
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
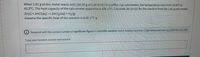
Transcribed Image Text:When 1.81 g of zinc metal reacts with 100.00 g of 1.00M HCl in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature rises from 20.8°C to
42.3°C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter apparatus is 109 J/°C. Calculate AH (in kJ) for the reaction from the 1.81 g zinc metal:
Zn(s) + 2HCI(aq)
Assume the specific heat of the solution is 4.18 J/°C-g.
ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
) Respond with the correct number of significant figures in scientific notation (Use E notation and only 1 digit before decimal e.g. 2.5E5 for 2.5 x 10")
Type your numeric answer and submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemist measures the enthalpy change AH during the following reaction: 2 Al(s) + Fe,03(s)→ Al,O3(s) + 2 Fe(s) AH=-852. kJ Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ/mol. ol. reaction ΔΗ Ar 4Al (s) + 2Fe,O,(s) → 2Al,0, (s) + 4Fe(s) Al, 0, (s) + 2Fe(s) 2A1 (s) + Fe, 03 (s) |kJ 3 Al,0, (s) + 6Fe(s) → 6A1(s) + 3Fe,0, (s) kJ Explanation Check © 2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardThe combustion of titanium with oxygen produces titanium dioxide: Ti (5) + 02 (g) TIO2 (s) When 2.060 g of titanium is combusted in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 25.00°C to 91.60°C. In a separate experiment, the heat capacity of the calorimeter is measured to be 9.84 kJ/K. The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter is, kJ/mol. O 1.43 e1 O -3.11 e2 O 1,52 e4 O 1.96 e1arrow_forwardWhen 0.418 g of pentene, C5H12, is burned in a bomb calorimeter the temperature rises by 4.21 ∘C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 2.46 kJ/∘C. Calculate the combustion energy (ΔE) for pentene, C5H12 in kJ/garrow_forward
- When a 8.52 g sample of solid potassium hydroxide dissolves in 123.2 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature rises from 21.6°C to 29.2°C. Write a balanced equation for the reaction and calculate AH in kJ/ mol KOH for the solution process. AHrm · mol = -msolnSsolnATsolnarrow_forwardYou mix 125 mL of 0.270 M CsOH with 50.0 mL of 0.675 M HF in a coffee-cup calorimeter, and the temperature of both solutions rises from 22.30 °C before mixing to 25.42 °C after the reaction. CsOH (aq) + HF (aq) yields CsF (aq) + H2O (l) What is the enthalpy of reaction per mole of CsOH? Assume the densities of the solutions are all 1.00 g/mL, and the specific heat capacities of the solutions are 4.2 J/g · K.arrow_forwardA 0.600 g sample of tristearin (C57H11O6), a common fat, is combusted in a bomb calorimeter containing 750.0 g of water. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 326 J/K. The initial temperature is 19.5 °C. It is known that the heat of combustion of tristearin is -38.0 kJ/g. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/g.K.(a) How much heat (in kJ) is released by this reaction? (b) What is the final temperature (in °C)?arrow_forward
- A piece of metal weighing 45.0 g was heated to 95.0oC, and the hot metal was added to 50.0 g of cold water in a Styrofoam cup calorimeter. The initial temperature of cold water was 20.0oC. If the final temperature of water and metal was 26.5oC, what is the specific heat of the metal? (The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g.oC) (A) 0.98 J/g.oC (B) 0.84 J/g.oC (C) 0.44 J/g.oC (D) 0.28 J/g.oCarrow_forward150 mL of a 0.728 M HCl aqueous solution is mixed with 150 mL of 0.364 M Ba(OH)2 aqueous solution in a coffee-cup calorimeter. Both the solutions have an initial temperature of 26.5°C. Calculate the final temperature of the resulting solution, given the following information: H+(aq) + OH- (aq) → H2O(ℓ) ΔHrxn = -56.2 kJ/mol Assume that volumes can be added, that the density of the solution is the same as that of water (1.00 g/mL), and the specific heat of the solution is the same as that for pure water, 4.184 J/(gK).arrow_forwardThe following reaction is endothermic. 2 ZnO(s) 2 Zn(s) + O2(g) AH(1) = 697 kJ Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction of the elements to form one mole of ZnO(s). Zn(s) + 1/2 O2(g) ZnO(s) AH(2) = kJarrow_forward
- When 3.12 g of glucose, CoH1206, is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 23.8 °C to 35.6 °C. The calorimeter contains 775 g of water, and the bomb itself has a heat capacity of 893 J/°C. How much heat was produced by the combustion of the glucose sample?arrow_forwardCalcium hydroxide is prepared by adding calcium oxide to water: CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (s) Calculate the enthalpy change (ΔH) for this reaction considering the following experiment. A 10.0 g sample of CaO (s) {MM = 56.08 g/mol} is added to 1.00 liter of water in a calorimeter with a total heat capacity of 4.37 kJ K-1 and the temperature increases by 2.70 K.arrow_forwardThe addition of 3.15 g of Ba(OH)2∙8H2O to a solution of 1.52 g of NH4SCN in 100 g of water in a calorimeter caused the temperature to fall by 3.1 °C. Assuming the specific heat of the solution and products is 4.20 J/g °C,calculate the approximate amount of heat absorbed by the reaction, which can be represented by the following equation:Ba(OH)2∙8H2O(s) + 2NH4SCN(aq) ⟶ Ba(SCN)2(aq) + 2NH3(aq) + 10H2O(l)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY