
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Please make sure to round the results to 2 decimal places.

Transcribed Image Text:Consider the hypotheses shown below. Given that x = 110, o 25, n 49, a= 0.01, complete parts a throughc below.
Ho: H=116
HA: H#116
a. State the decision rule in terms of the critical value(s) of the test statistic.
Reject the null hypothesis if the calculated value of the test statistic,
is
the critical value(s), Otherwise, do not reject the null hypothesis.
(Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
b. State the calculated value of the test statistic.
The test statistic is.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
C. State the conclusion.
Because the test statistic
V the null hypothesis and conclude the population mean
equal to 116.
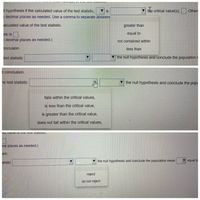
Transcribed Image Text:I hypothesis if the calculated value of the test statistic,
V is
the critical value(s),
Othen
o decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers
alculated value of the test statistic.
greater than
stic is
equal to
o decimal places as needed.)
not contained within
onclusion.
less than
test statistic
V the null hypothesis and conclude the population r
e conclusion.
he test statistic
▼ the null hypothesis and conclude the popi
falls within the critical values,
is less than the critical value,
is greater than the critical value,
does not fall within the critical values,
nal places as needed.)
ion.
V the null hypothesis and conclude the population mean
equal to
atistic
reject
do not reject
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the value of x to 2 decimal places:arrow_forwardA random sample of 30 colleges from Kiplinger’s list of the best values in private collegeprovided the data shown in the DATAfile named BestPrivateColleges (Kiplinger, October2013). The variable named Admit Rate (%) shows the percentage of students that appliedto the college and were admitted, and the variable named 4-yr grad. Rate (%) shows thepercentage of students that were admitted and graduated in four years.a. Develop a scatter diagram with Admit Rate (%) as the independent variable. Whatdoes the scatter diagram indicate about the relationship between the two variables?arrow_forwardSimplify the following: 1/ cubed square root of x^4arrow_forward
- Find the distance traversed by the tip of the minute hand on a clock between 4:18 P.M. and 6:58 P.M. on any given day if the length of the minute hand is 7 inches. Answer exactly or round to 3 decimal places. The minute hand travelled inches. Preview TIP Enter your answer as a number (like 5, -3, 2.2172) or as a calculation (like 5/3, 2^3, 5+4) Enter DNE for Does Not Exist, oo for Infinityarrow_forwardConvert 21 wobbles/m^3 to wiggles/in^3. 1 wobble = 9000 wiggles 1 meter = 39.37 inches Answer to the nearest decimal.arrow_forwardconvert an area of 225 square centimeters to square inches rounded to one decimal place. Be sure to show the units and canceling in your work.arrow_forward
- Hello Please help me make the correct decimal placement for 0.9854 if it is necessary to round to three decimal places as needed. Thank you for your time. Genearrow_forwardthe wooded area makes a right triangle in relation to the pond. One side of the woods is 19 feet long and the other side is 7 feet long. Find the distance across the pond. Answer as a decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forwardA set of 2-inch-wide by 5/8-inch-thick carbon brushes fits the brush holders too tightly. It is necessary to take 5/1000 inch off the width and 0.015 inch off the thickness by sanding. Give in decimal form the thickness dimension of the carbon brushes after sanding.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman