemical equation for the process is: Fe (s) + H2O (g) --> Fe2O3 (s) + H2 (g)arrow_forwardConsider the reaction N₂(g) + 3H₂(g)2NH3(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AGrxn for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 14.60 mm Hg. ANSWER: Submit Answer Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. A kJ/mol Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining W - Next> Save and Exitarrow_forwardCalculate G (question 3)arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction CO(g) + Cl₂(g) →COCI₂(g) Use the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above. Calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of COCl₂(g) is reduced to 17.43 mm Hg, while the pressures of CO(g) and Cl₂(g) remain at 1 atm. ANSWER: kJ/molarrow_forwardConsider the reaction CO(g) + 3H₂(g)- →CH4(g) + H₂O(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 16.50 mm Hg. ANSWER: kJ/molarrow_forwardConsider the reaction N₂(g) + 20₂(g)- >2NO₂(g) Use the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above. Calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of NO₂(g) is reduced to 16.22 mm Hg, while the pressures of N₂(g) and O₂(g) remain at 1 atm. ANSWER: I kJ/molarrow_forward
- Consider the reactionCO(g) + Cl2(g)COCl2(g)Use the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above. Calculate G for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of COCl2(g) is reduced to 10.06 mm Hg, while the pressures of CO(g) and Cl2(g) remain at 1 atm.ANSWER: kJ/molarrow_forwarda) b)arrow_forwardCalculate the Gibbs free energy change (∆GRXN) in kJ that occurs when one mole of solid iron (III) oxide is produced from solid iron and water. (One decimal place) The unbalanced chemical equation for the process is: Fe (s) + H2O (g) --> Fe2O3 (s) + H2 (g)arrow_forward
- 4HCI(g) + O₂(g) 2H₂O(g) + 2Cl₂(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 13.10 mm Hg. ANSWER: kJ/molarrow_forwardConsider the reaction 2502(g) + O2(g)- -2S03(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AGn for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 25.91 mm Hg. ANSWER: kJ/molarrow_forward2N2(g) + O₂(g)2N₂O(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate A Grxn for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 16.81 mm Hg. ANSWER: kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY