
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the information of Firm C on the attached figure and answer the following:
- Calculate TVC and Ceteris paribus, if the
price falls below_________, Firm C will have to shut down and exit the market - Ceteris paribus, Firm C will make a normal profit at the price of________
- Firm C achieves an
allocative efficient level of output by producing_______ units of output.
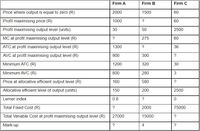
Transcribed Image Text:Firm A
Firm B
Firm C
Price where output is equal to zero (R)
2000
1500
60
Profit maximising price (R)
1000
?
60
Profit maximising output level (units)
30
50
2500
MC at profit maximising output level (R)
?
275
60
ATC at profit maximising output level (R)
1300
?
36
AVC at profit maximising output level (R)
900
300
?
Minimum ATC (R)
1200
320
30
Minimum AVC (R)
800
280
3
Price at allocative efficient output level (R)
160
580
?
Allocative efficient level of output (units)
150
200
2500
Lerner index
0.8
?
Total Fixed Cost (R)
2000
75000
Total Variable Cost at profit maximising output level (R)
27000
15000
?
Mark-up
?
4
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Introduction
When the price falls below the minimum of the average variable cost then the firm has to shut down.
Normal profit is when price equals a minimum of the average total cost.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose Jayden operates a handicraft pop-up retail shop that sells phone cases. Assume a perfectly competitive market structure for phone cases with a market price equal to $20 per phone case. The following graph shows Jayden's total cost curve. Jayden's profit is maximized when they produce a total of ____phone cases. At this quantity, the marginal cost of the final phone case they produce is ___, an amount ( greater or less)than the price received for each phone case they sell. At this point, the marginal cost of producing one more phone case (the first phone case beyond the profit maximizing quantity) is ____, an amount(greater or less)than the price received for each phone case they sell. Calculate the marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven phone cases they produce, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points to plot marginal revenue and the orange points to plot marginal cost at each quantity.arrow_forwardAm. 106.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 Mr. Stonewall has to set up a firm that produces calculators competing with the likes of Casio and Sharp calculators. In order for to estimate the amount of labour and capital needed to maximise profit in the long run, Mr. Stonewall has employed you to help him in this regard. Currently, the competitive wage rate is set at ¢4 per unit of labour and capital is rented at ¢5 per unit. The forces of demand and supply in the industry has also set the equilibrium price of calculators at ¢0.8 per unit. Suppose the production function of Mr. Stonewall's firm is given as Q 20K0.5 LO.5 + 7.5 and the firm total cost of production is ¢1690. Find the optimal levels of capital and labour needed to optimize output. The maximum profit of the firm at the optimal levels of labour and capital. 11.arrow_forward
- Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves Suppose Caroline runs a small business that manufactures shirts. Assume that the market for shirts is a competitive market, and the market price is $20 per shirt. The following graph shows Caroline's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for shirts quantities zero through seven (inclusive) that Caroline produces. Caroline's profit is maximized when she produces______ shirts. When she does this, the marginal cost of the last shirt she produces is ______, which is (GREATER OR LESS) than the price Caroline receives for each shirt she sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional shirt (that is, one more shirt than would maximize her profit) is _____, which is (GREATER OR LESS) than the price Caroline receives for each shirt she sells. Therefore, Caroline's profit-maximizing quantity corresponds to the…arrow_forwardam. 116.arrow_forwardOnly typed answerarrow_forward
- Suppose Amari operates a handicraft pop-up retail shop that sells phone cases. Assume a perfectly competitive market structure for phone cases with a market price equal to $20 per phone case. The following graph shows Amari's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for phone cases for quantities zero through seven (including zero and seven) that Amari produces. TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) 200 150 125 100 75 50 25 0 0 O Search Total Cost 20 Total Revenue Profit C Ccc Uarrow_forwardLauren grows grapes. Her average variable cost (AVC), average total cost (ATC), and marginal cost (MC) of production are illustrated in the figure to the right. Assume the market for grapes is perfectly competitive and that the market price is $2.00 per crate. Characterize Lauren's economic profits. Assume she produces such that she maximizes profits in the short run. Using the rectangle drawing tool, shade in Lauren's economic profits. Attach the correct label to indicate whether she is earning a profit (Profit) or incurring a loss (Loss). Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required object Quantity (crates) Price ($ per crate) 0.00 1.00- 2.00- 3.00- 4.00- 5.00- 6.00- 7.00- 8.00- 9.00- 10.00- 11.00- AVG 6 ATC र 9 2 12.00 00arrow_forwardYou decide to create a burger restaurant named BurgerDeals to help pay for college fees. The table below contains total pricing information for your single product, large extra-cheese burger. Your town's burger market is fiercely competitive, with big extra-cheese burger selling for $7 on average. Fill in the blanks in the table and answer the following question. What is AVC if you produce 6 burgers?arrow_forward
- Identification. Answer the following questions below. QUESTIONS: 1.) What is under allocation of resources? 2.) What can eliminate economic profit in the long run? 3.) What can eliminate costs in the long run?arrow_forwardWhat are the four conditions of a purely competitive market?arrow_forwardShow how could Market equilibrium be affected if the level of Technology is not used on effective way while the number of Consumers increased, ( the effect of Technology is higher than the other factor ) Enter your Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education