
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the daily market for hot dogs in a small city. Suppose that this market is in long-run competitive equilibrium with many hot dog stands in the city, each one selling the same kind of hot dogs. Therefore, each vendor is a price taker and possesses no market power.
The following graph shows the demand (D) and supply (S = MC) curves in the market for hot dogs.
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the market price and quantity that will result from competition.
Assume that one of the hot dog vendors successfully lobbies the city council to obtain the exclusive right to sell hot dogs within the city limits. This firm buys up all the rest of the hot dog vendors in the city and operates as a monopoly . Assume that this change doesn't affect demand and that the new monopoly's marginal cost curve corresponds exactly to the supply curve on the previous graph. Under this assumption, the following graph shows the demand (D), marginal revenue (MR), and marginal cost (MC) curves for the monopoly firm.
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the following graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity of a monopolist.
Consider the welfare effects when the industry operates under a competitive market versus a monopoly.
On the monopoly graph, use the black points (plus symbol) to shade the area that represents the loss of welfare, or deadweight loss , caused by a monopoly. That is, show the area that was formerly part of total surplus and now does not accrue to anybody.
Deadweight loss occurs when a monopoly controls a market because the resulting equilibrium is different from the competitive outcome, which is efficient.
In the following table, enter the price and quantity that would arise in a competitive market; then enter the profit-maximizing price and quantity that would be chosen if a monopolist controlled this market.
|
Market Structure
|
Price
|
Quantity
|
|---|---|---|
|
(Dollars)
|
(Hot dogs)
|
|
| Competitive |
|
|
| Monopoly |
|
|
Given the summary table of the two different market structures, you can infer that, in general, the price is higher under a (COMPETETIVE MARKET OR MONOPLY) , and the quantity is higher under a (COMPETETIVE MARKET OR MONOPLY).
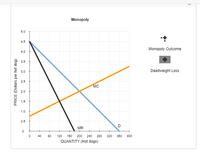
Transcribed Image Text:Monopoly
5.0
4.5
Monopoly Outcome
4.0
3.5
3.0
Deadweight Loss
2.5
MC
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
D
MR
0 40 80
120 100 200 240 280 320 300 400
QUANTITY (Hot dogs)
PRICE (Dollars per hot dog)
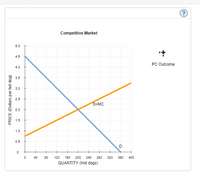
Transcribed Image Text:Competitive Market
5.0
4.5
PC Outcome
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
S=MC
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
D
40
80
120 100 200 240 280
320 300 400
QUANTITY (Hot dogs)
PRICE (Dollars per hot dog)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A retail chain will buy 900 cordless phones if the price is $30 each and 800 if the price is $40. A wholesaler will supply 350 phones at $40 each and 1400 at $70 each. Assuming that the supply and demand functions are linear, find the market equilibrium point and explain what it means.arrow_forwardConsider the market for ice cream cones. Suppose that supply in this market is given by PS = Q$ and demand is given by PD = 30 – 4 × QD. Answer the following questions. Notice that the competitive equilibrium (Qº,Pe) and the point (Q%,Pº) are both on the demand curve. Use them to compute the price elasticity of demand.arrow_forwardThe market supply curve for a certain product is given by the following formula: Ps(Qg)=10+5 Qg. The demand curve is given by PDQD)=190-10QD. a) What are the equilibrium price and quantity in the competitive equilibrium? b) Draw a diagram that shows the market supply and demand curve as well as the equilibrium price and quantity. Assume that the willingness-to-pay for the product drastically increases for most of the customers: The new demand curve is perfectly inelastic (i.e., the price elasticity of demand is zero). Assume that the new equilibrium price is still at 70. c) Draw the new demand curve in your diagram from b). Briefly explain, why you drew it that way? d) What is the new equilibrium demand? e) Are the producers better off after the increase in the willingness-to-pay for the product?arrow_forward
- Imagine that you run the toll authority for a city bridge. You must charge all of your customers the exact same toll. Initially, you have set the price at $2 per trip. The blue line on the following graph shows the weekly demand curve for trips across the city bridge. On the following graph, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing the total weekly revenue when the toll is $2 on the graph. Notice that when you click on the rectangle, the area is displayed. (? 10 TR at $2 8 Demand 7 TR at $3 5 2 1 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 38 40 QUANTITY (Thousands of vehicles per week) An advisor has suggested that you raise the toll to $3, the toll authority would bring in more revenue. To analyze this, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the total weekly revenue when the toll is $3 on the graph. When the toll is $2, total revenue is S per week, but when the toll is $3, total revenue is $ per week. Based on your analysis, you can…arrow_forwardConsider the daily market for hot dogs in a small city. Suppose that this market is in long-run competitive equilibrium, with many hot dog stands in the city, each one selling the same kind of hot dogs. Therefore, each vendor is a price taker and possesses no market power. The following graph shows the demand (D�) and supply curves (S=MC�=MC) in the market for hot dogs. Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the market price and quantity that will result from perfect competition. Assume that one of the hot dog vendors successfully lobbies the city council to obtain the exclusive right to sell hot dogs within the city limits. This firm buys up all the rest of the hot dog vendors in the city and operates as a monopoly. Assume that this change doesn't affect demand and that the new monopoly's marginal cost curve corresponds exactly to the supply curve on the previous graph. Under this assumption, the following graph shows the demand (D), marginal revenue…arrow_forwardAfter moving into Schine, Dunkin’ reported that their (donut) market equilibrium occurs when 450 donuts are sold at a price of $1.50 per donut. They also reported that the producer will supply no donuts when the price is $0.50 and the customers will demand no donuts at $2.00, what are that supply and demand equations, assuming that both are lineararrow_forward
- Imagine that you run the toll authority for a city bridge. You must charge all of your customers the exact same toll. Initially, you have set the price at $7 per trip. The blue line on the following graph shows the daily demand curve for trips across the city bridge. On the following graph, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing the total daily revenue when the toll is $7 on the graph. Notice that when you click on the rectangle, the area is displayed. TOLL (Dollars per vehicle) 10 9 8 7 4 2 1 0 0 Demand 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 QUANTITY (Thousands of vehicles per day) 90 When the toll is $7, total revenue is $ 100 TR at $7 TR at $8 An advisor has suggested that if you raise the toll to $8, the toll authority would bring in more revenue. To analyze this, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the total daily revenue when the toll is $8 on the graph. thousand per day, but when the toll is $8, total revenue is $ Based…arrow_forwardPlease match the following: ✓ Assume that both the demand curve and the supply curve for DVD players shift to the left but the demand curve shifts more than the supply curve. As a result ✓ Assume that both the demand curve and the supply curve for DVD players shift to the left but the supply curve shifts more than the demand curve. As a result ✓ Assume that the demand curve for DVD players shifts to the left and the supply curve for DVD players shifts to the right, but the supply curve shifts more than the demand curve. As a result ✓ Assume that the demand curve for DVD players shifts to the left and the supply curve for DVD players shifts to the right, but the supply curve shifts less than the demand curve. As a result A. Both the equilibrium price and quantity of DVD players will increase. B. Both the equilibrium price and quantity of DVD players will decrease. C. The equilibrium price of DVD players will increase; the equilibrium quantity will decrease. D. The equilibrium price of…arrow_forwardUse the photo at exercise 14 to solve the problem below With the Firm Y response function Qy=600-1/2Qx and the Firm XX response function Qx=600-1/2Qy Imagine that firm X chooses their quantity first, then firm Y observes the quantity of firm X and chooses their own quantity. What quantities will they end up choosing? Is there a first or second-mover advantage here? [You may assume that firm X can only choose quantities that are multiples of 200. This prevents you from having to deal with prices that are not on the schedule. just a little thinking about how equilibrium works in a sequential-move game. Oh, and just give me the quantity for each firm, don't worry about giving me a complete strategy for firm Y.]arrow_forward
- #2arrow_forwardOmari's HookNLadder is the only company selling fire engines in the fictional country of Alexandrina. Omari initially produced four trucks, but then decided to increase production to five trucks. The following graph gives the demand curve faced by Omari's HookNLadder. As the graph shows, in order to sell the additional fire truck, Omari must lower the price from $105,000 to $90,000 per truck. Notice that Omari gains revenue from the sale of the additional engine, but at the same time, he loses revenue from the initial four engines because they are all sold at the lower price. Use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue lost from the initial four engines by selling at $90,000 rather than $105,000. Then use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue gained from selling an additional engine at $90,000. PRICE (Thousands of dollars per fire engine) 165 150 135 120 105 Omari 90 75 60 45 30 15 Revenue Lost Demand…arrow_forwardDemand conditions in the market change. So, now the equation system describing (in inverse form) demand and supply in this competitive market is: p = 52 - 0.5 q, p = 2 + 0.1 q. Determine this market's equilibrium quantity q* (in units of the commodity).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education