
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
![**Statistical Significance Testing**
Complete parts (a) through (c) below:
(a) Determine the critical value(s) for a right-tailed test of a population mean at the α = 0.05 level of significance with 15 degrees of freedom.
(b) Determine the critical value(s) for a left-tailed test of a population mean at the α = 0.05 level of significance based on a sample size of n = 10.
(c) Determine the critical value(s) for a two-tailed test of a population mean at the α = 0.01 level of significance based on a sample size of n = 11.
- Click here to view the t-Distribution Area in Right Tail.
**Input Area:**
(a) t_crit = [dropdown] [input box] (Round to three decimal places as needed.)](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/d80315fc-9ba3-472b-8f03-e8ddf0a99e1b/c05ef420-2006-4cdc-95e1-c2a7ae2a4575/f9n2hff_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Statistical Significance Testing**
Complete parts (a) through (c) below:
(a) Determine the critical value(s) for a right-tailed test of a population mean at the α = 0.05 level of significance with 15 degrees of freedom.
(b) Determine the critical value(s) for a left-tailed test of a population mean at the α = 0.05 level of significance based on a sample size of n = 10.
(c) Determine the critical value(s) for a two-tailed test of a population mean at the α = 0.01 level of significance based on a sample size of n = 11.
- Click here to view the t-Distribution Area in Right Tail.
**Input Area:**
(a) t_crit = [dropdown] [input box] (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
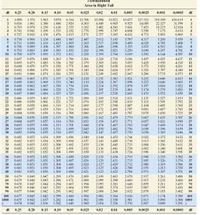
Transcribed Image Text:This is a T-Distribution Table showing the area in the right tail. It is typically used in statistical analyses to determine the critical t-values for different confidence levels and degrees of freedom.
### Structure of the Table:
- **Rows**: Represent the degrees of freedom (df), ranging from 1 to 1000.
- **Columns**: Represent different significance levels corresponding to the area in the right tail:
- 0.25
- 0.20
- 0.15
- 0.10
- 0.05
- 0.025
- 0.02
- 0.01
- 0.005
- 0.0025
- 0.001
- 0.0005
### Explanation:
- As the degrees of freedom increase, the t-values generally decrease, converging towards a normal distribution curve.
- Each cell in the table provides the t-value for the specified degree of freedom and significance level.
### Usage:
The table is integral in hypothesis testing, particularly in t-tests involving small sample sizes:
- **Step 1**: Determine the degrees of freedom for your test.
- **Step 2**: Identify the significance level for your test.
- **Step 3**: Locate the intersection of the respective row and column to find the critical t-value.
This table assists in deciding whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- comparison of the precisions of two machines developed for extracting juice from oranges is to be made using the following data. Is there sufficient evidence to indicate that there is a difference in the precision of the two machines at the 5% level of significance? Machine A Machine B s2 = 1.4 ounces2 s2 = 3.1 ounces2 n=25 n=20arrow_forwardUsing an evenly distributed data population of 8,000 samples, how many Would fall between a Z-score of -0.5 and +0.5? (blank)arrow_forwardBig babies: The National Health Statistics Reports described a study in which a sample of 310 one-year-old baby boys were weighed. Their mean weight was 24.4 pounds with standard deviation 5.3 pounds. A pediatrician claims that the mean weight of one-year-old boys is greater than 25 pounds. Do the data provide convincing evidence that the pediatrician's claim is true? Use the α = 0.10 level of significance and the P-value method with the TI-84 Plus calculator. Compute the P-value. Round the answer to at least four decimal places. P-value = ____ How do I solve this problem using the TI-84 calculator?arrow_forward
- A traffic safety company publishes reports about motorcycle fatalities and helmet use. In the first accompanying data table, the distribution shows the proportion of fatalities by location of injury for motorcycle accidents. The second data table shows the location of injury and fatalities for 2073 riders not wearing a helmet. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. (a) Does the distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet follow the distribution for all riders? Use α = 0.10 level of significance. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? A. Ho: The distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet follows the same distribution for all other riders. H₁: The distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet does not follow the same distribution for all other riders. B. Ho: The distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet does not follow the same distribution for all other riders. H₁: The distribution of fatal injuries for…arrow_forward(a) Find the critical value(s) assuming that the population variances are equal. (b) Find the critical value(s) assuming that the population variances are not equal.arrow_forwardOpposing a random sample of size and equal 16A sample average of 185 it is observed the P value of the sample statistic isarrow_forward
- (c) For a two-tailed test using the t-distribution, if the sample size is 10, find out the critical values based on the given significance levels: (1) a = 0.1, (2) a = 0.05, and (3) a = 0.01. %3Darrow_forwardWhich would be the appropriate way to test differences in proportions for more than two samples? t-test if variance is unknown z-test paired t-test F-test for equality of variances cross-tabulation procedure to conduct a chi-square testarrow_forwardTo determine diet quality, male weanling rats were fed diets with various protein levels. Each of 15 rats was randomly assigned to one of three diets, and their weight gain in grams was recorded in the following table: Diet protein level Medium Low High 9.72 8.54 9.19 9.67 9.32 11.11 8.15 8.76 14.45 6.75 9.30 10.39 9.55 10.45 12.16 Sample Mean Sample Variance 1.696 8.768 9.274 11.460 0.547 3.963 Suppose we fit the data with the following model: Xij = µ+a; + Eij, i = 1, 2, 3; j= 1,., 5, N(0, o²) independently. Define X;. i = 1,2, 3, X. = 1=1 Xij, and SS(E) = E-1E=1(Xij – X;.)². E- Xij for where a1 + a2 + az = 0 and Eij Some R output that may help. > p1 qf (p1, 2, 12) [1] 0.010 0.025 0.052 0.106 2.807 3.885 5.096 6.927 > qf (p1, 2, 14) [1] 0.010 0.025 0.051 O.106 2.726 3.739 4.857 6.515 > qf (p1, 3, 12) [1] 0.037 0.070 0.114 O.192 2.606 3.490 4.474 5.953 > qf (p1, 3, 14) [1] 0.037 0.070 0.115 0.192 2.522 3.344 4.242 5.564arrow_forward
- (b) For a one-tailed test using the t-distribution, if the sample size is 20, find out the critical values based on the given significance levels: (1) a = 0.1, (2) a = 0.05, and (3) a = 0.01.arrow_forwardA researcher wants to measure average cardiovascular health of university students and compare those scores to the average scores in the general population. Assuming that population variance is known, what statistical test is most appropriate for this study? independent-samples t-test single-sample t-test z-test for sample mean related-samples t-testarrow_forwardAt a 0.05, test to see if the population variances from which the following samples were drawn are equal. The test statistic is Group 1 n₁ = 21 Group 2 n₂ = 19 $1 = 20 S2 = 18 (A) 1.56 (B) 1.23 (C) 1.26 (D) 1.11arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman