
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
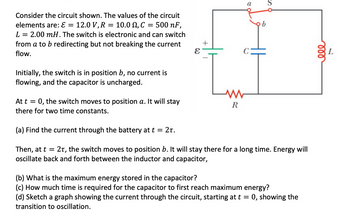
Transcribed Image Text:### Circuit Analysis Exercise
#### Circuit Description:
The circuit given includes the following components:
- **EMF (ε)**: 12.0 V
- **Resistor (R)**: 10.0 Ω
- **Capacitor (C)**: 500 nF
- **Inductor (L)**: 2.00 mH
The circuit features an electronic switch (S) that alternates between positions **a** and **b**, allowing current redirection without interrupting the flow.
#### Initial Conditions:
- **Switch Position**: Initially in position **b**.
- **Current**: No current flows.
- **Capacitor**: Uncharged.
#### Circuit Operation:
1. **Switch to Position a**: At time \( t = 0 \), the switch moves to position **a** and remains there for two time constants.
- **Task (a)**: Determine the current through the battery at \( t = 2\tau \).
2. **Switch to Position b**: At \( t = 2\tau \), the switch moves to position **b** and stays for an extended period, leading to energy oscillation between the inductor and capacitor.
- **Task (b)**: Calculate the maximum energy stored in the capacitor.
- **Task (c)**: Compute the time needed for the capacitor to reach maximum energy initially.
- **Task (d)**: Graph the current through the circuit from \( t = 0 \), illustrating the transition to oscillation.
#### Diagram Explanation:
The circuit diagram consists of:
- A voltage source indicated by \( ε \).
- A switch marked **S** that can alternate between contacts **a** and **b**.
- A resistor \( R \) in series with the capacitor \( C \).
- An inductor \( L \) in the loop, connected across the switch.
#### Analysis Goals:
- **Understand RC and LC Circuit Dynamics**: Analyze initial charging phase and periodic oscillations.
- **Time Constant Calculations**: Determine periods of significant current or energy changes.
- **Graphical Representation**: Articulate changes in current over time effectively through a graph.
This exercise explores time-dependent behavior in RLC circuits, highlighting crucial calculations and conceptual understanding areas in electrical engineering.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- C2 The next two questions refer to the following figure. The switch is initially open and both capacitors are initially uncharged. All resistors have the same value R, and both capacitors have the same value C. R2 R3 bat R1 ww (f) 1 pt. Immediately after the switch is closed, which resistor has the most current through it? (i) R1 (ii) R2 (iii) R3 (iv) Rị and R2 (v) R2 and R3 (vi) All have the same current (g) 1 pt. A long time after the switch is closed, which resistor has the most current through it? (i) R1 (ii) R2 (iii) R3 (iv) R1 and R2 (v) R2 and R3 (vi) None have currentarrow_forwardshow the complete solution for this problem, thanks!arrow_forwarda) With switch J2 open, close switch J1. Estimate the time it takes to do it. Obtain the equations for the voltage and current of the capacitor. Determine the energy stored by the capacitor. b) Open switch J1, close switch J2. Estimate the time it takes to do it. Obtain the equations for the voltage and current of the capacitor.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,