
ECON MACRO
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781337000529
Author: William A. McEachern
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
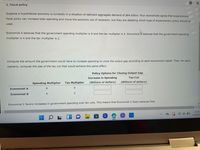
Transcribed Image Text:2. Fiscal policy
Suppose a hypothetical economy is currently in a situation of deficient aggregate demand of $64 billion. Four economists agree that expansionary
fiscal policy can increase total spending and move the economy out of recession, but they are debating which type of expansionary policy should be
used.
Economist A believes that the government spending multiplier is 8 and the tax multiplier is 4. Economist B believes that the government spending
multiplier is 4 and the tax multiplier is 2.
Compute the amount the government would have to increase spending to close the output gap according to each economist's belief. Then, for each
scenario, compute the size of the tax cut that would achieve this same effect.
Policy Options for Closing Output Gap
Increase in Spending
Tax Cut
(Billions of dollars)
Spending Multiplier
(Billions of dollars)
Tax Multiplier
4
Economist A
8
Economist B
4
2
Economist C favors increases in government spending over tax cuts. This means that Economist C likely believes that:
Y
O
6:34
4/29/20
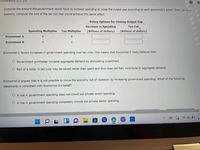
Transcribed Image Text:Homework (Ch 23)
Compute the amount the government would have to increase spending to close the output gap according to each economist's belief. Then, for each
scenario, compute the size of the tax cut that would achieve this same effect.
Policy Options for Closing Output Gap
Increase in Spending
Tax Cut
Spending Multiplier Tax Multiplier
(Billions of dollars)
(Billions of dollars)
Economist A
8
4
Economist B
4
2
Economist C favors increases in government spending over tax cuts. This means that Economist C likely believes that:
Government purchases increase aggregate demand by stimulating investment.
O Part of a dollar in tax cuts may be saved rather than spent and thus does not fully contribute to aggregate demand.
Economist D argues that it is not possible to move the economy out of recession by increasing government spending. Which of the following
statements is consistent with Economist D's belief?
O A rise in government spending does not crowd out private sector spending.
O A rise in government spending completely crowds out private sector spending.
O
O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain how automatic stabilizers work, both on the taxation side and on the spending side, first in a situation where the economy is producing less than potential GDP and then in a situation where the economy Is producing more than potential GDP.arrow_forwardWhy is spending by the U.S. government on scientific research at NASA fiscal policy while spending by the University of Illinois is not fiscal policy? Why is a cut in the payroll tax fiscal policy whereas a cut in a state income tax is not fiscal policy?arrow_forwardUnder what general macroeconomic circumstances might a government use expansionary fiscal policy? When might it use contractionary fiscal policy?arrow_forward
- What is the main advantage of automatic stabilizers over discretionary fiscal policy?arrow_forwardWhat is the main reason for employing expansionary fiscal policy during a recession?arrow_forwardWhat is the main reason for employing contractionary fiscal policy in a time of strong economic growth?arrow_forward
- What would happen if expansionary fiscal policy was implemented in a recession but, due to lag, did not actually take effect until after the economy was back to potential GDP?arrow_forwardWhat would happen if contractionary fiscal policy were implemented during an economic boom but, due to Lag, it did not take effect until the economy slipped into recession?arrow_forwardAssume there is no discretionary increase in government spending. Explain how an improving economy will affect the budget balance and, in turn, investment and the trade balance.arrow_forward
- Specify whether expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy would seem to be most appropriate in response to each of the situations below and sketch a diagram using aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves to illustrate your answer: A recession. A stock market collapse that hurts consumer and business confidence. Extremely rapid growth of exports. Rising inflation. A rise in the natural rate of unemployment. A rise in oil prices.arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between discretionary fiscal policy and automatic stabilizers?arrow_forwardWhat are some of the ways fiscal policy might encourage economic growth?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
