
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the following reaction, with the table of values provided. Calculate the ΔSº of the reaction in J/mol-K. Express your answer in three significant figures. Do not include the unit in your answer.
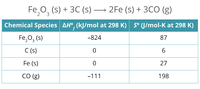
Transcribed Image Text:Fe,0, (s) + 3C (s) → 2Fe (s) + 3CO (g)
Chemical Species AH°, (kJ/mol at 298 K) s° (J/mol-K at 298 K)
Fe,0, (s)
-824
87
C (s)
6.
Fe (s)
27
Со (g)
-111
198
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Measurements show that the enthalpy of a mixture of gaseous reactants decreases by 323. kJ during a certain chemical reaction, which is carried out at a constant pressure. Furthermore, by carefully monitoring the volume change it is determined that -162. kJ of work is done on the mixture during the reaction. Calculate the change in energy of the gas mixture during the reaction. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? kJ exothermic O endothermic x10 X 3arrow_forwardWhen 2.232 g of AX (s) dissolves in 147.5 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter the temperature rises from 21.4 °C to 34.8 °C. Calculate the enthalpy change (in kJ/mol) for the solution process. AX (s) → A*(aq) + X¯ (aq) Assumptions for this calculation: · The specific heat of the solution is the same as that of pure water (4.18 J/gK) • The density of water = 1.000 g/mL · The liquid's final volume is not changed by adding the solid · The calorimeter loses only a negligible quantity of heat. The formula weight of AX = 59.1097 g/mol. Be sure you include the correct sign for the enthalpy change. Note: Do not use scientific notation or units in your response. Sig figs will not be graded in this question, enter your response to four decimal places. Carmen may add or remove digits from your response, your submission will still be graded correctly if this happens.arrow_forward4. When 1.00 L of 1.05 M Ba(NO3)2 solution is mixed with 1.00 L of 1.10 M NazSO4 solution at 25.0°C in a coffee-cup calorimeter. The reaction is Ba(NOs)2(aq) + NazSO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NANO:(aq). The final temperature of the mixture increases to 28.1°C. Calculate the enthalpy change per mole for this process. (Assuming C=4.18 J °C' g' and density of the final solution is 1.05 g/ml).arrow_forward
- Measurements show that the enthalpy of a mixture of gaseous reactants increases by 195.kJ during a certain chemical reaction, which is carried out at a constant pressure. Furthermore, by carefully monitoring the volume change it is determined that 69.kJ of work is done on the mixture during the reaction. Calculate the change in energy of the gas mixture during the reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIn a constant‑pressure calorimeter, 60.0 mL of 0.320 M Ba(OH)2 was added to 60.0 mL of 0.640 M HCl.The reaction caused the temperature of the solution to rise from 24.50 ∘C to 28.86 ∘C. If the solution has the same density and specific heat as water (1.00 g/mLand 4.184J/g⋅°C, respectively), what is ΔH for this reaction (per mole H2O produced)? Assume that the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes. ΔH= _________ kJ/mol H2Oarrow_forwardWhen 3.50 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was dissolved in 50.00 g of water a value of 9.50oC was obtained for ΔT. Calculate the value (calories) for the heat of solution of 3.50 g of NaOH. Calculate the number of calories that would be produced if one mole of sodium hydroxide was dissolved. (ΔHsolnNaOH)arrow_forward
- A system does 501 kJ of work and loses 216 kJ of heat to the surroundings. What is the change in internal energy, AE, of the system? Note that internal energy is symbolized as AU in some sources. AE = kJarrow_forwardA student dissolves 10.7 g of lithium chloride (LiCl)in 300. g of water in a well-insulated open cup. She then observes the temperature of the water rise from 22.0 °C to 28.4 °C over the course of 3.6 minutes. Use this data, and any information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: LiCl (s) Lit (aq) + Cl(aq) You can make any reasonable assumptions about the physical properties of the solution. Be sure answers you calculate using measured data are rounded to 2 significant digits. Note for advanced students: it's possible the student did not do the experiment carefully, and the values you calculate may not be the same as the known and published values for this reaction. Is this reaction exothermic, endothermic, or neither? If you said the reaction was exothermic or endothermic, calculate the amount of heat that was released or absorbed by the reaction in this case. Calculate the reaction enthalpy ΔΗ. per mole of LiCl. rxn 0 exothermic…arrow_forwardMany barbeque grills use propane gas, C3H8(g) as a fuel source. Using standard enthalpies of formation, calculate the quantity of heat produced, in kJ, when 25 liters of liquid propane is completely combusted in air. (The density of liquid propane is 582 kg/m3.) Note: The propane is in the condensed liquid state in the tank but changes to the gas phase as it is released. Calculate the change in enthalpy for the reaction assuming all reactants and products are in the gas phase.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY