Question
The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the right when it is at A (Figure 3). It then travels down along the smooth guide. Determine the speed of the collar when it reaches point B, which is located just before the end of the curved portion of the rod. The spring has an
unstretched length of 100 mm and B is located just before the end of the curved portion of the rod.
Transcribed Image Text:Conservation of Energy
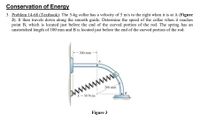
3. Problem 14-68 (Textbook): The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the right when it is at A (Figure
3). It then travels down along the smooth guide. Determine the speed of the collar when it reaches
point B, which is located just before the end of the curved portion of the rod. The spring has an
unstretched length of 100 mm and B is located just before the end of the curved portion of the rod.
200 mm
ww
200 mm
AN
k = 50 N/m
Figure 3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a car's suspension system, each wheel is connected to a vertical spring; these springs absorb shocks when the car travels on bumpy roads. In one car, each spring has a spring constant of 4.6×104N/m.If this 1500 kg car is driven at 27 m/s through the bottom of a circular dip in the road that has a radius of 625 m, by how much do these springs compress compared to when the car is driven on a flat road?arrow_forwardProblem 10: Show how to resolve each force into its x, y, z components. Set up the calculation used to find the magnitude of each component. (a) F-600 N (b F = 500 Narrow_forwardIn a science museum, you may have seen a Foucault pendulum, which is used to demonstrate the rotation of the earth. In one museum's pendulum, the 110 kg bob swings from a 15.0-m-long cable with an amplitude of 5.0°. What is the pendulum's maximum kinetic energy?arrow_forward
- A pen contains a spring with a spring constant of 240 N/m. When the tip of the pen is in its retracted position, the spring is compressed 5.00 mm from its unstrained length. In order to push the tip out and lock it into its writing position, the spring must be compressed an additional 6.60 mm. How much work is done by the spring force to ready the pen for writing? Be sure to include the proper algebraic sign with your answer.arrow_forwardA pulley P is attached to the ceiling at O by a piece of metal that can swing freely. One end of a rope is attached to the ceiling at A. The rope is passed through the pulley P and a weight is attached to the other end of the rope at M, as shown in the diagram. A M The distance OA is 1 m, the length of the rope is 2 m, and the length of the piece of metal OP=r metres, where 0arrow_forwardA block with mass 6.00 kg sliding on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to one end of a horizontal spring (with constant 110.0 N/m) which has its other end fixed. If the maximum distance the block slides from the equilibrium position is equal to 22.0 cm, what is the speed of the block (in cm/s) at the instant when it is a distance of 11.0 cm from the equilibrium position? Round your answer to 1 decimal place.arrow_forwardThis, the length of the pendulum is 2.16 m. Now you start with the pendulum at 30.5 degrees with respect to the vertical, but rather than releasing it from rest, you give it a push downward. It swings to the other side, and reaches a maximum angle of 50.8 degrees with respect to the vertical. What must have been the initial speed of the pendulum just after you pushed it? 3.12 m/s 3.95 m/s 2.42 m/s 6.32 m/sarrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forwardSolve Carrow_forwardIt takes a flea 1.25 × 10−3 s to reach a peak speed of 0.757 m/s. Mass of the flea is 0.462 × 10−6 kg and insect muscle has a maximum output of 56.4 W/kg. If 20.0% of the flea’s weight is muscle, what is the muscular power output of the flea?arrow_forwardA 5.00 kg partridge is suspended from a pear tree by an ideal spring of negligible mass. When the partridge is pulled down 0.100 m below its equilibrium position and released, it vibrates with a period of 3.40 s. What is its speed as it passes through the equilibrium position? What is a magnitude of its acceleration when it is 0.050 m above the equilibrium position? When it is moving upward, how much time is required for it to move from a point 0.050 m below its equilibrium position to a point 0.050 m above it?arrow_forwardThe string in the figure is L = 121 cm long, has a ball attached to one end, and is fixed at its other end. The distance d from the fixed end to a fixed peg at point P is 82 cm. When the initially stationary ball is released with the string horizontal as shown, it will swing along the dashed arc. What is its speed when it reaches (a) its lowest point and (b) its highest point after the string catches on the peg? L. (a) Number 48.69 Units m/s (b) Number 29.0 Units m/sarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios