
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
J 4
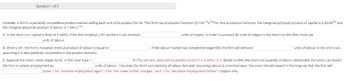
Transcribed Image Text:Question 1 of 5
Consider a firm in a perfectly competitive product market selling each unit of its product for $9. This firm has production function Q=10K1/4L 3/4 For this production function, the marginal (physical) product of capital is 2.5(L/K)3/4 and
the marginal (physical) product of labour is 7.5(K/L)1/4
A. In the short run, capital is fixed at K-4096. if the firm employs L-81 workers it can produce
units of output. In order to produce 80 units of output in the short run this firm must use
units of labour.
. If the labour market has competitive wage $59, the firm will demand
units of labour in the short-run,
B. When L=81, the firm's marginal revenue product of labour is equal to
assuming it is also perfectly competitive in the product industry.
E. Suppose the union raises wages by $2. In this case %4w = |
% (This percent value will be graded correct if it is within 0.1). Based on the new short-run quantity of labour demanded, the union can expect
the firm to reduce employment by
units of labour. Calculate the short-run elasticity of labour demand. Assuming labour is a normal input, the union should expect in the long run that the firm will
(Enter 1 for "increase employment again." O for "not make further changes," and -1 for "decrease employment further"). Explain why.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward6. At the local high school, one-fourth of the students are freshman, one-eighth are sopho- mores, 153 students are juniors, and two-fifth are seniors. How many students attend the local high school?arrow_forwardCom Steelarrow_forward
- Shoes 05 O 0.5 2 30 What is pButter/pShoes? 1/5 150 Butterarrow_forwardC is 200 and Y is 1003 Find APS and APYarrow_forwardAccording to the Keynesian model of macroeconomic equilibrium, a decrease in aggregate demand Select one: O a. will cause the price level to fall substantially. O b. will cause an increase in aggregate supply that will restore full employment. O c. will not cause unemployment. O d. will not cause nominal wages to decline sufficiently to restore full employment.arrow_forward
- (Corporate values) help a company determine A-how to behave with its employees , shareholders , and the wide • B- what is important for the company's reputation . C- where to sell its products or services . D- the types of products or services to offer .arrow_forwardwhy choose A?arrow_forwardapter 16 Problems LO ? eBook Refer the figure given below to answer the question. ¹2 Wage rate ($ per hour) 9 8 7 6 LD 5 Mc Graw Hill Type here to search 4 M 3 2 1 0 S₁ D 10 20 30 40 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 O ○ 발 Number of people employed (in millions) Tools 7 dropline 2 O **********arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education