
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
have a step by step soluton and explain please
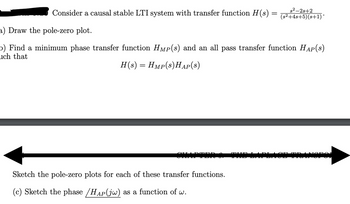
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a causal stable LTI system with transfer function H(s)
=
$2-2s+2
(s²+4s+5)(s+1)*
a) Draw the pole-zero plot.
o) Find a minimum phase transfer function HMP(s) and an all pass transfer function HAP(s)
uch that
H(s) = Hmp(s)HAP(S)
Sketch the pole-zero plots for each of these transfer functions.
(c) Sketch the phase /HAP(jw) as a function of w.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 38 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
can you redo part c? i dont thnk its right.
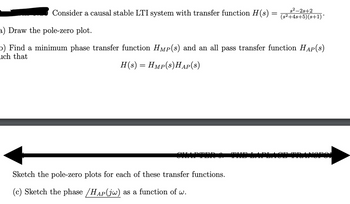
Transcribed Image Text:s2-2s+2
Consider a causal stable LTI system with transfer function H(s) = (s²+4s+5)(s+1)*
a) Draw the pole-zero plot.
b) Find a minimum phase transfer function HMP(s) and an all pass transfer function HAP(s)
ch that
H(s) = Hmp(s)HAP(S)
Sketch the pole-zero plots for each of these transfer functions.
(c) Sketch the phase /HAP (jw) as a function of w.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
can you redo part c? i dont thnk its right.

Transcribed Image Text:s2-2s+2
Consider a causal stable LTI system with transfer function H(s) = (s²+4s+5)(s+1)*
a) Draw the pole-zero plot.
b) Find a minimum phase transfer function HMP(s) and an all pass transfer function HAP(s)
ch that
H(s) = Hmp(s)HAP(S)
Sketch the pole-zero plots for each of these transfer functions.
(c) Sketch the phase /HAP (jw) as a function of w.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Figure shows a transistor switching circuit. Find the Vcc and Rc, which causes the output voltage to have a peak to peak value of 6V (given that the input voltage signal Vi, and the output voltage signal Vo, have units of Volt) Fone: V₁ 10k2 www +Vcc Rc V₂ B-100arrow_forwardFirst,Calculate the input resistance Rin defined as Vin/Iin . Hint: Assuming you know the variable Vin, find Iin in terms of Vin. Substitute Iin into Vin/Iin, then variables Vin will cancel each other on the numerator and denominator. You will get a number that represents Rin. Second,Construct the resistive network in figure 5 with Vin = 5V from the Arduino POWER section. Measure Vin. Then, measure Iin by inserting the DMM between node n1 and n2. Divide these two values to get Rin. Report Vin, Iin, and Rin. Then, Are the measured input resistance values the same when you use Vin = 3.3V and when you use Vin = 5V? Is Rin independent from Vin and Iin? Explain it. Also, include a photo of your circuit!arrow_forwardThe multiplexer has the input states of Do=1, D1=1, D2=1, D3=0 So=1, S1=0 Determine the output of this multiplexer. Do Di Output D2 D3 s0 mux MUXarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,