
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider a world with only two countries (i.e., two large open economies), the home country and the foreign country. In the home country the following relationships hold:
{ refer to image }
b) Suppose that in the home country the desired investment increases by 100, that is, I^d = 400−100r^w. What is the world equilibrium interest rate? What are the equilibrium values of consumption, national saving, investment, and the current account balance in each country?
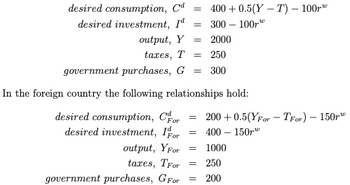
Transcribed Image Text:desired consumption, Cd
desired investment, Iª
300-100
output, Y
2000
taxes, T =
250
government purchases, G = 300
In the foreign country the following relationships hold:
desired consumption, Cor
desired investment, Ifor
= 400+0.5(YT) - 100
government purchases, GFor
=
=
= 200+ 0.5(YFor - TFor) - 150r
= 400-150
1000
output, YFor =
taxes, TFor = 250
= 200
W
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please show work with explanation! I’m not really sure what to do.arrow_forwardPlease answer both of the question with the solutions( how you got the final answers to both questions).arrow_forwardThe Golden Rule capital-labor ratio maximizes investment per worker in the steady state. capital per worker in the steady state. output per worker in the steady state. consumption per worker in the steady state.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is an example of U.S. foreign portfolio investment? Select one: a.Erica, a U.S. resident, buys bonds issued by the Swiss government. b.Neither A nor B are examples of U.S. portfolio investment. C.A U.S. legal office opens a branch office in Holland. d.Both A and B are examples of U.S. portfolio investment.arrow_forwardWhen there are two large open economies in the world, if capital goods become relatively cheaper compared to consumption goods in the foreign country, the world real interest rate will and the home country's current account will fall; rise fall; fall rise; rise rise; fallarrow_forwardConsider the following model of an economy with no international trade, and in which the price level is fixed: C = 40 + (8/9)∙DI I = 30 G = 30 Taxes = (1/8)∙GDP where C is consumption demand, DI is disposable income, I is planned investment, G is government purchases, and all whole numbers are in billions of dollars. Determine the equilibrium level of production (GDP) in this economy (show your work), and draw this equilibrium situation on a graph. Use the multiplier to determine the change in equilibrium GDP that would result from an exogenous 16 billion dollar increase of government purchases. Then determine…arrow_forward
- Consider the following equations for a small open economy for both the goods and money markets. Goods Market: C = 2000 + 0.8Yd; T = 1000 + 0.3Y; G = 6000; TR = 1200; I = 4000 + 0.24Y – 100r; M = 3000 + 0.2Y; X = 1500; Money Market: LP = 500 + 0.1Y; LT = 2000 + 0.2Y – 10r; Ls = 1000 – 20r; MS = 40,000; P= 5 a. Derive both the IS and LM equations for the economy and compute the Equilibrium level of Income and Interest Rate. Then compute the values of investment demand, speculative demand for money and disposal income. b. Suppose the government undertook an expansionary fiscal policy by increasing government expenditure by 20 percent and cutting lump sum tax by 20%. Clearly demonstrate how this would result in the crowding out phenomena, using the IS – LM model. Also, briefly explain how investment demand and speculative demand…arrow_forwardWhat are the assumptions in the small open economy.vs closed or largeopen? What would be an example country today?arrow_forwardIn an open economy,a change in domestic net foreign asset depends on how much is saved, and on investment,which reduces the domestic net foreign asset. True or False.arrow_forward
- Q4. Suppose that Brazil initially has a higher capital rental rate (r) than the United States. What would be the direction of foreign direct investment (FDI)? Use a world-capital-market graph to show the effects of FDI on the two countries’ rental rates of capital, GDP, and return to labor owners. Identify the net change in world output in the above graph. Discussion: what other effects could FDI cause in the recipient and source countries that are not captured in the model? Your answerarrow_forwardConsider a world with only two countries (i.e., two large open economies), the home country and the foreign country. Both countries have a zero current account balance initially. When answering the following questions, clearly label the lines and show the changes in the graph provided below. Give an intuitive explanation for the effects in each case. b-What are the effects on the world equilibrium interest rate, national saving, investment, and the current account balance in each country if home expected future marginal productivity of capital increases? c- What are the effects on the world equilibrium interest rate, national saving, investment, and the current account balance in each country if foreign country experiences a temporary adverse supply shock?arrow_forwardWhich of the following would not be counted in the U.S. BOP current account? Martha receives a $50 dividend check on stock she owns in business in Germany. A wealthy Italian purchases numerous antiques in the United States for his villa. Helen, an American oil engineer, is a paid adviser to Middle Eastern countries in the area of petroleum extraction. General Motors Corporation owns buildings that are situated in Mexico. France purchases a new jet fighter aircraft from the Boeing Company in the U.S.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education