
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the following
C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) +4 H2O(g)
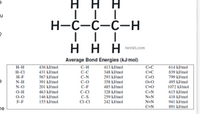
Transcribed Image Text:н
нн
Н-С-С—С—н
ннн
H
H
twinkl.com
Average Bond Energies (kJ/mol)
436 k/mol
C-H
413 kJ/mol
348 kJ/mol
293 k/mol
358 kJ/mol
485 kJ/mol
328 kl/mol
259 k/mol
242 Кпю
H-H
H-CI
H-F
N-H
C-C
614 kl/mol
839 kJ/mol
799 kl/mol
495 kl/mol
431 k/mol
C-C
567 kl/mol
391 k/mol
201 kl/mol
C-N
CO
C-O
O-0
N-O
C-F
CHO
1072 kJ/mol
O-H
0-0
F-F
463 kl/mol
146 k/mol
155 k/mol
C-CI
C-S
C-CI
C=N
N-N
NHN
CHN
615 kl/mol
418 kl/mol
941 kl/mol
891 k/mol
ne
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The compound WO3(s) is utilized in the refining process of tungsten from its mineral ore. Tungsten can be produced as follows: Reaction 1: WO3(s) + 3H2(g) → W(s) + 3H2O(g) a) From the following data calculate the enthalpy of the above reaction Reaction 2: 2W(s) + 3O2(g) → 2WO3(s) ΔH = –1685.4 kJ Reaction 3: 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) ΔH = –477.84 kJb) Estimate the change of internal energy for Reaction 1. c) Is Reaction 1 exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardA chemist measures the enthalpy change AH during the following reaction: COC1₂(9) + 4 NH3(9)→ CO(NH₂),(s) + 2NH4Cl(s) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ/mol. esc COC₁₂ (8) + 2NH₂(g) → CO(NH₂), (s) + NH₂Cl(s) 1 1 ẩCO(NH,),() + ≈NH,C() → † COCI,(8) + NH, (8) CO(NH₂)₂ (s) + 2NH₂Cl(s) → COCL, (g) + 4NH, (g) Explanation THE Check reaction I > AH=-559. kJ Costa ΔΗ kJ ☐ kJ KJ MacBook Pro x10 X S © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Acc You MOSISO Larrow_forwardCalculate the energy required to heat 1.80kg of ammonia from 21.5°C to 41.0°C . Assume the specific heat capacity of ammonia under these conditions is ·4.70J·g−1K−1 Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward
- Calculate ΔHrxn for the reaction: 7 C (s) + 8 H2 (g) → C7H16 (g) The following reactions and associated ΔHrxn values are may likely be helpful to you: Reaction A: C7H16(g) + 11 O2 (g) → 7 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (g) ΔHrxn = -4817 kJ Reaction B: C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ΔHrxn = -393.5 kJ Reaction C: 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2 H2O (g) ΔHrxn = -483.6 kJarrow_forwardWhen 29.5 mL of 0.500 M H2SO4 is added to 29.5 mL of 1.00 M KOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter at 23.50°C, the temperature rises to 30.17°C. Calculate ΔH of this reaction. (Assume that the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes and that the density and specific heat capacity of the solution are the same as for pure water.) (d for water = 1.00 g/mL; c for water = 4.184 J/g · ° C.)arrow_forwardCalculate ΔH∘ in kilojoules for the synthesis of lime (CaO) from limestone (CaCO3), the key step in the manufacture of cement. CaCO3(s)→CaO(s)+CO2(g) ΔH∘f[CaCO3(s)]=−1207.6kJ/molΔH∘f[CaO(s)]=−634.9kJ/molΔH∘f[CO2(g)]=−393.5kJ/molarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction 2H2O(g) →2H2(g) + O2(g) ΔH = +483.60 kJ/mol at a certain temperature. If the increase in volume is 52.7 L against an external pressure of 1.00 atm, calculate ΔU for this reaction. (The conversion factor is 1 L · atm = 101.3 J.) put your answer in KJarrow_forwardA 15.00 g sample of CaO is dissolved in water in a calorimeter with a heat capacity of 4.37 kJ/oK. The temperature decreases by 4.05oK. Calculate ΔHrxn in kJ/mol for the reaction CaO(s) + H2O(l) => Ca(OH)2(s)arrow_forwardCalculate ΔHo for the process ½ N2(g) + ½ O2(g) → NO(g) from the following information N2(g) + 2 O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) ΔHo = -105.8 kJ/mol 2 NO(g) + O2 → 2 NO2(g) ΔHo = -216.7 kJ/molarrow_forward
- The enthalpy change for the following reaction is given below. Pb (s) + CO2 (g) → PbO (s) + CO (g) ΔH° = +131.4 kJ Using the standard enthalpies of formation (∆Hf°) of CO2(g) = −393.5 kJ/mol, and CO(g) = −110.5 kJ/mol, determine the standard enthalpy of formation of PbO(s) A. −151.6 kJ ∕ mol B. −283.0 kJ ∕ mol C. +283.0 kJ ∕ mol D. −372.6 kJ ∕ mol E. +252.1 kJ ∕ molarrow_forwardA typical fat in the body is glyceryl trioleate, C57H104O6. When it is metabolized in the body, it combines with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and 3.022 × 104 kJ of heat per mole of fat. Write a balanced thermochemical equation for the metabolism of fat. How many kilojoules of energy must be evolved in the form of heat if you want to get rid of 15 pounds of this fat by combustion? How many nutritional calories is this? (1 nutritional calorie = 1 × 103 calories)arrow_forward(1)Consider the reaction: 2A (g) + 3 B (g) → 2 C (g) ΔHrxn = +254.3 kJ What will be the enthalpy change (in kJ) if 0.471 mol B reacts in excess A? (2)Consider the reaction: C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ΔHrxn = -393.5 kJ What mass of carbon (in g) must be reacted via this mechanism to release 581.2 kJ of heat?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY