
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Compute the standard error for L1 (L1 = A + B - GA - GB). Keep in mind this is a repeated-measures design.
A GA B GB
9 6 8 5
10 6 9 7
10 5 8 7
8 4 7 5
10 5 8 5
9 7 7 6
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

arrow_forward
Step 2
The mean and standard deviation can be calculated as;
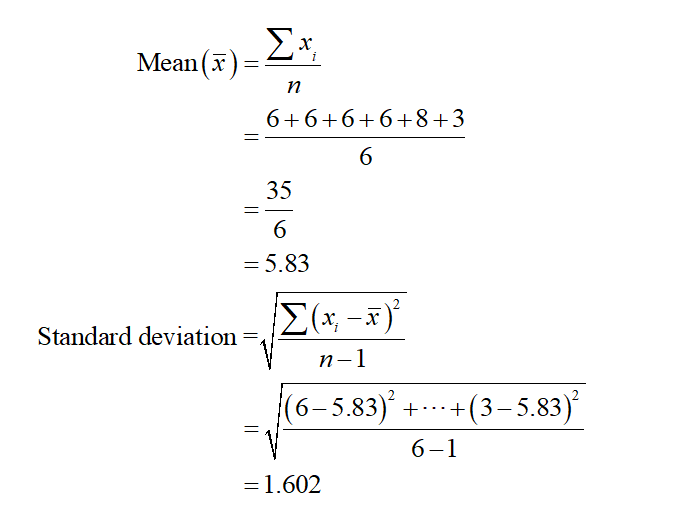
Therefore, the mean and standard deviation are 5.83 and 1.602.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- According to a study, 58% of all males between the ages of 18 and 24 live at home. (Unmarried college students living in a dorm are counted as living at home.) Suppose that a survey is administered and 152 of 226 respondents indicated that they live at home. (1a) P(X≥152)=__________ (Round to four decimal places as needed.) (1b) Do the results from part (a) contradict the study? yes or noarrow_forwardUse one of these two formulas below:arrow_forwardlecture(12.11A): Researchers were interested in the effects of co-sleeping on nightime waking and crying in infants. .They assesed the number of minutes parents reported that their infants were awake and crying for a period of three days. Five of the infants co-slept with thier mothers(Co) and four infants slept in crib(Cr).The researchers wanted to see if there was a difference in the total number of minutes of crying during the 3 nights. for the two groups. A summary of the data is given below Co-sleepers night time crying in minutes: 8, 4, 7, 7, 6 Crib-sleepers night time crying in minutes: 30, 17, 22, 25 Test the hypotheses at (aplha=.05) level of signifcance. using the 5 step hypotheses testing procedure. Clealy state the null and alternative hypotheses. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- Hi, could you please solve Question 3 using R? For the questions, use the data I provided in the screenshot. (I would like to upload the data, but the program does not let me) Please, write the codes with the explanations. Thank you.arrow_forwardM4arrow_forwardEvery day a school bus driver passes the same traffic light twice, once before school and once after. Each time he passes the light, he records if it is red, green, or yellow. Here is a summary of the data he got after 200 days. Traffic light before school red red red green green green yellow yellow yellow Traffic light after school red green yellow red green yellow red green yellow Number of days 25 38 12 34 36 11 16 13 15 Suppose the driver will continue recording the colors for 150 more days. In how many of these 150 days will the light be yellow exactly once? Use the data to make a prediction.arrow_forward
- Please help me, I can't seem to figure it out and it is due in 25 minutes. Someone, please help me ASAP! Thank you!arrow_forwardSuppose Aaron recently purchased an electric car. The person who sold him his new car told him that he could consistently travel 200 mi before having to recharge the car's battery. Aaron began to believe that the car traveled even farther than the company claimed, and he decided to test this hypothesis formally. Aaron drove his car only to work and he recorded the number of miles that his new car traveled before he had to recharge its battery a total of 17 separate times. The table shows the summary of his results. Assume his investigation satisfies all conditions for a one-sample t-test. Mean miles traveled Sample size t-statistic P-value P 207 17 1.48 0.079 The results statistically significant at a = 0.01 because P 0.01. are are not Varrow_forwardBack: It has been estimated that only about 30% of California residents have adequate earthquake supplies. Suppose you randomly survey 12 California residence. We are interested in the number who have adequate earthquake supplies.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman