
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
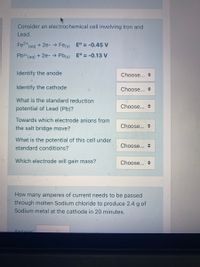
Transcribed Image Text:Consider an electrochemical cell involving Iron and
Lead.
Fe2+
(aq)
+ 2e- → Fes) E° = -0.45 V
Pb2+ (ag) + 2e- → Pb(s) E° = -0.13 V
Identify the anode
Choose... +
Identify the cathode
Choose... +
What is the standard reduction
Choose... +
potential of Lead (Pb)?
Towards which electrode anions from
Choose...
the salt bridge move?
What is the potential of this cell under
Choose...
standard conditions?
Which electrode will gain mass?
Choose... +
How many amperes of current needs to be passed
through molten Sodium chloride to produce 2.4 g of
Sodium metal at the cathode in 20 minutes.
Ancwor:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider these two entries from a fictional table of standard reduction potentials. X+ +3e X(s) E° = -1.94 V Y3+ +3e Y(s) E° = -0.31 V What is the standard potential of a galvanic (voltaic) cell where X is the anode and Y is the cathode? V %3D 'cellarrow_forwardConsider the galvanic cell based on the following half-reactions: Mn2+ + 2e → Mn e° = -1.18 V Fe²+ + 2e¯ → Fe ɛ° = -0.44 V a. Determine the overall cell reaction and calculate e- (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) + + E cell b. Calculate G° and K for the cell reaction at 25°C. AG° kJ K = [Pe**] = c. Calculate Ecell at 25°C when = 0.10 M and = 1.5 x 10-5 M. Ecell =arrow_forwardUse the standard reduction potentials given below to predict if a reaction will occur between Zn(s) and Cl2(g), when the two are brought in contact via standard half-cells in a voltaic cell. | Cl2(g) + 2e¯¯ →2C1¯¯ (aq) E Zn2+ = 1.360 V red (aq) + 2e → Zn(s) E = = -0.763 V red If a reaction will occur, write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction, assuming that the product ions are in aqueous solution. If no reaction will occur, leave all boxes blank. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) + +arrow_forward
- 11. What is AG° for the reaction driving the following voltaic cell? Co (s) | Co²+ (aq) || Mn³+ (aq), Mn²+ (aq) | Pt (s) A. -175 kJ +175 kJ B. -351 kJ +351 kJ C. -527 kJ D. E.arrow_forwardA voltaic cell using Pb²⁺/Pb and Ni²⁺/Ni half-cells is set up at standard conditions, and each compartment has a volume of 355 mL. What is the cell potential, in V, after it has delivered 0.150 A for 51.0 hours at 25 °C? (E° for Pb²⁺/Pb = -0.130 V and E° for Ni²⁺/Ni = -0.250 V.)arrow_forwardA standard galvanic cell is constructed in which a Pb2+ | Pb half cell acts as the cathode. Which of the following statements are correct? Hint: Refer to a table of standard reduction potentials. (Choose all that apply.) The anode compartment could be I2|I-. The cathode reaction is Pb2+ + 2e- -> Pb Pb is oxidized at the cathode. Pb2+ is reduced at the cathode. In the external circuit, electrons flow from the other compartment to the Pb2+|Pb compartment.arrow_forward
- Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment): Ni Ag 1.0 M Ni2+ 1.0 M Ag* The standard reduction potentials are as follow: Ni2+ + 2 e- → Ni(s), E° = -0.25 Ag* + e - Ag(s), E° = 0.7996 When current is allowed to flow, which species is oxidised? Select one: а. Ag b. Cannot be determined from the data given. C. Ni2+ O d. Ag* O e. Niarrow_forwardA voltaic cell is constructed with an Ag/Ag+ half-cell and a Pb/Pb+2 half cell. All solutions are 1.0 M. Ag+(aq) + e- → Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V Pb+2(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) E° = -0.13 V a.Diagram the cell, labeling electrodes and solutions, show the direction of electron flow in the circuit and what occurs in the salt bridge. b. If the cell were made with [Pb+2] = 0.10 M and [Ag3+] = 3.0 M, would the voltage increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain using Q. c.Identify the electrode that is gaining massarrow_forwardEnter electrons as e". A voltaic cell is constructed in which the anode is a Mn Mn2+ half cell and the cathode is a CI|Cl, half cell. The half- cell compartments are connected by a salt bridge. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) The anode reaction is: The cathode reaction is: The net cell reaction is: In the external circuit, electrons migrate v the Mn|Mn2+ electrode | v the Cl|Cl, electrode. In the salt bridge, anions migrate v the Cl|Cl2 compartment v the Mn|Mn²+ compartment. +arrow_forward
- Consider the following voltaic cellat 25°C: Al(s) | Al3*(0.20 M, aq) || Al3+(0.75 M, aq) | Al(s) If the standard reduction potential for the Al3+(aq) /Al(s) redox couple is -1.66 V, what is the overall cell reaction and the cell potential of the voltaic cell shown above? (Reference the cell as written above.) The overall cell reaction is Al3+(0.75 M, aq) AIS*(0.20 M, ag) and E°cell = +0.0113 V. There is no overall cell reaction and E°cell = 0.00 V. The overall cell reaction is Al3+(0.20 M, aq) Als*(0.75 M, aq) and E°cell = +0.0113 V. The overall cell reaction is Al3+(0.20 M, aq) →A13+(0.75 M, ag) and E°cell| = -0.0113 V. The overall cell reaction is Al3*(0.75 M, aq) →AI3*(0.20 M, aq) and E°cell = -0.0113 V. None of thesearrow_forward12. A typical car/truck battery is a cell made by transferring 2 e- by a reaction between lead and sulfuric acid. If the voltage produced (Eᵒcell) is 12 V, what is AG° of this reaction at 25° C? AG° =arrow_forwardWhat is the voltage of the following cell? Use the Reduction Potential Table found in Chapter 17 notes. Cr(s)|Cr³*(0.25 M) || |2(s)|1-(0.20 M)|Pt(s)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY