
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
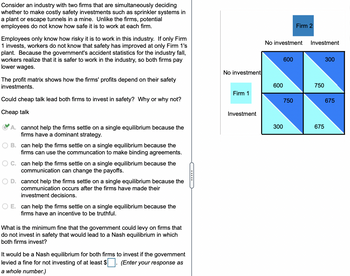
Transcribed Image Text:Consider an industry with two firms that are simultaneously deciding
whether to make costly safety investments such as sprinkler systems in
a plant or escape tunnels in a mine. Unlike the firms, potential
employees do not know how safe it is to work at each firm.
Employees only know how risky it is to work in this industry. If only Firm
1 invests, workers do not know that safety has improved at only Firm 1's
plant. Because the government's accident statistics for the industry fall,
workers realize that it is safer to work in the industry, so both firms pay
lower wages.
The profit matrix shows how the firms' profits depend on their safety
investments.
Could cheap talk lead both firms to invest in safety? Why or why not?
Cheap talk
A. cannot help the firms settle on a single equilibrium because the
firms have a dominant strategy.
B. can help the firms settle on a single equilibrium because the
firms can use the communcation to make binding agreements.
OC. can help the firms settle on a single equilibrium because the
communication can change the payoffs.
D. cannot help the firms settle on a single equilibrium because the
communication occurs after the firms have made their
investment decisions.
O E. can help the firms settle on a single equilibrium because the
firms have an incentive to be truthful.
What is the minimum fine that the government could levy on firms that
do not invest in safety that would lead to a Nash equilibrium in which
both firms invest?
It would be a Nash equilibrium for both firms to invest if the government
levied a fine for not investing of at least $. (Enter your response as
a whole number.)
—…………….
No investment
Firm 1
Investment
No investment
600
600
300
Firm 2
750
Investment
750
675
300
675
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hi! Can you help me with the question below? Todd has a job that presents zero risk of death or injury, but has always craved something more exciting. His current annual salary is $50,000. He has been offered a job on an Alaskan fishing boat that will pay$55,000 annually. This new job offer, however, comes with a 10% risk of severe injury that will cause Todd to have no income. Which of the following is true? (Assume the severe injury has no relevant implications besides reducing Todd’s income) A) Todd will definitely take the new job if he’s risk averse.B) Todd will definitely take the new job if he’s risk neutral.C) Todd will definitely decline the new job if he’s risk averse or risk neutral.D) Todd will definitely accept the new job if he’s risk seeking.E) Not enough information to determine.arrow_forwardWile E. Coyote has placed an order for 30 tons of TNT from Acme Enterprises. Acme can manufacture TNT using raw materials (Z) found in a remote underground mine. Acme needs 1/3 ton of Z to produce 1 ton of TNT and they are deciding where to locate their factory in order to minimize transportation costs. The mine and Wile E. Coyote's house are 50 miles apart. By train, the cost of shipping 1 ton of both TNT and Z is $2 per mile. However, Acme faces an additional cost because a river passes between the mine and Wile E. Coyote's house, and the river has no bridge. Wile E. Coyote's House River Mine Both Z and TNT must be loaded onto barges to cross the river, which is located 16 miles from the mine. Barge operators charge $1 per ton of TNT shipped across the river. However, since the raw material Z is highly explosive when mixed with water, barge operators charge Acme $195 to ship one ton of Z across the river. Using the above information, find the transport-cost-minimizing location for…arrow_forwardConsider two prospects. Problem 1: Choose between Prospect A: $2,500 with probability 0.33 $2,400 with probability 0.66 Zero with probability 0.01 Prospect B: $2,400 with probability 1.00 Problem 2: Choose between Prospect C: $2,500 with probability 0.33 Zero with probability 0.67 Prospect D: $2,400 with probability 0.34 Zero with probability 0.66 It has been shown by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky (1979, “Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk,” Econometrica 47(2), 263-291) that more people choose B when presented with problem 1 and when presented with problem 2, most people choose C. These choices violate expected utility theory. Why?arrow_forward
- Each year, the lumberjacks choose independently how many acres of trees to cut down; specifically, they choose whether to log intensively (that is, to clear-cut a section of the forest, which hurts the sustainability of the forest if enough people do it) or to log nonintensively (which does not hurt the sustainability of the forest). None of them has the ability to control how much the others log, and each lumberjack cares only about his own profitability and not about the state of the forest. Assume that as long as no more than one lumberjack logs intensively, there are enough trees to regrow the forest. However, if two or more log intensively, the forest will become useless in the future. Of course, logging intensively earns a lumberjack more money and greater profit because he can sell more trees. The forest is an example of Kevin's Profit-Maximizing Response because the trees in the forest are Depending on whether Rajiv and Yakov both choose to log either nonintensively…arrow_forwardThe value of a successful project is $420,000; the probabilities of success are 1/2 with good supervision and 1/4 without. The manager is risk neutral, not risk averse as in the text, so his expected utility equals his expected income minus his disutility of effort. He can get other jobs paying $90,000, and his disutility for exerting the extra effort for good supervision on your project is $100,000. (a) Show that inducing high effort would require the firm to offer a compensation scheme with a negative base salary; that is, if the project fails, the manager pays the firm an amount stipulated in the scheme. (b) How might a negative base salary be implemented in reality? (c) Show that if a negative base salary is not feasible, then the firm does better to settle for the low-pay, low-effort situation.arrow_forwardApple and Google are interested in hiring a new CEO. Both firms have the same set of final candidates for the CEO position: Indra, Cao, and Virginia. Both firms need to decide who to make a job offer to, and the hiring process is such that they each only make one job offer. If, say, Apple makes a job offer to Indra and Google makes a job offer to one of the other candidates, then Apple’s probability of success in hiring Indra is pIndra. The same is true for Google. If they both make a job offer to Indra, each has probability pIndra/2 of success. It has been estimated that pIndra = 20%, and pCao = pVirginia = 30% (Note that these probabilities need not add up to 100%). Suppose that both Apple and Google attach a valuation of 10 to successfully hiring Indra, and a valuation of 7 to successfully hiring each of the other candidates. A hiring attempt, if unsuccessful, has a valuation of zero. Convert this story into a game by completing the following game table; Google…arrow_forward
- In the Hawaiian Beach Boy surf board vendor scenario, what if the fine was increased to $190 but the probability of a fine decreased to one in 20 days, 5%? What would be the expected value – Exp(RS) -- of continuing to rent surfboards? Assume the other numbers stay the same. He makes $300/day and to rent boards from friends costs him $100 a day. So, he makes $200 a day. Write out the expected value formula, plug in the numbers, and show the math. Hint: the Exp(RS) should be higher than the previously calculated $160.arrow_forward Time remaining: 01 :53 :32 Economics A dealer decides to sell an antique automobile by means of an English auction with a reservation price of $900. There are two bidders. The dealer believes that there are only three possible values, $7,200, $3,600, and $900, that each bidder’s willingness to pay might take. Each bidder has a probability of 1/3 of having each of these willingnesses to pay, and the probabilities for each of the two bidders are independent of the other’s valuation. Assuming that the two bidders bid rationally and do not collude, the dealer’s expected revenue from selling the car is approximately Group of answer choices $3,600. $2,500. $3,900. $5,400. $7,200.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education