
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
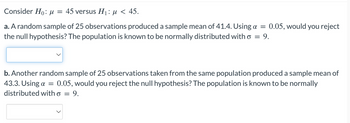
Transcribed Image Text:Consider Ho: μ = 45 versus H₁: μ< 45.
a. A random sample of 25 observations produced a sample mean of 41.4. Using a = 0.05, would you reject
the null hypothesis? The population is known to be normally distributed with o = 9.
b. Another random sample of 25 observations taken from the same population produced a sample mean of
43.3. Using a = 0.05, would you reject the null hypothesis? The population is known to be normally
distributed with o
=
9.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The following table shows the weights (in pounds) and the number of hours slept in a day by a random sample of infants. 1. Calculate the test statistic. t = ____. 2. Calculate the P-value. P=____.arrow_forwardA simple random sample of size n=15 is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean is found to be x=21.1 and the sample standard deviation is found to be s=6.3. Determine if the population mean is different from 24 at the a=0.01 level of significance. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. (a) Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H₁B 24 24 Aarrow_forwardFind the corresponding z-score for a sample of n = 16 and M = 38 taken from a population with a mean of μ= 40 and σ = 8.arrow_forward
- 156% of studentss entering four-year colleges receive a degree within six years. Is this percent larger than for students who play intramural sports? 183 of the 286 students who played intramural sports received a degree within six years. What can be concluded at the level of significance of a = -0.10 a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho: 7 v ||Select an answer V (please enter a decimal) H [?v||Select an answer v (Please enter a decimal) c. The test statistic 7v (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) d. The p-value (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) e. The p-value is ? va f. Based on this, we should Select an answer vthe null hypothesis. g. Thus, the final conclusion is that ,arrow_forwardGiven the following null and alternative hypotheses, conduct a hypothesis test using an alpha equal to 0.05. (Note: The population standard deviations are assumed to be known.) H0: µ1 ≤ µ2 HA: µ1 > µ2 The sample means for the two populations are shown as follows: sample mean 1 = 144, sample mean 2 = 129 population standard deviation 1 = 11, population standard deviation 2 = 16 sample size 1 = 40, sample size 2 = 50 Answer: Decision Rule : Reject H0 if Zcal > citical value Z = Test statistic: (Z calculated) Zcal = (use 4 decimal places)Conclusion: H0.arrow_forwardThe dean of a university estimates that the mean number of classroom hours per week for full-time faculty is 11.0. As a member of the student council, you want to test this claim. A random sample of the number of classroom hours for eightfull-time faculty for one week is shown in the table below. At α=0.10, can you reject the dean's claim? Assume the population is normally distributed. 12.3 9.1 11.8 6.7 6.2 10.6 14.6 9.1 What is the P value? Reject or fail to reject Ho? At α=0.10, can you reject the dean's claim?arrow_forward
- Laura asks whether the type of school students attend (private versus public) results in different performance on a test. A sample of N=100 students from a private school produce a mean of 71.30 on a test, and the mean of the population of public school students is µ=75.62 with ?௫ =28. a. Write the alternative hypothesis. b. Write the null hypothesis. c. With α=.05, what is zcrit? d. Compute zobt e. What should Laura conclude?arrow_forwarda sample is selected from a normal population with u=40 and σ =12. If the sample mean of M=36 corresponds to z=-2.00, then the sample size is n=64. is it true or falsearrow_forwardWe test the null hypothesis Ho:μ = 10 against the alternative Ha:μ<10 for a normal population with σ = 4. A random sample of 16 observations is drawn from the population, and we find the sample mean of these observations to be x̅ = 12. The P-value is?arrow_forward
- A sample of 30 observations is selected from a normal population. The sample mean is 59, and the population standard deviation is 8. Conduct the following test of hypothesis using the 0.02 significance level.H0: μ = 62H1: μ ≠ 62 a. Is this a one- or two-tailed test? (One-tailed or Two-tailed) b. What is the decision rule? (Reject H0 if −2.326 < z < 2.326 or Reject H0 if z < −2.326 or z > 2.326) c. What is the value of the test statistic? (Negative amount should be indicated by a minus sign. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)The value of the test statistic is d. What is your decision regarding H0? (Reject H0 or Fail to reject H0) e-1. What is the p-value? (Round your z value to 2 decimal places and final answer to 4 decimal places.)The p-value is e-2. Interpret the p-value? (Round your z value to 2 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.)There is a % chance of finding a z value this large by "sampling error" When H0 is true.arrow_forwardWe have specified the “tailedness” of a hypothesis test for a population mean with null hypothesis H0: μ = μ0. a. draw the ideal power curve. b. explain what your curve in part (a) portrays. left-tailedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman