
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
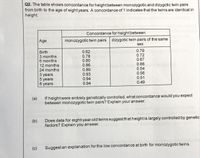
Transcribed Image Text:Q2. The table shows concordance for height between monozygotic and dizygotic twin pairs
from birth to the age of eight years. A concordance of 1 indicates that the twins are identical in
height
Concordance for height between
Age
monozygotic twin pairs dizygotic twin pairs of the same
sex
Birth
3 months
6 months
12 months
24 months
0.62
0.78
0.80
0.86
0.89
0.93
0.94
0.94
0.79
0.72
0.67
0.66
0.54
0.56
0.51
0.49
3 years
5 years
8 years
(a)
If heightwere entirely genetically controlled, what concordance would you expect
between monozygotic twin pairs? Explain your answer.
Does data for eight-year-old twins suggest that heightis largely controlled by genetic
factors? Explain you answer.
(b)
(c)
Suggest an explanation for the low concordance at birth for monozygotic twins.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 28arrow_forward1₁ F3 8 A = all of the dominant alleles for a particular trait in a specific population; a = all of the recessive alleles for a particular trait in a specific population In the following equations "A" is represented by "p" "a" is represented by "q" Hardy Weinberg equations: Allele distributions in Generation 1: 36 homozygous dominant individuals 13 heterozygous individuals 1 homozygous recessive individual Explanation of terminology: px p=p² There are 50 individuals in this particular population. We want to see if allele distributions change from generation to generation. We will use the Hardy Weinberg equations to find out. Due to migration and random mating of the parent generation, the percentage of homozygous recessive genotypes in Generation 2 offspring increases, changing_"a" to 40%, so a = 40 If "a" = .40, and "a"=q, then q = $ Remember that p + q = 1.0 If q, then p must = How many of these 50 offspring are homozygous dominant, heterozygous, or homozygous recessive? p² + 2pq+q²=…arrow_forwardStudent Name: Alyssa york The Hardy-Weinberg Equation 4. Cystic fibrosis is a homozygous recessive condition that affects 1 in 10,000 of the Hispanic population in the United States. Calculate the frequency of the dominant allele, the frequency of the recessive allele, and the percentage of heterozygous individuals (carriers) in the Hispanic population. P qFrequency of the recessive allele 2 p² q² Frequency of the dominant allele 2pq % homozygous dominant % homozygous recessive % heterozygous 0.98 0.02 96.04.7. 0.0.4%arrow_forward
- Assume you know the frequency of each allele p=0.8 so q=0.2. How can we calculate the heterozygote? Think about the punnett square. Either the father donated the freckle allele ie. (Ff = pq) or the mother did (fF = qp) so the equation for heterozygotes should be 2pq Determine the frequency of the heterozygote 2pq=arrow_forwardIn humans the absence of a cleft chin is dominant to the presence of a cleft chin. Two individuals, both of whom are heterozygous for a recessive allele that causes the cleft chin phenotype have 5 children, what is the probability that 3 of their children would not have a cleft chin and 2 would have a cleft chin? 0.0037 0.026 0.237 0.264arrow_forward?action=Donresume&submissionld%3D459115049 Trait Dominant Allele Recessive Allele Body Color Brown (B) Albino (b) Back Stripe No Stripe(N) Stripe (n) Fill in the blanks (1-4) in the Punnett square below and answer the questions. Bn Bn Bn Bn bN BbNn BbNn BbNn bn Bbnn Bbnn Bbnn bN BbNn BbNn BbNn bn Bbnn Bbnn Bbnn For the next two questions below, fill in the allele(s) that you are looking for to determine the number of each type of traits specified. (HINT: Remember how many alleles do you need to have the dominant trait vs the recessive trait) How many gecko offspring will be brown and have a stripe? How many gecko offspring will be albino and have no stripe? What is the phenotype of the genotype BbNn? : B :: b :: N : BB :: Bb :: bb :: NN : Nn :: nn :: Brown and no stripe : Brown and a stripe : Albino and no stripe : Albino and a stripe : 0 :: 4 :: 6 :: 9 :: 8 : 12 :: 16 : BBNN :: BBNN : BBnn :: BBNN : BBN. : Bbnn : bbNN : bbNn :: bbnnarrow_forward
- I am confused.arrow_forward26arrow_forwardtrue for false? 1a) In Drosophila flies, there are wing shapes such as curly, apterous, miniature and others. These would be considered continuous traits (as opposed to discontinuous traits). 1b) The reason we assess the narrow sense heritability is because there are hidden genetic components that are simply too difficult to include in the calculation of VG 1c) You can figure out the heritability of a trait if you compare the variation of the trait in a clonal population of organisms to a wild type (heterogeneous) population.arrow_forward
- Search the menus (Alt+/) 90% Normal text Calibri BI UA 11 + ... I 1 2 I 3 I: 4 | 5 6 7 8 11. Farmer Jorge is not very happy. His cows keep attacking him with their horns. He heard from his friend, Ta Lay that some cows do not have horns. These cows are known as polled cows. Farmer Jorge can only afford to buy one polled cow. He buys a purebred male (called a bull), with no horns. He is going to have the bull mate with his cow that is homozygous recessive for horns. Can his cows make a baby (called a calf) with no horns? Create a Punnett Square to show the possibilities that could result from this mating. Alleles and Phenotype All Genotype and Phenotype Possibilities Parent Genotypes Punnett Square Allele Phenotype Genotype Phenotype Dad Mom 4 of 7 a. Bull's Genotype b. Cow's Genotype c. What is the probability of having a polled calf? d. What is the probability of having a horned calf? e. What is the probability for a homozygous recessive? f. Can Jorge's cows make a calf with no horns?arrow_forwardplease dont copy ur answer from chegg since the answers there on this quiestion are not correct/reliablearrow_forwardThe variance for weight in a particular herd of cattle is 484 pounds2.The mean weight is 562 pounds. How heavy would an animal haveto be if it was in the top 2.5% of the herd? The bottom 0.13%?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education