
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Consider the parallel-plate capacitor shown in the figure. The plate separation is 2.1 mm and the electric field inside is 15 N/C. An electron is positioned halfway between the plates and is given some initial velocity, vi.
a) What speed, in meters per second, must the electron have in order to make it to the negatively charged plate?
b) If the electron has half the speed needed to reach the negative plate, it will turn around and go towards the positive plate. What will its speed be, in meters per second, when it reaches the positive plate in this case?
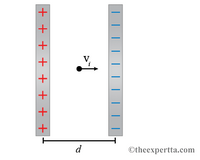
Transcribed Image Text:V.
d
©theexpertta.com
| || | | | ||||
+ + + + + + + +
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 0.079 μF capacitor is being held at a potential difference of 490 μV. a) What is the charge, in coulombs, on one of the plates? b) If you measure the size of each plate to be 49 cm2, how far apart are the plates, in micrometers? c) What is the magnitude of the electric field inside this capacitor, in newtons per coulomb?arrow_forwardMY N An electron is to be accelerated in a uniform electric field having a strength of 1.90 x 106 v/m. (a) What energy in kev is given to the electron if it is accelerated through 0.790 m? kev (b) Over what distance would it have to be accelerated to increase its energy by 50.0 GeV (as in the Stanford Linear Accelerator, which is actually smaller than this)? km Additional Materialsarrow_forwardOne type of ink-jet printer, called an electrostatic ink-jet printer, forms the letters by using deflecting electrodes to steer charged ink drops up and down vertically as the ink jet sweeps horizontally across the page. The ink jet forms 35.0 μm-diameter drops of ink, charges them by spraying 800,000 electrons on the surface, and shoots them toward the page with a horizontal velocity of 17.0 m/s. Along the way, the drops pass through the long axis of two horizontal, parallel electrodes that are 6.0 mm long, 4.0 mm wide, and spaced 1.0 mm apart. The distance from the center of the electrodes to the paper is 1.90 cm. To form the letters, which have a maximum height of 6.0 mm, the drops need to be deflected up or down a maximum of 3.0 mm. Ink, which consists of dye particles suspended in alcohol, has a density of 800 kg/m³. 3 E D 80 C $ 4 R 888 F4 F V % 5 FS T ^ G 6 B Part A What electric field strength is needed between the electrodes to achieve this deflection? Express your answer with…arrow_forward
- Particle A has a charge of 10uC and a mass of 0.001kg. Particle A starts out at a speed of v = 1000m/s. At some time later, particle A has come to rest. What is the electric potential difference AV from where particle A started to where it stopped? Ignore gravity.arrow_forwardOppositely charged parallel plates are separated by 5.36 mm. A potential difference of 600 V exists between the plates. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field strength between the plates? N/C(b) What is the magnitude of the force on an electron between the plates? N(c) How much work must be done on the electron to move it to the negative plate if it is initially positioned 2.92 mm from the positive plate? Jarrow_forwardCathode ray tubes (CRTS) used in old-style televisions have been replaced by modern LCD and LED screens. Part of the CRT included a set of accelerating plates separated by a distance of about 1.38 cm. If the potential difference across the plates was 24.0 kV, find the magnitude of the electric field (in V/m) in the region between the plates. HINT V/marrow_forward
- Two small metal cubes with masses 2.0 g and 4.0 g are tied together by a 5.3-cm-long massless string and are at rest on a frictionless surface. Each is charged to +1.7 μC. (a). The string is cut. What is the speed of 2-g-cube when the cubes are far apart? (b). The string is cut. What is the speed of the 4-g-cube when the cubes are far apart?arrow_forwarda parallel plate capacitor creates an electric field of strength 10N/C between its plates, which are separated by 10mm. If a small sphere with charge 2 nC and mass of 20 g is held next to the positive plate, what is the force on that sphere? What will the acceleration of the sphere be? how long will it take to reach the other plate? What will its speed be when it reaches the other plate?arrow_forwardA parallel-plate capacitor has a charge Q and plate separation d, as shown below. We assume that the size of plates is much larger than the separation d. Each particle is initially at rest and then released, allowing it to accelerate. Assuming each particle has the same mass, rank the speeds of the particles when they impact the left plate. 1. A parallel-plate capacitor has a charge Q and plate separation d, as shown below. We assume that the size of plates is much larger than the separation d. Rank the force that each particle feels at its given position within the capacitor. E>D=C>A=B D>E>B=C>A D>B>E>C>A A>E>C>D>B E>A=C>D=B 2. A parallel-plate capacitor has a charge Q and plate separation d, as shown below. We assume that the size of plates is much larger than the separation d. Each particle is initially at rest and then released, allowing it to accelerate. Assuming each particle has the same mass, rank the speeds of the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON