
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
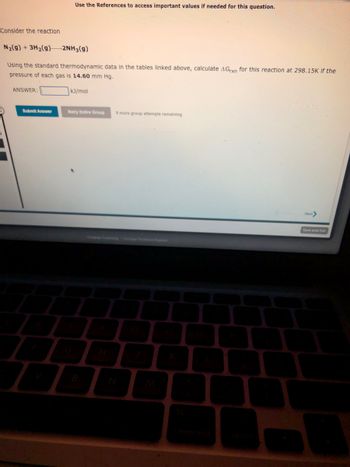
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the reaction
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g)2NH3(g)
Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AGrxn for this reaction at 298.15K if the
pressure of each gas is 14.60 mm Hg.
ANSWER:
Submit Answer
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
A
kJ/mol
Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining
W
-
Next>
Save and Exit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- F3 Consider the reaction 80 H₂(g) + F₂(g)—2HF(g) Use the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above. Calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of HF(g) is reduced to 12.02 mm Hg, while the pressures of H₂(g) and F₂(g) remain at 1 atm. ANSWER: Submit Answer $ Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. 30 Q F4 do % kJ/mol Retry Entire Group 9 F5 tv < e 4 8 more group attempts remaining MacBook Air C F6 & K F7 * DII F8 Previous Email Instructor F9 Next Save and Exit F10 Iarrow_forwardConsider the reaction H,(g) + F2(g) 2HF(g) Use the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above. Calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of HF(g) is reduced to 20.42 mm Hg, while the pressures of H,(g) and F,(g) remain at 1 atm. ANSWER: kJ/mol Submit Answer Retry Entire Group No more group attempts remain Previous Next Save and Exit Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support OPEN FILES MacBook Air EZ F8 F9 F10 F1 FIarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solutionarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction2SO2(g) + O2(g)->2SO3(g)Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate deltaGrxn for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 39.97 mm Hg.ANSWER: kJ/molarrow_forwardWhen LiBr dissolves in water the AHsolution = -49 kJ/mol The sum of the AHhydration of Lit and Br is -868 kJ/mol Using these data, what is the AH for the reaction Lite () + Brg) → LiBr(s) -819 kJ/mol -917 kJ/mol cannot be determinedarrow_forwardSHOK hae A gend 5. Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: M + N Q+R AH = + 350 kJ a) What would have to this system if it was placed in an ice water bath? Explain you reasoning. b) What would happen to this system if it was placed in a hot water bath? Explain your reasoning. 88 EXPERIMENT 5arrow_forward
- For the reaction 2HBr(g) + Cl₂ (g) → 2HCl(g) + Br₂ (g) AH = -81.1 kJ and AS° = -1.20 J/K The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 288.0 K is | Assume that ΔΗ° and AS are independent of temperature. Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward#3 Calculate the standard entropy, AS in, of the reaction at 25.0 C using the table of thermodynamic properties. C₂H₂(g) + H₂O(1)→ C₂H₂OH(1) ASixn = Calculate the standard Gibbs free energy of the reaction, AGixn. The standard enthalpy of the reaction, AHxn, is -44.2 kJ.mol-¹. AGixn= TOOLS x10 Determine in which direction the reaction is spontaneous as written at 25.0 °C and standard pressure. $ 4 % 5 Okay MacBook Pro & N You 8 ( BABAE 9 J-K-¹-mol-1 A kJ-mol-1 O delet-arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction at 298 K. I1(s) + Fe(s) 2 I (aq) + Fe2*(aq) Which of the following statements are correct? Choose all that apply. On=2 mol electrons %3D OK0 DE°cell >0 Submit Answer Try Another Version 1 item attempt remainingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY