
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
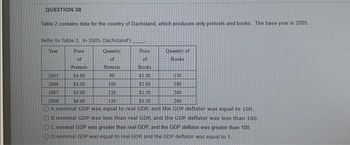
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 38
Table 2 contains data for the country of Dachsland, which produces only pretzels and books. The base year is 2005.
Refer to Table 2. In 2005, Dachsland's
Year
Price
of
Price
of
Pretzels
Pretzels
Books
$4.00
90
$1.50
$4.00
100
$2.00
2007
$5.00
120
$2.50
2008
$6.00
150
$3.50
200
A nominal GDP was equal to real GDP, and the GDP deflator was equal to 100.
OB. nominal GDP was less than real GDP, and the GDP deflator was less than 100.
OC. nominal GDP was greater than real GDP and the GDP deflator was greater than 100.
OD. nominal GDP was equal to real GDP, and the GDP deflator was equal to 1.
Quantity
of
2005
2006
Quantity of
Books
150
180
200
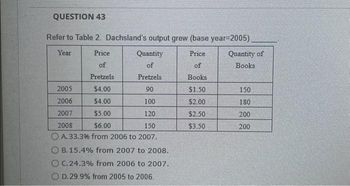
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 43
Refer to Table 2. Dachsland's output grew (base year-2005)
Year
Price
of
Books
$1.50
$2.00
$2.50
$3.50
Price
Quantity
of
of
Pretzels
Pretzels
2005
$4.00
90
2006
$4.00
100
2007
$5.00
120
2008
$6.00
150
A. 33.3% from 2006 to 2007.
OB. 15.4% from 2007 to 2008.
OC.24.3% from 2006 to 2007.
OD. 29.9% from 2005 to 2006.
Quantity of
Books
150
180
200
200
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following table pertains to Wrexington, an economy in which the typical consumer's basket consists of 20 pounds of meat and 10 toys. Price of a Toy Price of Meat (Dollars per pound) (Dollars per toy) 3 Year 1 2 3 1 4 Refer to Table 25-2. The cost of the basket 2 7 5 increased from Year 1 to Year 2 and increased from Year 2 to Year 3. increased from Year 1 to Year 2 and decreased from Year 2 to Year 3. decreased from Year 1 to Year 2 and increased from Year 2 to Year 3. decreased from Year 1 to Year 2 and decreased from Year 2 to Year 3.arrow_forwardThe following table is a supply and demand schedule for the eggs market. PRICE (per dozen eggs) DEMAND (in million dozens) SUPPLY (in million dozens) AED 10 340 160 AED 11 320 200 AED 12 300 240 AED 13 280 280 AED 14 260 320 AED 15 240 360 AED 16 220 400 Based on the above data answer the following questions. Need to use correct units in the answer (AED, million dozens, etc) ( a) What is the equilibrium price? b) What is the equilibrium quantity ? c) Is there a surplus or shortage at AED 16? d) With respect to question c, how much is the surplus or shortage?arrow_forwardNote:please bro,hand written solution should not be uploaded.arrow_forward
- Other goods per month 2. (10 points) RB Inc., is a wholesaler specializing in dry foods, such as rice and dry beans. Assume that these dry goods are all considered inferior goods. RB, Inc.'s manager is troubled by a recent article in The Wall Street Journal that says a recession is imminent and that income will fall by 3 percent over the next year. What do you think is likely to happen to the equilibrium price of the products RB Inc. sells, if there is a recession and income falls? You have to explain what is expected to happen to demand and/or supply and therefore to the equilibrium price. You may include a graph if you wish to. 3. (10 points) (a) Angela 1112 (b) Betty Other goods per month 2 3 L' L², BOGOF 3 Rooms, Nights per month L2, BOGOF 4 Rooms, Nights per month (BOGOF indicates the Buy Three Get One Free budget line, which is L² in both graphs)) Angela and Betty are deciding how many nights to stay at a resort. Given above are the budget lines and indifference curves for both…arrow_forwardnumber 12 pleasearrow_forwardPurchase of tables and chairs by a restaurant is ___________ expenditurearrow_forward
- The following graph shows the market for orange juice. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in the grey field will change accordingly. PRICE (Dollars per gallon) 12 Graph Input Tool ? Price 2 (Dollars per gallon) Supply 10 Quantity 112 Quantity supplied demanded (Millions of gallons) 22 22 (Millions of gallons) 00 Surplus 0 (Millions of gallons) Shortage (Millions of gallons) 00 90 + Demand 0 0 15 30 45 60 75 90 105 QUANTITY (Millions of gallons) 120 135 The market price of orange juice without government intervention is $ per gallon. Consider legislation that doesn't allow the price of orange juice to be below $9 per gallon and stipulates that the government buy any surplus orange juice produced at that price. In order to raise the price to $9 per gallon, the government would need to buy million gallons of…arrow_forwardThe relative price of hamburgers this year has A. increased. B. decreased. C. stayed the same. D. Not enough information has been given to calculate an answer.arrow_forwardIn 1973, the price of a Big Mac was $0.50. Use the information in the table below to find the price of a Big Mac in 2006 dollars. Year 1973 2006 CPI 44.4 201.6 Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics. Base year 1962-84. The value of a 1973 Big Mac in 2006 dollars is $ The actual price of a Big Mac in 2006 was approximately $2.99. Thus the price of Big Macs has risen (Round your answer to two decimal places.) faster than the cost of living. at the same rate as slower thanarrow_forward
- Suppose seafood price and quantity data for the years 2000 and 2009 follow. Use 2000 as the base period.Seafood 2000 Qty. (lb) | 2000 Price ($/lb) | 2009 Price ($/lb)Halibut 75,090 1.91 2.33Lobster 83,080 3.72 3.09Tuna 50,779 1.87 1.97(a)Compute a price relative for each type of seafood. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)Seafood Price RelativeHalibut 122.0 Lobster _________ Tuna 105.3 (b)Compute a weighted aggregate price index for the seafood catch. (Round your answer to one decimal place.)I2009 = ___________ Comment on the change in seafood prices over the nine-year period. (Enter your percentage as a positive value. Round your answer to one decimal place.)Seafood prices have decreased by ______ % over the 9-year period according to the index.arrow_forwardI'm stuck need help for second steparrow_forwardA typical consumer in Lykesville has a market basket consisting of 4 strawberries, 9 grapefruits, and 5 blueberries. The data table below provides information on Lykesville's prices of strawberries, grapefruits, and blueberries from 2008 through 2010. 2008 2009 2010 unit of strawberries $1.1 $1.5 $1.2 Price per unit of grapefruits $1 Price per unit of blueberries $0.9 $1.2 Price per $1.4 $1.4 $2 What was the cost of the market basket in 2009? What was the price index in 2009, assuming 2008 is the base year?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education