
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
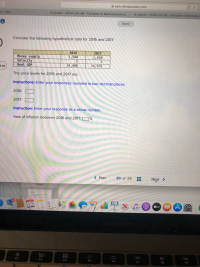
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following hypothetical data for 2016 and 2017:
2016
2017
Money supply
Velocity
1,500
1,650
Real GDP
14,400
14,976
The price levels for 2016 and 2017 are:
Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to two decimal places.
2016:
2017:
Instruction: Enter your response as a whole number.
Rate of inflation between 2016 and 2017:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Economists widely agree that the Consumer Price Index understates the true U.S. inflation rate. a. True b. Falsearrow_forwardQuestion 7 Which of the following are true about real and nominal demand? There may be more than one answer. a) A rise in the demand for real balances (Ma/P) raises equilibrium prices in the short-run. b) A drop in the demand for nominal balances (Ma) reduces equilibrium prices in the long-run. c) A change in government purchases can affect aggregate demand in the long-run. d) A change in government purchases can affect aggregate demand in the short-run.arrow_forwardConsider a simple economy that produces only loaves of bread. The table contains information on the economy's output, money supply, velocity, and price level. For example, in 2009, the money supply was $200, the price of a loaf of bread was $5, and the economy produced 400 loaves of bread. Use the information in the table and your previous answers. The money supply grew at a rate of % from 2009 to 2010 and the inflation rate (percentage change in prices) grew at a rate of % from 2009 to 2010. [Use one decimal place in your answer] 2009 2010 Quantity of Money $200 $216 Velocity of Money 10 Price Level $5.00 Quantity of Output 400 400arrow_forward
- The economy of Macro Island is described by the quantity equation with constant velocity. All residents of Macro Island understand the quantity theory and use it to form their expectations of inflation. Real income grows at a steady 2 percent per year, and the nominal interest rate is 5 percent. In one year, people had expected the money supply to grow by 4 percent, but in fact it grew by only 3 percent. a. What was the inflation rate? (3% 4% 1% 2%) b. What was the expected inflation rate? (1% 4% 3% 2%) c. What was the ex ante real interest rate? (4% 2% 1% 3%) d. What was the ex post real interest rate? (2% 1% 4% 3%) e. Did the deviation of inflation from what was expected hurt creditors or debtors? ( Creditors Debtors)arrow_forwardConsider the following: Price Index in 2017 86 Price Index in 2018 100 Price Index in 2019 108 Price Index in 2020 120 Price Index in 2021 146 a. The base year is 2018 b. Calculate the inflation rate from 2018 to 2019. 8 % (Enter your response as a percentage rounded to two decimal places.) c. Calculate the inflation rate from 2019 to 2020. 11.11 % (Enter your response as a percentage rounded to two decimal places.) d. Assume the cost of a market basket in 2018 is $2,137.0. (Enter your responses rounded to one decimal place.) Calculate the cost of the same basket of goods and services in 2017. Calculate the cost of the same basket of goods and services in 2021.arrow_forward4) If actual inflation is more than expected inflation, which of the following groups will most certainly benefit? а. Lenders b. Borrowers с. Minorities d. Women е. Men Suppose that the consumer price index of a country was 160 at year-end 2004 and 168 at the 5) end of 2005. What was the country's inflation rate during 2005? 5 percent b. а. 8 percent 60 percent d. с. 68 percent 6) If the consumer price index (CPI) at the end of year one was 100 and was 108 at the end of year two, the inflation rate during year two was zero; the CPI of 100 indicates that prices were stable. b. а. 8 percent. 5 percent. d. c. 108 percent.arrow_forward
- Discussion Question Ch 12 33 unread replies.33 replies. Discussion Question (DQ) Chapter 12: According to the textbook, How do economists use the equation m * v = p * yR to explain the cause of inflation? Required: In not less than 300 words and not more than 600 words, use a term(s) or idea(s) or concept(s) from the chapter of your textbook you are currently assigned to respond to the DQ. Every response should have three elements: a textbook term(s); section citation and correct grammar and punctuation Use of a TEXTBOOK term(s) or idea(s) or concept(s) from the assigned chapter textbook . Textbook citation—however, since your e-textbook does not have page numbers you can cite to a relevant chapter “section” (see below for an example of what a chapter sections look like). For example, you could say “I used the comparative advantage section’s discussion of _________ to answer this question.)arrow_forwardMeasuring Inflation and Unemployment: Around the World The growth of American tourism to Cuba has dramatically affected private sector employment, as Cuban entrepreneurs start ventures focused on this new group of tourists. The influx of American tourists to Cuba is likely to lead to Ohyperinflation, as the Cuban economy begins to expand, and new businesses begin to flourish. disinflation, as employment flourishes in the informal market. inflation, as more money chases the limited volume of goods and services available in the Cuban economy. O deflation, as Cuban businesses compete for tourist dollars.arrow_forwardWhat is inflation? A) A decrease in the general price level B) An increase in the general price level C) A decrease in the money supply D) An increase in the money supplyarrow_forward
- Research suggests that macroeconomic factors can explain the dynamics of interest rates in the economy. Suppose we are interested in understanding whether inflation plays a role in explaining interest rates. Fitting a line between the current nominal interest rate i and current inflation we obtain: i = 0.041 -0.147 What is the expected level of interest rates when inflation is at the level of 4%?arrow_forward=0. An economy is described by the following equations: AD: SRAS: Okun's law: Y = 4000 + 2(M/P) Y = ybar + 100(P-P) (Y-ybar)/ybar =-2(u-ubar). Assume ybar 6000 and ubar=0.05. = A) Suppose that the nominal money supply has long been at M = 4000 and is expected by the public to remain constant forever. The equilibrium value of P is The equilibrium value of P is, The equilibrium value of Y is, The equilibrium value of u is The equilibrium value of x is, (2 points each) B) A totally unexpected increase in in the money supply occurs, raising it from 4000 to 5250. [Part B is for extra credit] The short run equilibrium value of P is The short run equilibrium value of Pe is_ The short run equilibrium value of Y is The short run equilibrium value of u is. The value of unanticipated inflation, which is defined as (P-P)/P, is, The value of the slope of the short-run Phillips curve is (2 points each)arrow_forwardConsider a simple economy that produces only pies. The following table contains information on the economy's money supply, velocity of money, price level, and output. For example, in 2016, the money supply was 100, the price of a pie was $5.00, and the economy produced 200 pies. Fill in the missing values in the following table, rounding to the nearest cent when necessary. Year Money Supply Velocity of Money Price Level Quantity of Output Nominal GDP (Dollars) (Dollars) (Pies) (Dollars) 2016 100 5.00 200 2017 105 10 200 The money supply grew at a rate of______% from 2016 to 2017. Since pie output did not change from 2016 to 2017 and the velocity of money _______ , the change in the money supply was reflected _________ in changes in the price level. The inflation rate from 2016 to 2017 was _____%.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education