Question
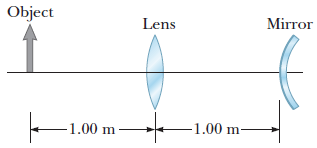
Consider the optical system shown in the figure. The lens and mirror are separated by d = 1.00 m and have focal lengths of f1 = +86.0 cm and f2 = −42.8 cm, respectively. An object is placed p = 1.00 m to the left of the lens as shown.
(a) What is the distance (in cm) and location of the final image formed by light that has gone through the lens twice? (Give the magnitude of the distance and select its location with respect to the lens.)
distance ????? cm
location (to the right of the lens or to the left of the lens)
to the right of the lens
(b) Determine the overall magnification of the image.
(c) State whether the image is upright or inverted.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A system of two converging lenses forms an image of an arrow as shown. The first lens is located at x = 0 and has a focal length of f₁ = 8.8 cm. The second lens is located at x = x2 = 58.13 cm and has a focal length of f2 = 21 cm. The tip of the object arrow is located at (x,y) = (xo,Y)= (-12.3 cm, 6.9 cm). AY (X,Y) 1) What is x₁, the x-coordinate of image of the arrow formed by the first lens? cm Submit 2) What is y₁, the y-coordinate of the image of the tip of the arrow formed by the first lens? cm Submit Virtual and Inverted Virtual and Upright Submit X₂ cm Submit X 3) What is x3, the x co-ordinate of image of the arrow formed by the two lens system? cm Submit 5) What is the nature of the final image relative to the object? Real and Inverted Real and Upright ++++ 4) What is y3, the y-coordinate of the image of the tip of the arrow formed by the two lens system? + 6) Which of the following changes to the locations of the lenses would result in a virtual and inverted image of the…arrow_forwardChapter 34, Problem 011 Spherical mirrors. Object O stands on the central axis of a spherical mirror. For this situation object distance is ps = +12 cm, the type of mirror is convex, and then the distance between the focal point and the mirror is 15 cm (without proper sign). Find (a) the radius of curvature r (including sign), (b) the image distance i, and (c) the lateral magnification m. Also, determine whether the image is (d) real or virtual, (e) inverted from object O or noninverted, and (f) on the same side of the mirror as O or on the opposite side. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (p) (e) (f)arrow_forwardA concave spherical mirror has a radius of curvature, R = 18.2 cm. If an object is placed 53.4 cm in front of the lens, what is the magnification of the image produced?arrow_forward
- (a) An object is 4 inches from a concave mirror whose focal lens has a magnitude of 12 inches. Where will the image be formed? (b) An object is 4 inches from a concave lens whose focal lens has a magnitude of 12 inches. Where will the image be formed? (c) An object is 12 inches from a convex mirror whose focal lens has a magnitude of 6 inches. Where will the image be formed? Please answer all parts with detailed information.arrow_forwardConsider the compound optical system shown in the diagram, where two thin lenses of focal lengths 7.5 cm (left lens) and 35 cm (right lens) are separated by a distance 25 cm. If a 2.9 cm tall object is placed as indicated in part (a), and the image formed is 0.74 cm tall, what is the magnification of the first lens? M1 = b. Using the information from part (a), calculate the image distance, in centimeters, from the first lens. di1 =arrow_forwardAn object of height 9.00 cm is placed 26.0 cm to the left of a converging lens with a focal length of 10.5 cm. Determine the image location in cm, the magnification, and the image height in cm. HINT (a) the image location in cm cm (b) the magnification (c) the image height in cm cm (d) Is the image real or virtual? real virtual (e) Is the image upright or inverted? upright invertedarrow_forward
- A technician needs to verify that a parabolic mirror intended for use in a telescope has been properly manufactured. The mirror's focal length should be 226 centimeters. How high above the base of the mirror (in cm) should a point on the mirror's surface located 28 cm horizontally from the base be (ie, what should be the value of y at the location x = 28 cm)?arrow_forwardA student notices that the image produced from a large concave mirror of a distant skyscraper (h = 106 m) is inverted and the magnitude of the height is |hi| = 1.16 m tall. The image is located d = 152 cm in front of the mirror. Numerically, what is the focal length of the mirror, f, in cm?arrow_forwardThe image of the Moon is formed by a concave mirror (aka telescope) whose radius of curvature is 9.62m at a time when the Moon's angular diameter is 0.523degrees. What is the diameter (magnitude only) of the image (cm) of the moon? HINT: What is the property of the rays coming from one point on the edge of the Moon (think of the moon as being infinitely far away)? Where do those rays converge to form an image of that point? Use the small angle approximation: sin(x)=tan(x)=x for |x|<<1, when x is measured in radians.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios