
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Consider an object has a mass of 33.8 kg. Now imagine taking all the protons out of the object and stuffing them into a box. Also take all the electrons out of the object and stuff them in a second box.
Youve separated the boxes of protons and electrons by a distance of 78 m. If you were to release the clump of protons from their box, how much acceleration would the clump of protons undergo due to its attraction to the clump of electrons in the other box?
|
9.16E+23 m/s^2
|
||
|
1.15E+23 m/s^2
|
||
|
2.29E+23 m/s^2
|
||
|
4.58E+23 m/s^2
|
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
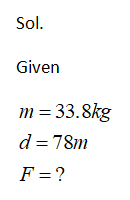
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a charge of size +3.8 x 10-4 C and mass 8 kg is traveling to the left towards a +1.7 x 10-4 C charge with speed 119 m/s. The +1.7 x 10-4 C charge is so massive that it does not recoil in response to the repulsion of the approaching charge. Calculate how close the two charges get, in m. Use k = 9 x 109 N m2 / kg2. (Please answer to the fourth decimal place - i.e 14.3225)arrow_forwardGiven the arrangement of charged particles in the figure below, find the net electrostatic force on the 91 = 5.55-μC charged particle. (Assume q2 = 16.33 µC and 93 = -24.12 μC. Express your answer in vector form.) →> F = N 91 (-2.00 cm, 0) 93 (1.00 cm, 1.00 cm) 92 (0, -1.00 cm) Xarrow_forwardWhat acceleration in m/s2 would a 1 kg sphere of charge 5 x 10-6 C experience if placed in a region where the electric field were 5 x 104 N/C? Round to two decimal places.arrow_forward
- 6. For vectors B = -î – 4ĵ and Å = -31 – 2j, calculate: a. Ā +B and its magnitude and direction angle b. A-B and its magnitude and direction angle.arrow_forwardGiven the arrangement of charged particles in the figure below, find the net electrostatic force on the q₁ = 5.25-μC charged particle. (Assume 92 = 12.33 μC and 93 = -17.12 μC. Express your answer in vector form.) 7 8970000i - 9035000j 9₁ (-2.00 cm, 0) X N 93 (1.00 cm, 1.00 cm) ● 92 (0, -1.00 cm)arrow_forwardBased on diagrams in Fig. 2, identify which particle reach the plate first after travelling based on their respective charges and directions. Assuming charge of 1e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, mass of electron 9.1 × 10-31 kilograms and distance between plate for both cases E1 and E2 is 500 cm.arrow_forward
- Two small balls with a mass of 2 g each are hanging on two separate strings 0.25 m (25 cm) long attached to a common point. They are given an identical negative charge and spread apart to a distance 3 cm from each other. Determine the charge on each ball by finding the forces in equilibrium and using Coulomb's law. How many electrons are there on each ball? What will happen in an identical situation if the mass of the balls is cut in half? What would happen if the charge on each ball is doubled?arrow_forwardProblem 20.03 A proton traveling at 4.40 km/s suddenly enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.750 T, traveling at an angle of 55.0° with the field lines (see (Figure 1)). Figure 55.0⁰ Ł Proton B < 1 of 1 ▾ Part B Find the magnitude of the force this magnetic field exerts on the proton. Express your answer in newtons to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ F= Submit ▾ Part C Fmax = Submit V Part D 4 Request Answer If you can vary the direction of the proton's velocity, find the magnitude of the maximum force you could achieve. Express your answer in newtons to three significant figures. [V] ΑΣΦ ^ ? Request Answer 13 ? N ⒸE ? If you can vary the direction of the proton's velocity, find the magnitude of the minimum force you could achieve. Express your answer in newtons to three significant figures. VG] ΑΣΦ | € P Pearson Narrow_forwardTHIS IS THE PREVIOUS QUESTION IT IS REFERRING TOO!! Your object has a mass of 35.6 kg. You separate an equal amount of protons and electrons into two boxes. You place the boxes at a distance of 80 m apart from one another. How much force attracts the two boxes to one another? Similar situation to the previous question, but now the object s mass is 60.0 kg and you initially put the boxes of protons and electrons 24 m apart. Now you want to take the two boxes and move them farther apart, to a new distance of 45 m apart. How much work (that is, energy) would you have to expend to pull the boxes that much farther apart, fighting against the electrostatic attraction between them? 1.44E+27 J 2.88E+27 J 5.76E+27 J 7.20E+26 Jarrow_forward
- In a thundercloud there may be electric charges of +45.0 C near the top of the cloud and -45.0 C near the bottom of the cloud. These charges are separated by 2.50 km. What is the electric force on the top charge? magnitude Ndirection Read It O attractive O repulsive Need Help?arrow_forwarda. Draw the electric field lines around a system that consists of two equal negative charges. b. Calculate the electric force that exists between two objects that are 7.3 × 10 –2 m apart and carry charges of 4.5 × 10 –6 C and –7.2 × 10 –6 C. Is this force attractive or repulsive? c. Write two or three sentences to explain the effect on the electric force between two charged objects if the amount of charge on one of the objects is doubled at the same time as the distance between the objects is doubled.arrow_forwardSolve the following word problems with solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON