
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Conjugate Beam: Find theta C, delta C using conjugate beam method
(constant EI)
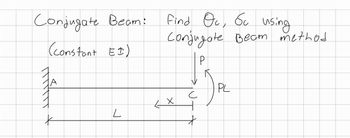
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Conjugate Beam Method for Deflection Analysis**
---
**Objective:**
To find the slope (\(\Theta_c\)) and deflection (\(\delta_c\)) at point C using the Conjugate Beam Method.
**Description:**
The problem involves a beam fixed at point A with a length \(L\). There is a point load \(P\) applied at point C, located at a distance \(x\) from A. The load causes a moment \(PL\).
- **Beam Details:**
- Length: \(L\)
- Point of interest: C
- Load applied: \(P\) at point C
- Distance from fixed support A to point C: \(x\)
- Moment caused by load: \(PL\)
- Material's flexural rigidity assumed constant (\(EI\)).
**Goal:**
Use the conjugate beam method to determine:
- The slope at point C, \(\Theta_c\)
- The deflection at point C, \(\delta_c\)
**Approach:**
The conjugate beam method involves analyzing an imaginary beam (the "conjugate beam") with the same length as the original. Reactions and loads on this beam correspond to the bending moments and slopes from the original beam.
**Note:**
To fully solve the problem, apply equilibrium equations and use appropriate boundary conditions and material properties to calculate \(\Theta_c\) and \(\delta_c\) at point C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- part darrow_forwardConsider the cantilever beam in the figure,subject to a concentrated force P = 20kip at Band a concentrated moment Mo = 100k-ft at C.Knowing that a = 5ft, use the conjugate beammethod to calculate the following in terms ofgeneric E and I:(a) The slope of point C(b)The deflection of point Barrow_forwardProblem 5 The cantilever beam shown below is non-prismatic and is loaded with a concentrated load at free end B. Determine: a) the vertical deflection at B, b) the rotation at B (use either double integration or moment area) A is ft I₁ = 6000 in 4 10 ft = 3000 in 4 H 20 B K E=29000 ksiarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning