
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
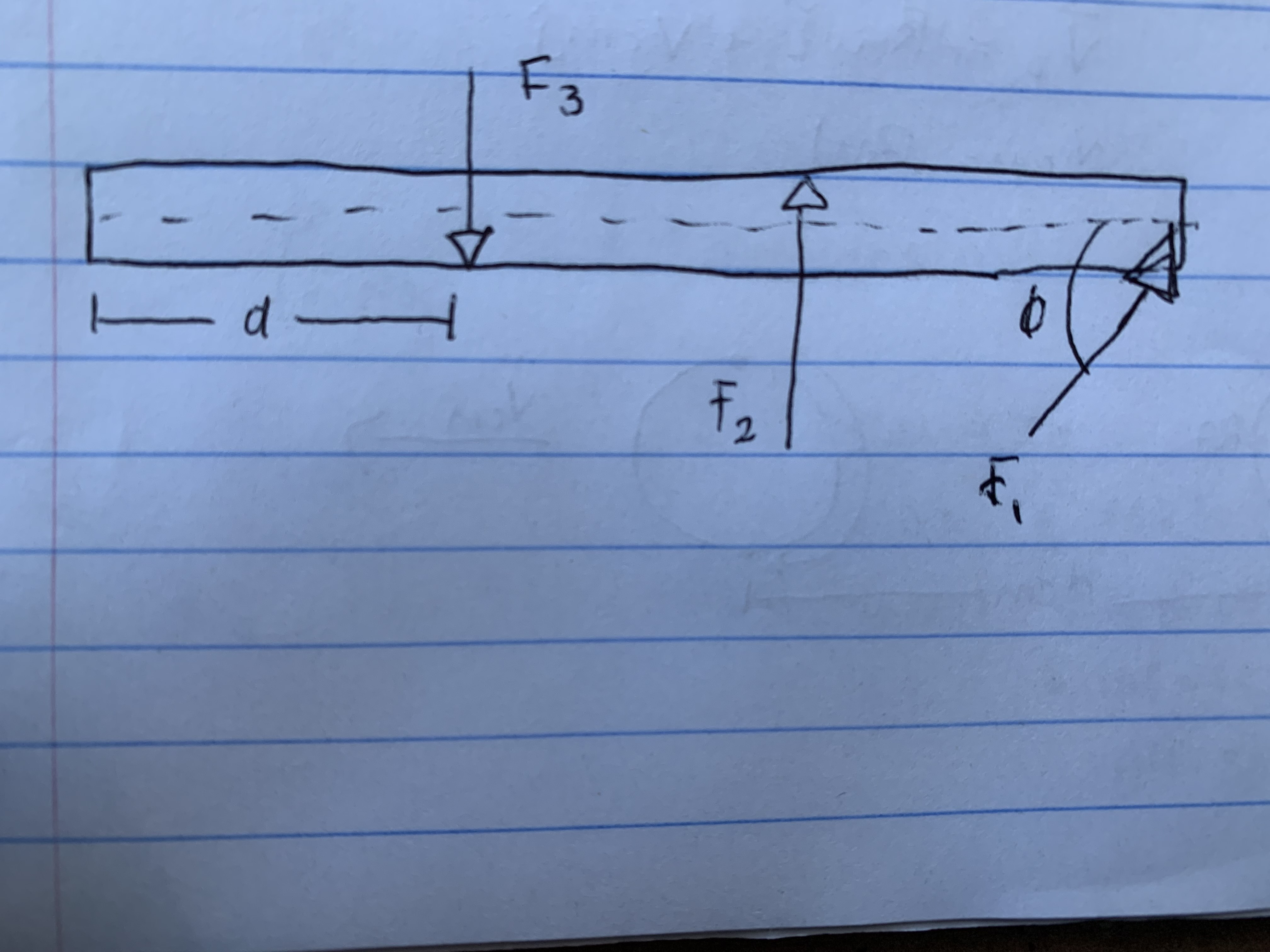
Consider a bar of length 5.5 m, being acted on by three forces and constrained to rotate about its left end. The magnitudes of the first two forces are 19 N and 26 N and the first force is acting on the end of the bar at an angle of 53
What is the torque in newton-meters, due to F1 on this bar relative to the left end?
What is the torque in newton-meters, due to F2 on this bar relative to the left end, if this force is acting at the midpoint of the bar? Use a coordinate system with positive directed out of the screen.
What is the magnitude of the force F3, in newtons, if the force is a distance 0.25 m from the left end and the bar is not rotating?
Transcribed Image Text:F3
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A waiter holds two plates of food in one hand. His forearm has a mass of 2.8kg and the centre of mass of his forearm is located 11cm from his elbow joint. The centre of mass of the two plates is located 32cm from his elbow joint and the total mass of the two plates is 1.75kg. His bicep is attached to the bones of his forearm is 3.6cm from his elbow joint. Assume his forearm is held completely horizontal. a. What is the torque produced by the mass of the two plates? Torque = Nm b. What is the torque produced by the mass of the waiter's forearm? Torque = Nm c. What force must be exerted by the waiter's biceps muscle to ensure that the plates and forearm are motionless? =ONŷ Force =arrow_forward= 13.4 cm and outer radius r, = 35.0 cm shown in the figure below is free to rotate about the axle through the origin O. What is the magnitude of the net torque on the wheel due to the three forces shown? (Assume A wheel of inner radius r, = 4.20 N, F, = 6.60 N, and F, = 13.0 N.) F. %3D N m F 12 45.0° F3arrow_forwardhere are lots of ways to play the classic game "spin the bottle". The figure below shows three ways. In each case, assume that the magnitude of the force is the same. O O B B A amb u In which case will the magnitude of the torque be greatest? A B exc C Oc C it's not possible to tell without specifying the size of the grid spacingarrow_forward
- axis is directed perpendicular to the plane of a square as shown in the figure. Two forces, F₁ and F2, are applied to diagonally opposite corners and act along the sides of the square, first as shown in part a and then as shown in part b of the figure. In each case the net torque produced by the forces is zero. The square is 1.00 m on a side, and the magnitude of F₂ is two times that of F₁. What are the distances a and b? F₁ t Axis F₂ O a=0.50 m, b = 0.50 m Oa=0.40 m, b = 0.50 m O a 0.20 m, b = 0.40 m a=0.40 m, b = 0.20 m a = 0.40 m, b = 0.40 m F₁ b (b) F₂arrow_forwardWhat are the torques for A, B and C? Note:use the given informationarrow_forwardSuppose two long straight wires run perpendicular to one another without touching. Does one exert a net force on the other?If so, what is its direction? Does one exert a net torque on the other? If so, what is its direction? Justify your responses by using the right hand rules.arrow_forward
- A circular-shaped object of mass 10 kg has an inner radius of 8 cm and an outer radius of 22 cm. Three forces (acting perpendicular to the axis of rotation) of magnitudes 13 N, 25 N, and 16 N act on the object, as shown. The force of magnitude 25 N acts 34◦ below the horizontal. Find the magnitude of the net torque onthe wheel about the axle through the centerof the object.Answer in units of N · m.arrow_forwardWhat is the torque produced by a force F = (-3î + 53)N being applied at * = (-2i – 2j)m ?arrow_forwardThe answers are provided; please explain the purpose of each equation and why they were used Consider a bar of length 5.5 m, being acted on by three forces and constrained to rotate about its left end. The magnitudes of the first two forces are 19 N and 28 N and the first force is acting on the end of the bar at an angle of 43° What is the torque in newton-meters, due to F1 on this bar relative to the left end? Ans. = 78.87 Nm Equation used: τ1 = rFsinθ What is the torque in newton-meters, due to F2 on this bar relative to the left end, if this force is acting at the midpoint of the bar? Use a coordinate system with positive directed out of the screen. Ans. = 77 Nm Equation used: τ2 = F2 x (L / 2) What is the magnitude of the force F3, in newtons, if the force is a distance 0.85 m from the left end and the bar is not rotating? Ans. = 183.38 N Equation used: F = (τ1 + τ2) / darrow_forward
- A wheel of inner radius r, = 13.4 cm and outer radius r, = 35.0 cm shown in the figure below is free to rotate about the axle through the origin O. What is the magnitude of the net torque on the wheel due to the three forces shown? (Assume F, = 3.80 N, F, = 6.60 N, and F = 14.6 N.) N. m 45.0 F,arrow_forwardA uniform rod is set up so that it can rotate about an axis at perpendicular to one of its ends. The length and mass of the rod are 0.769 m and 1.09 kg , respectively. A force of constant magnitude ? acts on the rod at the end opposite the rotation axis. The direction of the force is perpendicular to both the rod's length and the rotation axis. Calculate the value of ? that will accelerate the rod from rest to an angular speed of 6.03 rad/s in 8.01 s .arrow_forwardA bolt requires 272 Nm of torque to be unscrewed. If the maximum force you can apply is 232 N, what is the shortest wrench you can use to unscrew the bolt in cm?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON