
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Assume that the expected future exchange rate is unchanged and that the central bank holds the real money supply fixed.
Draw an IS-LM-IP diagram to show the effect of the drop in consumer confidence. Label all axes and curves and mark all the values and equilibrium points appropriately.
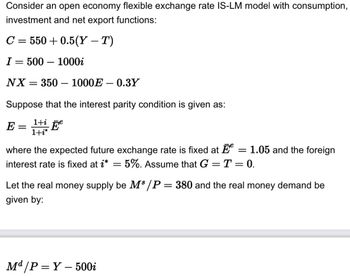
Transcribed Image Text:Consider an open economy flexible exchange rate IS-LM model with consumption,
investment and net export functions:
C = 550 +0.5(Y – T)
I= 500-1000i
NX = 350 - 1000E-0.3Y
Suppose that the interest parity condition is given as:
E = 1+ Ee
1+i*
where the expected future exchange rate is fixed at = 1.05 and the foreign
interest rate is fixed at i* = 5%. Assume that G = T = 0.
Let the real money supply be M³/P = 380 and the real money demand be
given by:
Md/P=Y-500i
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using the Mundell - Fleming short-run model of a small and open economy, with well-labeled diagrams, predict what would happen to i) income, ii) interest rate, iii) consumption, iv) investment, v) exchange rate, and vi) trade balance of the US economy, in response to each of the following shocks under flexible exchange rate system i) banks decide to loan out less funds ii) more foreigners visit USarrow_forwardIf President Erdogan wants to keep interest rates low, according to the Trilemma components, this suggests that one of his key policy priorities is: Group of answer choices a fixed exchange rate for the Lira to support lower interest rates monetary policy autonomy international capital mobilityarrow_forwardConsider the AA-DD model with flexible exchange rates. Assume the economy is initiallyat full employment.a) Suppose a temporary shock to the money demand pushes the economy intorecession. Describe one policy intervention that takes the economy back to its preshock equilibrium position.arrow_forward
- Use the money market and FX diagrams to answer the following questions. This question considers the relationship between the Indian rupee (Rs) and the U.S. dollar ($). The exchange rate is in rupees per dollar, ERs/$. On all graphs, label the initial equilibrium point A. a. Illustrate how a permanent increase in India’s money supply affects the money and FX markets. Label your short-run equilibrium point B and your long-run equilibrium point C. b. By plotting them on a chart with time on the horizontal axis, illustrate how each of the following variables changes over time (for India): nominal money supply MIN, price level PIN, real money supply MIN/PIN, interest rate iRs, and the exchange rate ERs/$. c. Using your previous analysis, state how each of the following variables changes in the short run (increase/decrease/no change): India’s interest rate iRs, ERs/$, expected exchange rate EeRs/$, and price level PIN. d. Using your previous analysis, state how each of the…arrow_forwardEvaluate the usefulness of relative power purchasing parity (PPP) in predicting movements in foreign exchange rates on: a. Short-term basis (for example, three months). b. Long-term basis (for example, six years).arrow_forwardAssume that prices are sticky in the short run. Use the MM-FX model to demonstrate the effects of each event below. After explaining your reasoning, answer clearly whether there is exchange rate overshooting in each case. In addition, display the time paths of the dollar interest rate, the euro interest rate, and the dollar-euro exchange rate. a) The US central bank decreases money supply by 5% and reverses the policy in three months. b. The US central bank decreases money supply by 5% and reverses the policy in three months. At the same time, US output declined by 2% over the same three-month period. Assume that the elasticity of money demand with respect to output is 1. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- Imports and short-run output: In addition to depending on the exchange rate (and therefore on the interest rate), imports may depend on short-run output: when the economy is booming, consumers tend to demand more foreign goods. To incorporate this result into our short-run model, suppose the new net exports equation is Derive the IS curve with this new equation, and explain how it differs from the standard IS curve in the short-run model.arrow_forwardThe financial account balance of the Canadian balance of payments decreases in all of the following cases except one. Which? Please choose an answer: at. Decrease in international reserves held by the Bank of Canada; b. Increase in Canadian direct investment in Mexico. vs. Increase in foreign bonds held by Canadians; d. Decrease in American direct investment in Canada; e. Decrease in Canadian bonds held by non-residents of Canada;arrow_forward17. Consider two exchange rates X/Y and Z/Y. (For example EUR/USD and JPY/USD.) They both follow perfectly correlated geometric Brownian motions with parameters (1,01) and (μ2,02). (a) The cross-exchange rate X/Z (for example EUR/JPY) follows a standard Brownian motion (b) The cross-exchange rate X/Z (for example EUR/JPY) follows a general Brownian motion (c) The cross-exchange rate X/Z (for example EUR/JPY) follows a geometric Brownian motion (d) The cross-exchange rate X/Z (for example EUR/JPY) does not follow a geometric Brownian motionarrow_forward
- How will the following event affect variables 1 through 3 in the foreign exchange market under a flexible exchange rate system; other things unchanged. Event: The U.S. Central Bank (the Fed) starts buying Chinese currency using dollar reserves: Variable 1: Supply of dollar in the foreign exchange market ___(increase, decrease, unaffected: briefly explain why). Variable 2: Value of dollar in the foreign exchange market unaffected: briefly explain why). Variable 3: American goods exported to China unaffected: briefly explain why). (appreciate, depreciate, (increae, decrease,arrow_forwardSuppose that you are given the following model for the goods market: C=100 +0.4(Y-T), I=20+.1 Y-200r, G=400, X=200 +0.2Y*-10e, IM=300 +0.3Y+10e and you know that r = 2%, Y*=1,500, e=1 and T =50. Note: e= real exchange rate. The equation for the demand for domestic goods (Z) is and the multiplier for this economy is If the economy were closed, the equation for the demand for domestic goods (Z') would be and the multiplier for the closed economy would be Z = 576 + 0.2Y; multiplier open eco is 2; Z' = 526 + 0.5Y ; multiplier closed eco is 4 O Z = 1000+ 0.4Y; multiplier open eco is 1.67; Z' = 500+ 0.5Y ; multiplier closed eco is 5 Z = 676 + 0.2Y; multiplier open eco is 5; Z' = 496 + 0.5Y; multiplier closed eco is 2 OZ = 576 +0.2Y; multiplier open eco is 5 ; Z' = 500+ 0.4Y; multiplier closed eco is 1.67arrow_forwardConsider an IRP AS/AD Model with sticky wages initially with yo = 100. Suppose we know that an increase in the money supply in a flexible exchange rate regime will result in y3 = 120. If monetary authorities took steps to maintain the exchange rate fixed at eo, then the most like outcome for real GDP would be closest to Group of answer choices 100 115 120 125arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education