
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
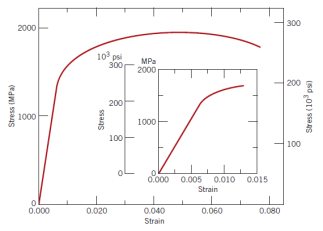
Consider a cylindrical specimen of a steel alloy (Please see the figure) 0.33 in. in diameter and 3.15 inches long that is pulled in tension.
given:
-Elongation is 0.018 in
-Tensile stress = 200 ksi
-Tensile strain = 6.83*10^-3
-Ultimate stress = 281.82 ksi
-Ultimate strain = 0.05
solve:
Fracture point (stress and strain values)
Transcribed Image Text:Stress (MPa)
A
2000
1000
0.000
103 p
Stress
0.020
300
200
100
MPa
2000
1000
0.000 0.005 0.010 0.015
0.040
Strain
Strain
I
0.060
0.080
300
200
100
Stress (10 psi)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Stress analysisarrow_forwardAn extruded polymer beam is subjected to a bending moment M. The length of the beam is L = 880 mm. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam are b1 = 37 mm, d1 = 86 mm, b2 = 22 mm, d2 = 22 mm, and a = 7.5 mm. For this material, the allowable tensile bending stress is 11 MPa, and the allowable compressive bending stress is 9 MPa. Determine the largest moment M that can be applied as shown to the beam.arrow_forwardThe modulus of elasticity is measured as the secant for a stress at: a) 30% b) 45% c) 25% d) 40%arrow_forward
- Calculate the stress and strain at each force interval. Plot a graph of the stress-strain curve. Estimate the yield point of the steel and note its location on the curve. Estimate the ultimate strength of the steel and note its location on the curve.arrow_forwardAn extruded polymer beam is subjected to a bending moment M. The length of the beam is L = 500 mm. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam are b₁ = 33 mm, d₁ = 109 mm, b₂ = 20 mm, d₂ = 20 mm, and a = 6.5 mm. For this material, the allowable tensile bending stress is 16 MPa, and the allowable compressive bending stress is 11 MPa. Determine the largest moment M that can be applied as shown to the beam. b₂ a M B A Answer: M = L d₂ N•m b₁ d₁arrow_forwardI need typing answer urgentarrow_forward
- An extruded polymer beam is subjected to a bending moment M. The length of the beam is L = 580 mm. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam are b1 = 36 mm, d1 = 106 mm, b2 = 22 mm, d2 = 22 mm, and a = 7 mm. For this material, the allowable tensile bending stress is 20 MPa, and the allowable compressive bending stress is 9 MPa. Determine the largest moment M that can be applied as shown to the beam.arrow_forward2. A steel bar, whose cross section is 0.55 inch by 4.05 inches, was tested in tension. An axial load of P = 30,500 lb. produced a deformation of 0.105 inch over a gauge length of 2.05 inches and a decrease of 0.0075 inch in the 0.55-inch thickness of the bar. Determine the lateral strain. * Your answer Determine the axial strain. Your answer Determine the Poisson's ratio v. * Your answer Determine the decrease in the 4.05-in. cross-sectional dimension (in inches). * Your answerarrow_forwardThe following shaft is composed of two materials, both rigidly bonded. The data is provided in the table: Determine: The maximum torque that can be applied based on the maximum stresses of each material. The total deformation of the shaft with the torque from the previous section. The maximum torque that can be applied if the maximum deformation of the shaft is 2.50 rad.arrow_forward
- A steel component is subjected to alternate cyclical loading. The steel follows Basquin's law for high cycle fatigue, o, x N = C, (where the stress amplitude is in MPa). Ignore the geometric detail and assume that Marin's modifying factors are all equal to 1. You are given the minimum stress ain = -213 MPa, the maximum stress omax = 213 MPa. The material data are Tensile strength oUTS = 539 MPa, Basquin's constant c, = 875 MPa, Basquin's exponent a = 0.085. a) Calculate the stress ratio R, the stress amplitude o, in MPa and the mean stress am in MPa. The answers are acceptable with a tolerance of 0.01 for R and of 1 MPa the stresses. R: MPa MPа b) Calculate the corresponding life, in 10° cycles, (tolerance of 0.1 106 cycles) N :arrow_forwardAn extruded polymer beam is subjected to a bending moment M. The length of the beam is L = 760 mm. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam are b1 = 33 mm, d1 = 110 mm, b2 = 20 mm, d2 = 20 mm, and a = 6.5 mm. For this material, the allowable tensile bending stress is 11 MPa, and the allowable compressive bending stress is 12 MPa. Determine the largest moment M that can be applied as shown to the beam.arrow_forwardAn aluminum shaft has a diameter of 50.1 mm. Determine the maximum shear stress in the shaft when subjected to a torque of 26.5 Nm? (answer in MPa or MN/m² to 1 decimal place, use pi = 3.142)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning